![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What forms the anatomical crown? |
Epithelia |
|
|
The main substance of a tooth is |
dentin |
|
|
This tissue covers the anatomical root of a tooth |
cementum; functionally it is part of the periodontium |
|
|
During enamel and dentin formation, ondontoblats move ___ and ameloblasts move ___. |
inward; outward |
|
|
What is the difference between anatomical and clinical crown using proper terms? |
Anatomical: incisor border to CEJ Clinical: incisor border to GM (gingival margin) |
|
|
How much hydroxyapatite is in: 1) enamel 2) dentin 3) Cementum |
1) 96% 2) 65% 3) 61% |
|
|
Of Bone, dentin, enamel and cementum which has the largest crystallite dimensions? Which not have a collagen matrix? |
enamel; enamel |
|
|
Dentin is made by Enamel is made by |
odontoblasts ameloblasts |
|
|
What is the direction of the enamel prisms? |
Perp to enamel surface |
|
|
T/F. Enamel formation is completed by time tooth erupts. |
True |
|
|
Describe differential density of dentinal tubules |
Get more dense as you move deeper. |
|
|
T/F. Pulp gets thicker as you age. |
FALSE. Dentin gets thicker |
|
|
What is one (of four) cases where you don't need a pulpectomy? |
Chronic symptoms w/ no pulpal exposure |
|
|
What are the 4 components of periodontium? |
Cementum, alveolar bone, periodontal ligament, dentogingival junction |
|
|
The PDL is between |
cementum and alveolar bone |
|
|
T/F. Cementum can be acellular or cellular. |
True |
|
|
Oral mucosa consists of masticatory mucosa, specialized mucosa, and lining mucosa. Which one is gingiva? |
Masticatory mucosa |
|
|
Gingiva consists of an epithelial layer and an underlying connective tissue layer called the ___. |
lamina propria |
|
|
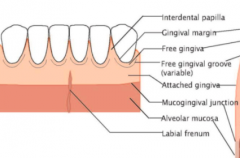
Coronal portion of gingiva terminates in the ___ which is usually scalloped in appearance. The apical portion is continuous with ___. |
free gingival margin alveolar mucosa |
|
|
Gingiva and alveolar mucosa are usually separated by a recognizable border called the |
mucogingival junction |
|
|
Where is there no mucogingival junction? |
On palate since the hard palate and maxillary alveolar processes are covered by the same type of masticatory mucosa. |
|
|
Macroscopically what is gingiva composed of (two things): |
Free gingiva (all epi and CT coronal to horizontal line placed at CEJ) Attached to gingiva (extends from free gingiva to mucoginvial junction) |
|
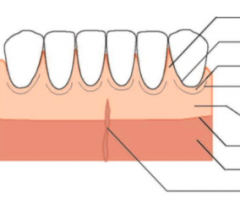
Label |
|
|
|
After eruption is complete, free gingival margin is located ____ coronal to the CEJ. |
1.5-2mm |
|
|
T/F. The free gingiva forms the interdental papilla. |
True |
|
|
In posterior teeth, the interdental papillae may have a ___ or concavity in the middle that conforms of the outline of the interdental contact surface. |
col |
|
|
Attached gingiva often show small depressions in surface named ___ and have an orange peel appearance. |
Stippling |
|
|
What type of epithelium covers gingiva? |
Stratified squamous |
|
|
Gingival epithelium is divided into 3 parts microscopically: |
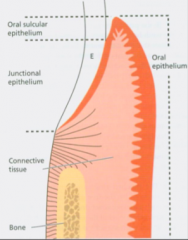
1) Gingival oral epithelium 2) Gingival sulculuar epithelium 3) Gingival junctional epithelium |
|
|
What are rete pegs and where are they found/not found? |
Rete pegs are epithelial projections into underlying connective tissue. Present in oral and sulcular epithelium. Lacking in healthy junctional epithelium. |
|
|
T/F. Stipplings occur at function points between epithelial ridges. |
True |
|
|
T/F. Gingival oral epithelium is keratinized. |
True |
|
|
T/F. Subsulcular epithelium is attached to the tooth. |
False! It is facing the tooth extending from oral epithelium to gingival sulcus (apical order is junctional epithelium) |
|
|
Is subsulcular epithelium keratinized? |
No- parakeratinized or not keratinized. |
|
|
Where is the apical termination of the junctional epithelium |
the CEJ |
|
|
T/F. Junctional epithelium is keratinized. |
False |
|
|
Describe the basal laminas of the junctional epithelium. |
There are two of them: external and internal. External attaches JE to underlying CT. Internal attaches JE to tooth surface via hemidesmosomes. |
|
|
What comprises the "epithelial attachment"? |
Internal basal lamina + hemidemosomes |
|
|
Of the three types of oral epithelium which is most permeable with fewer desmosomes? |
junctional epithelum |
|
|
T/F. The junctional epithelium serves as the passage for gingival crevicular fluid and cells from CT to sulcus including bacteria |
True |
|
|
Gingival CT is mainly composed of |
networks of collagen fibers (mainly type I) |
|
|
T/F. CT components of gingival CT are embedded in an amorphous ground substance. |
True |
|
|
These are gingival fiber groups named based on location and insertion. Know their functions: circular, dente-gingival, alveolo-gingival, dento-periosteal, trans-septal |
- |
|
|
Which of the following is not true about the periodontal ligament? a) Continuous with CT of gingiva b) Approximately 0.25 mm in width c) soft, avascular CT surrounding root |
C- it is vascular |
|
|
Principle fibers are: alveolar crest fibers, horizontal fibers, oblique fibers, apical fibers, and interradibular fibers. Which: 1) Are most numerous 2) are in furcation area only in multirooted teeth AHOAI (A ho artificial intelligence) |
1) oblique 2) interradicular |
|
|
What are Sharpey's fibers? |
The terminal portions of the principal fibers that are embedded in cementum and bone. |
|
|
Where are Sharpey's fibers more numerous: in cementum or in bone? |
Cementum (but smaller in diameter) |
|
|
What is between the fibers of the PDL? |
Ground substance consisting of glycosaminoglycans, laminin and fibronectin. Note that it si 70% water. |
|
|
T/F. Tooth mobility is largely determined by PDL |
True |
|
|
T/F. The main cellular component of the PDL is collagen. |
False. It is FIBROBLAST. The PDL has mesenchymal cells that can differentiate into cementoblasts, fiber, and osteo to regenerate all tissues. |
|
|
Describe the coronal margin of alveolar processes. |
Follows a wavy configuration that follows the course of the CEJ and is located 1.0-1.5 mm from CEJ |
|
|
T/F. The alveolar socket walls are sometimes referred to as cribriform plates due to the numerous perforations that allow nerves and vessel to enter the PDL. |
True |
|
|
What is dehiscence and fenestration? |
Dehiscence- When bone covering is missing at the coronal portion Fenestration- window. Some bone present in most coronal portion. |
|
|
Does cementum have blood vessel and innervation? |
No. |
|
|
Intrinsic fibers of cementum produced by cementoblasts are oriented in which way? |
Parallel to long axis of tooth |
|
|
What are the 4 types of cementum? |
1) Acellular, afibrillar (found at cervical portion of enamel) 2) Acellular, extrinsic fiber (found at coronal/middle portion of root) 3) Cellular, mixed stratified (apical third of root contains extrinsic and intrinsic fibers) 4) Cellular, intrinsic fiber (mainly resorbtion lacunae) |

