![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
vascular palpation
|
- dorsalis pedis, post tib, popliteal, femoral, radial, ulnar, brachial, carotid
|
|
|
pulsus parodoscu
|
10mmHg, SS of asthma, COPD, PE, tamponade, constrictive pericarditis
|
|
|
Kussmaul signs
|
JVP increase on inspiration
|
|
|
MVP increases with what maneuvers
|
1. valsalva maneuver
2. squatting/standing |
|
|
position that helps to > S3/S4
|
left lateral decubitis listen at apical area
|
|
|
MS increased
|
LLD position
|
|
|
AR increased with?
|
sitting up and leaning forward post expiration
|
|
|
Valsalva incrased which mumurs?
|
increased MR, HCM, AS
|
|
|
AR is increased by? + findings
|
inspiration
musset's sign - head bobbing w/ carotid pulsation quincke's signs - pulsation in nail beds widened pulse pressure hill's sign - > in BP in legs compared to arms Water-hammer pulse pulsus bisferiends pistol shot sound over femoral arteries |
|
|
S4 occurs when
|
is atrial kick largely due to stiff ventricle as with ventricular hypertrophy, fibrosis of ventricle, AS
by definition it can't be present in AF |
|
|
S3 is a sign of ...
|
increased volume /ventricular filling as with. MR, VSD, and more commonly heart failure
|
|
|
murmurs
|
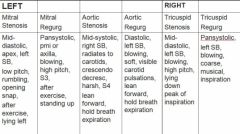
|
|
|
AS findings
|
pulsus tardus et parvus, narrowed pulse pressure, incraesed w/ leaning forward, rad to carotid
|
|
|
The only valvular disease not causing LVH
|
Mitral stenosis
|
|
|
JVP char (POLICE)
|
non Palpable
Occludable Location (between SCM heads) < on Inspiration Countour (double waveform) Erect position - < lvls |
|
|
Homan's signs =
|
For DVT/disc herniation. - knee flexed fast dorsiflexion of ankle produces pain
|
|
|
Buerger's test
|
elevate leg at 60degree --> pallor if arterial insuff. rubor on dependancy
|
|
|
SS of coarcatation of aorta
|
1. < femoral pulses
2. radial-femoral delay 3. aortic bruits 4. arm BP>leg BP |
|
|
hyperthyroidsism SS
|
termor, aggitation, diarrhea, hair changes, goiter, hyperreflexia, a. fib, wide pulse pressure, exophthalmos, lid lag, periorbital edema. pretibial myxedema.
|
|
|
RESPiratory system hx
|
SPACED
* smoking, SOBOE, Sputum productions *pain, pigeons *Asthma, atopy, alpha 1 antitrypsin *cough, CXR *excersise tolerance, environmental/occpuation exposure *dyspnea |
|
|
P/E procedure
|
IPPA
|
|
|
quiet chest with astham
|
warning for possible impending respiratory failure as either fatigue or small airway obstrution
|
|
|
cruveilhier's sign
|
hum over liver indicates increased collateral circulation between portal and systemic circulation
|
|
|
first percussion over liver
|
like CVA for tenderness
|
|
|
splenic ausculation
|
hums
friction rub = suggests inflammation on surface ie from splenic infarct |
|
|
exam for hernias
|
indirect are lateral of inferior epigastric artery
ausculate mass cough/ bear down. translumination |
|
|
liver stigmata
|
fetor heapticus
jaundice change in level of consciouness spider nevi (blanceable radiating capillary brnches) parotid gland hypertrophy virchows node (palpable firm Lt infraclav LN) gynecomastia hepatomegally, gall baldder or small liver splenomegally asterixis, palmar erythema, dupuytrens ascites superficial abdominal veins clubbing leukonychia testicular atrophy/loss of pubic hair hemorrhoids bruising edema excoriation caput medusa petechiae ecchymosis dark urine, pale stool |
|
|
Charcot's triad what is it for and what are its parts?
|
cholecystitis. Fever, jaundice RUQ pain
|
|
|
Reynold's pentad. what is it for and what are the parts?
|
ascending cholangitis
altered mental status, hypotention, fever, RUQ pain, jaundice |
|
|
pendular reflex. what is it and what does it signify?
