![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
282 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four functions of the digestive system?
|
Ingest food
Digest food Absorb nutrients Eliminate indigestible waste |
|
|
What seven organs are considered to be part of the alimentary canal?
|
Mouth
Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Anus |
|
|
What six organs are considered to be accessory organs in the digestive system?
|
Teeth
Tongue Salivary glands Gall bladder Liver Pancreas |
|
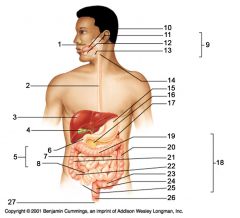
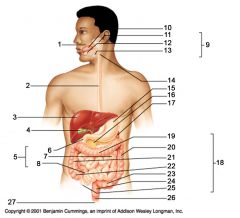
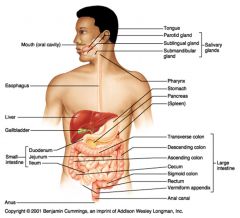
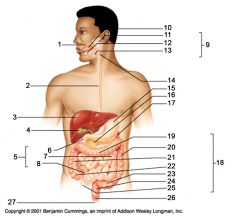
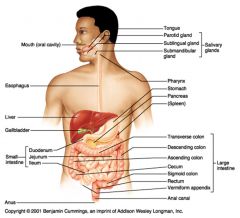
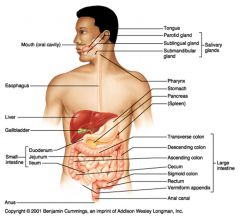
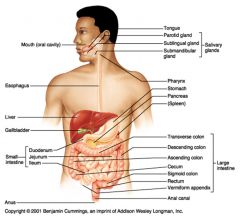
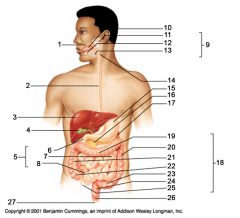
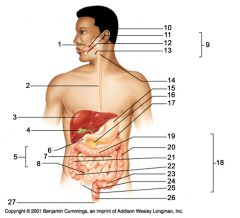
Identify 1
|
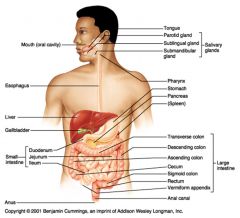
Mouth (oral cavity)
|
|
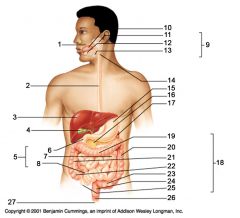
Identify 2
|
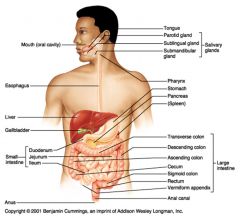
Esophagus
|
|
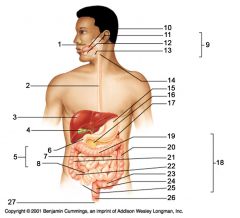
Identify 3
|
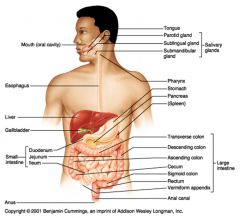
Liver
|
|