|
1. continued swing post tendon stretch
2. cerebellar sign |
|
|
Optic nerves names
|
CN I= olfactory
II = optic = acuity, fundal exam, color sat, visual fields, pupil response, relative afferent pupillary defect III= oculomotor = EOM, nystagmus at extremes of vision is normal IV = trochlear - if palsy will be unable to see down and in V =trigeminal = motor (masseter/temporalis), sens, tough. corneal reflex VI - abducens = if palsy will be unable to see lateral VII = facial = puff, eye closed, raise forehead. taste in ant 2/3 of tongue VIII = vestibulocochlear - dix hallpike IX = glossopharyngeal - "ahh", swallowing, taste on post 1/3 of tongue X - vagus - with IX + "pataka" XI = accessory spinal - shrug agaisnt resistance, turn side to side XII = hypoglossal = tongue ous. look for fasciulations or atrophy |
|
|
holmes rebound phenom
|
like pronator drift but push down hand see if over compensates/oscillates
|
|
|
reflex how to rate?
|
0= none
1+ = diminished 2+ normal 3+ increased 4+ clonus/hyperactive |
|
|
chaddock sign what is it?
|
stroek lateral foot, extension of toe w/ famming of other toes =UMN lesion
|
|
|
oppenheim sign what is it?
|
exert dowward pressure on shin, extension of big to e+ fanning of other toes suggest UMN lesion
|
|
|
UMN lesion ss:
|
forhead sparing facial paralysis. Horner's with anhidrosis (ptosis, miosis of pupil, +/- conjunctivitis)
incraed motor tone incl rigidity and spacticity, power is decreased reflexeds plantar up, decreased sensation, neglect, etc fasciculations |
|
|
GCS grading
|
eye opening: never, with pain, with verbal, spontaneous
verbal: none, incomprehensible, inappropriate, confused but talking, oriented and talking motor:none, extension (decerebrate), flexion (decorticate), withdraws, localizes to pain, obeys commands |
|
|
test in unconsiouc person?
|
cold caloric reflex
corneal reflex oculocephalic reflex (turn head to side eyes should go opposite) pupils babinski DTR gag reflex (if intubated) |
|
|
MSK inspection
|
SEEADS
Swelling, Erythema, Ecchymosis, Atrophy, Deformity, Skin changes, warmth |
|
|
power scale (oxford)
|
0- no power
1- flicker of movment 2 = moves but cna'tovercome gravity 3= moves against gravity 4= moves against gravity and with some resistance 5= normal |
|
|
spurlings test
|
pt rotate and laterall flexes neck to affected area. if has radicular pain likely cervical root impingement
|
|
|
lhermittles sigsn
|
electric like shocks down back when forward flexing
|
|
|
Function of 1. Lumbricals 2. Interossei how to test
|
1. Flexion at mcp with extended IPs
2. Digit abduction and adduction |
|
|
CTS is assoc with which conditions?
|
DM, hypothy, acromegally, gout, pregnancy, obesity
|
|
|
Where to check for enthesitis
|
chest wall, achilles, plantar fascia, tib tuberosity, patella, iliac crest
|
|
|
Anknspon articular and extra articular involvement
|
1. Articular - axial skeleton, periph joint, enthesitis. 2. Ocular ( ant uveitis, iridocyclitis) cardiac ( AR, conduction abN, pericarditis, ascending aortitis), resp apical fibrosis - late), renal, neuro
|
|
|
Most common areas of fragility frac
|
hip, distal wrist, vertebrae
|
|
|
Testing for tenis elbow
|
forced wrist extension and lateral epicondyle tenderness
|
|
|
Test for golfers elbow
|
forced wrist flexion and medial epicondyle tenderness
|
|
|
Osteoporosis endo causes
|
hyperpara, hyperthy, cushings, hypogonadism, acromegaly
|
|
|
Osteoporosis gi test
|
malabsorbtion, ibd, celiac, pancretic insuff, TPN
|
|
|
Osteoporosis meds causes
|
steroids, anticonvulsants, immunosup, gnrh antagonist,
|
|
|
acne DDX
|
roseacea,
acne excoriee, steroid acne perioral dermatitisallergy, bacterial folliculitis adenoma sebaceum in tuberous clerosis |
|
|
nikolsky sign
|
- rub skin is produces blister (+) - present in pemphigus vulgaris, toxic epidermal necrolysis
|
|
|
ddx painful nodule, welling, brusing on shins
|
vasculitis, thrombophlebitis, cellulitis, TB, trauma, SLE assoc panniculitis, pnacreatic panniculitis, necrobiosis lipoidica, lymphoma, alpha1 antitrypsin defin panniculitis, erythema nodosum (may occur post strep) may come w/ arthralgias.