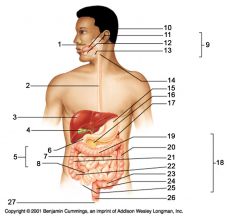
Identify 4
|
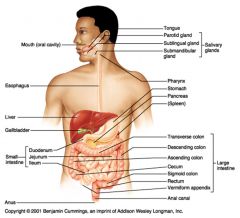
Gallbladder
|
|
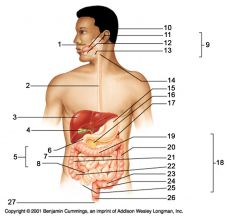
Identify 5
|
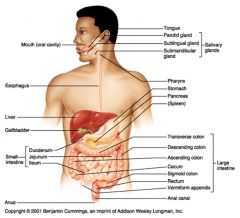
Small intestine
|
|
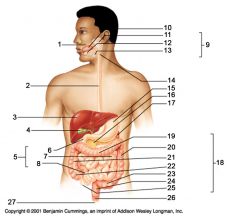
Identify 6
|
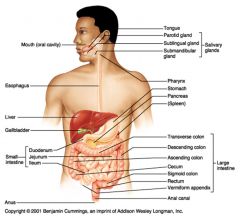
Duodenum
|
|
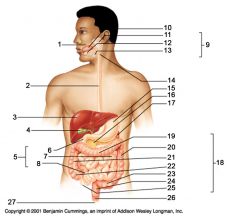
Identify 7
|
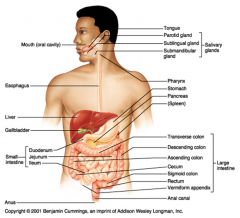
Jejunum
|
|
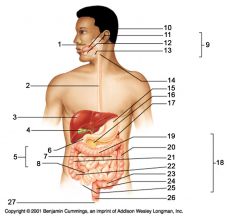
Identify 8
|
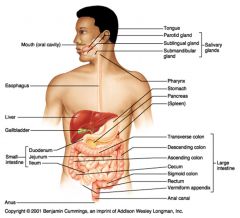
Ileum
|
|
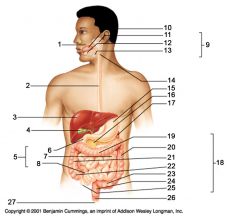
Identify 9
|
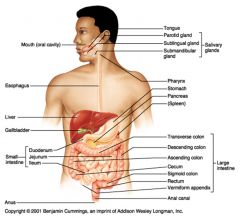
Salivary glands
|
|
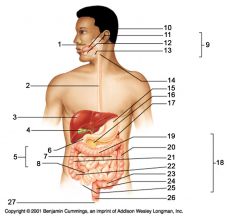
Identify 10
|
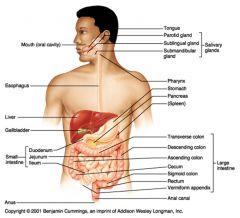
Tongue
|
|
Identify 11
|
Parotid gland
|
|
Identify 12
|
Sublingual gland
|
|
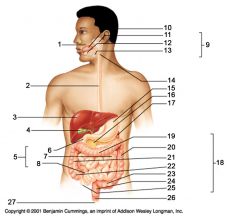
Identify 13
|
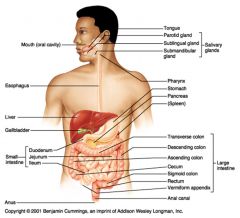
Submandibular gland
|
|
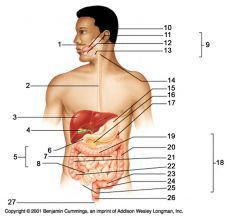
Identify 14
|
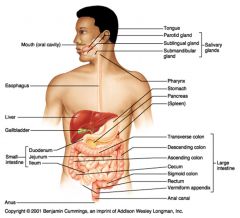
Pharynx
|
|
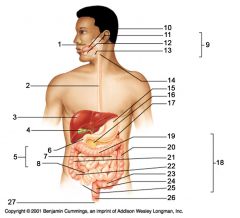
Identify 15
|
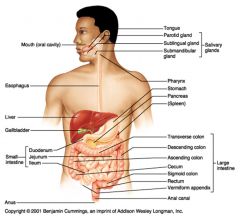
Stomach
|
|
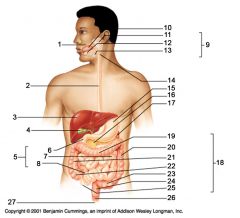
Identify 16
|
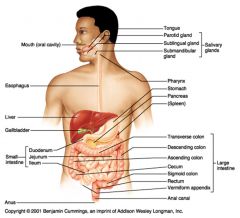
Pancreas
|
|
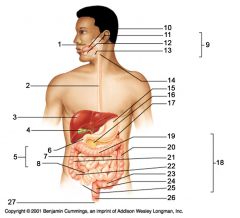
Identify 17
|
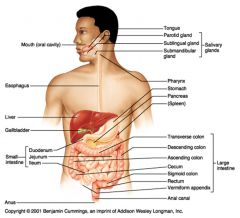
Spleen
|
|
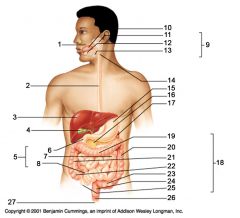
Identify 18
|
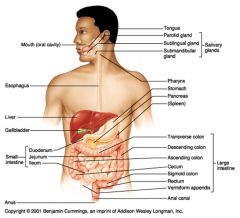
Large intestine
|
|
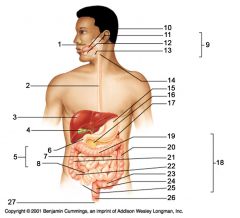
Identify 19
|
Transverse colon
|
|
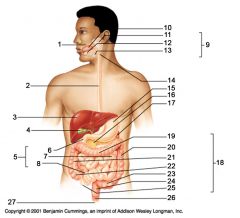
Identify 20
|
Descending colon
|
|
Identify 21
|
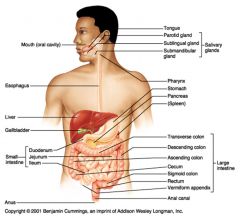
Ascending colon
|
|
Identify 22
|
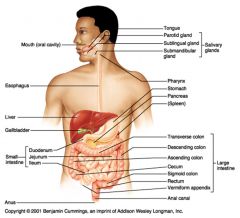
Cecum
|
|
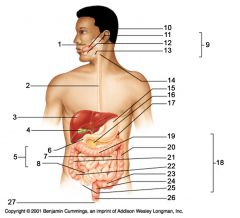
Identify 23
|
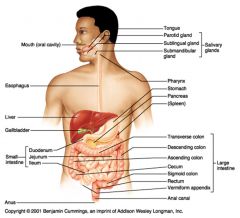
Sigmoid colon
|
|
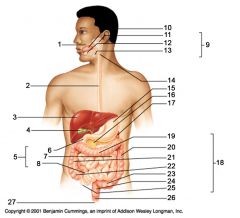
Identify 24
|
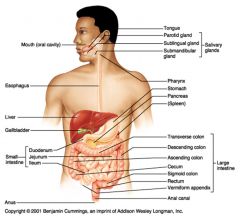
Rectum
|
|
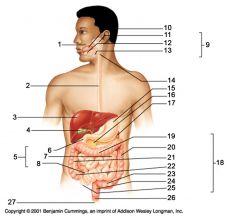
Identify 25
|
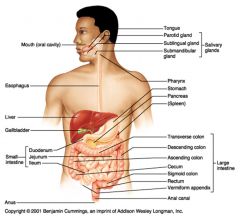
Vermiform appendix
|
|
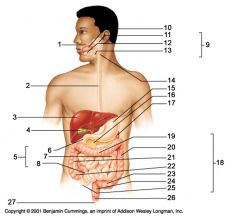
Identify 26
|
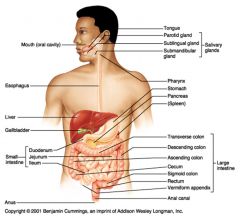
Anal canal
|
|
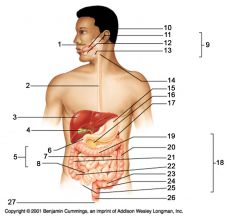
Identify 27
|
Anus
|
|
|
What are the three salivary glands?