|
|
|
descritpion of SK
|
warty, brown, stuck on-appearance
|
|
|
description of AK
|
flat, rough, scaly w/ ill-defined borders
|
|
|
skin lesions one risk factor to remember
|
ask re: immune suppression. increased risk of cancers!!!
|
|
|
psoriasis exam
|
palms, soles, scalp, anogenital area, nails (pitting, onycholysis, oil drop sign.
sausage digits auspitz sign - micro bleeding spots seen when scales srapped joint exam look at insertion sof tendons for enthesitis makes sure no widespread pustues or erythroderma - both are med emergencies can be fatal. |
|
|
ddx hirtuism
|
1 cushings,
2. androgen secreting tumors 3. PCOS 4. CAH 5. acromegaly 6. drugs |
|
|
fundoscopy cup to disc ratio
|
normal cup to disc ratio is <0.4
|
|
|
? to ask re breast cancer
|
1. constitnutaional ss
2. fam hx 3. pain, discharge, lump, change w menstrual cycle 4. eczema / rash 5. age of menarche, menopause, parity, radiation esplosrue 6. prev mammograms 7. hx ofn lynch ii = endometrail , colon, ovarian + breast ca 8. soc hx |
|
|
screening for alcohol 4 questions/
|
CAGE
ever tried to cut down amount? annoyed at people criticizing drinking? guilty about drinking? need eye-opener? |
|
|
mneumonic for suicide risk. SAD PERSONS
|
Sex: male
Age < 19 >45 Depression Previous attempts EtOH Rational thinking loss Separated, divorced, widowed Organized plan No social support Stated future intent |
|
|
SS of mania
|
D = Distractibility and easy frustration
I = Irresponsibility and erratic uninhibited behavior G = Grandiosity F = Flight of ideas A = Activity increased with weight loss and increased libido S = Sleep is decreased T = Talkativeness |
|
|
myosis means
|
constricted pupil
|
|
|
midriasis means?
|
dilated pupil
|
|
|
anisocoria means?
|
pupils separated by >1mm
|
|
|
normal visual acuity in children
|
20/40 in age 3
20/20 in age 6 |
|
|
Rashes on palms DDX
|
erythema multiforme
rocky mountain spotted fever drug eruption secondary syphilis scabies hand foot and mouth |
|
|
Dx of SJS or TEN (toxic epidermal necrolysis)
|
fever >39, blisters on dusky macules, involvmend of mucous membranes (mouth, eyes, genitals)
SJS<10%, TEN >30% |
|
|
SJS / TEN tmt
|
fluids +++ treat like burn, stop cause, +/- IVIG
|
|
|
Lyme disease BAKE symptoms
|
bell's palsy
Arthritis Kardiac blocks Erythema migrans tick bite >24 hrs |
|
|
key features of Parkinsons
|
TRAP
Tremor Rigidity Akinesia/bradykinesia Postural instability |
|
|
RESting tremor DDX
|
idiopathic parkinsons disease, parkinsonism, Wilson's disease
|
|
|
criteria for restless leg syndrome
|
All 4:
1. urge to move legs with dysesthesia 2. onset or exacerbation with rest 3. relief with movement 4. circadian pattern consider CBC r/o anemia |
|
|
RLS ddx
|
nocturnal leg cramps
periphral neuropathy varicose veins akathisia intermittent claudication periodic limb movement of sleep pesitional discomfort leg pain from arthritis nervous shaking |
|
|
RLS tmt
|
lifestyle = avoid caffeine, ETOH, chocolate, smoking/nicotine, good sleep hygiene, stretching/exercise
treat underlying causes meds - pramipexole (DA receptor agonist), anti-epileptics, DA precursons (levodopa), benzo, opioids |
|
|
RLS causes
|
1. DM
2. iron def 3. pregnancy 4. < MG 5. ESRF 6. RX (Li, SSRI, TCA, antipsych, CCB, antinausea - domperidone, ondansetron) |