|
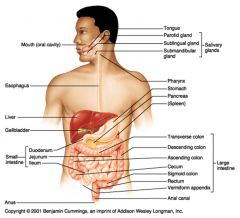
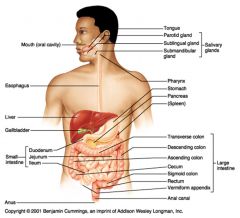
The parotid gland (superior and posterior to the oral cavity)
The sublingual gland (inferior to the tongue) The submandibular gland (inferior to the oral cavity, near the temporomandibular joint) |
|
|
Name the major organs that food will encounter as it transits the digestive system, in the order that it would encounter them.
|
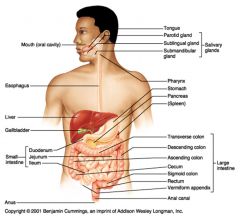
Mouth > Pharynx > Esophagus > Stomach > Small Intestine > Large Intestine > Anus
|
|
|
Name the portions of the small intestine, in the order that food would encounter them.
|
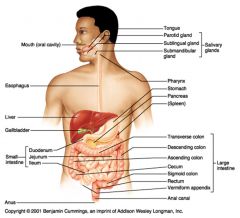
Enters the small intestine from the stomach through the pyloric sphincter:
Duodenum > Jejunum > Ileum Exits from the small intestine to the large intestine through the ileocecal sphincter |
|
|
Name the portions of the areas of the large intestine, in the order that food would encounter them.
|
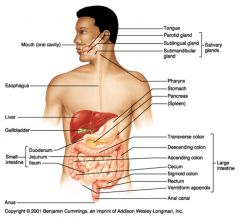
Enters from the small intestine to the large intestine through the ileocecal sphincter
Cecum (passing, but not entering the Vermiform appendix) > Ascending colon (along right side of body) > Transverse colon (from right to left side of body) > Descending colon (along left side of body) > Sigmoid colon > Rectum Exits the large intestine through the two anal sphincters and out of the body via the anus |
|
|
If you have appendicitis, on what side of your abdomen are you likely to feel pain?
|
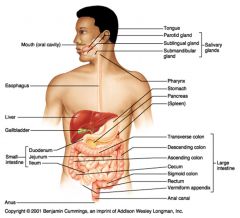
Right (because that's where the vermiform appendix is)
|
|
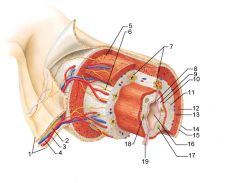
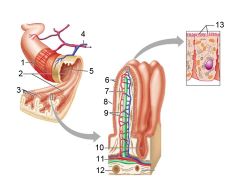
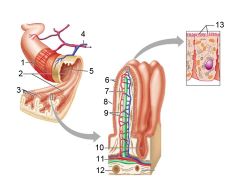
Identify 1
|
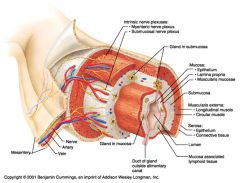
Mesentery
|
|
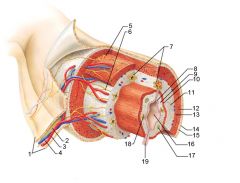
Identify 2
|
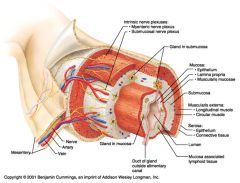
Nerve
|
|
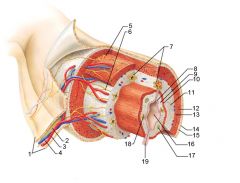
Identify 3
|
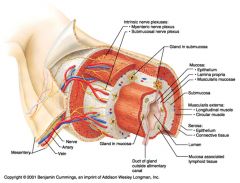
Artery
|
|
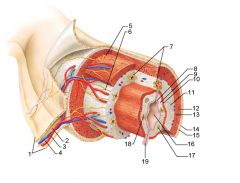
Identify 4
|
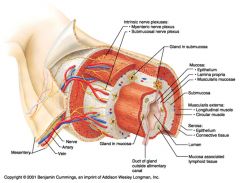
Vein
|
|
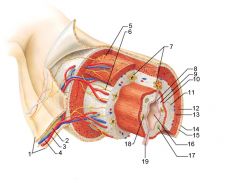
Identify 5
|
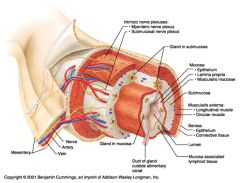
Myenteric nerve plexus (one of the intrinsic nerve plexuses)
|
|
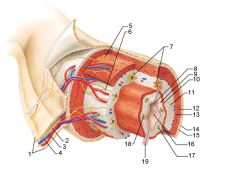
Identify 6
|
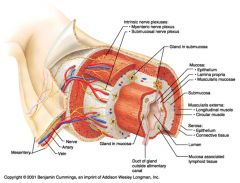
Submucosal nerve plexus (one of the intrinsic nerve plexuses)
|
|
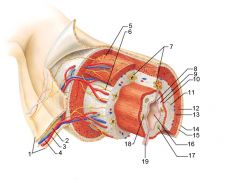
Identify 7
|
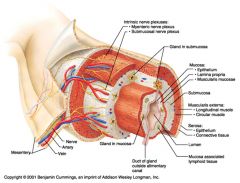
Gland in submucosa
|
|
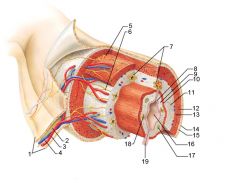
Identify 8
|
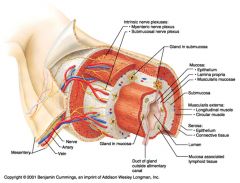
Epithelium (part of the mucosa)
|
|
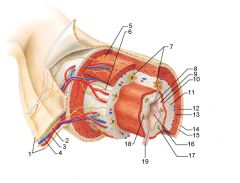
Identify 9
|
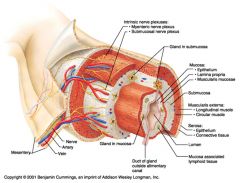
Lamina propria (part of the mucosa)
|
|
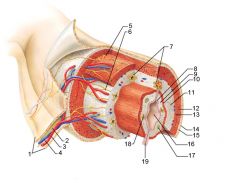
Identify 10
|
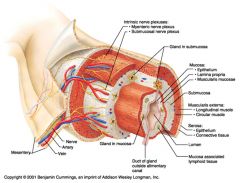
Muscularis mucosae (part of the mucosa)
|
|
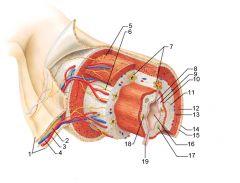
Identify 11
|
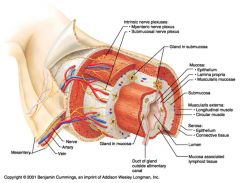
Submucosa
|
|
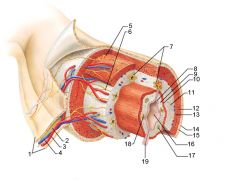
Identify 12
|
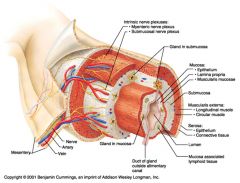
Longitudinal muscle (part of the muscularis externa)
|
|
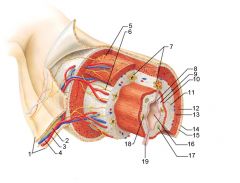
Identify 13
|
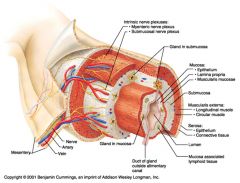
Circular muscle (part of the muscularis externa)
|
|
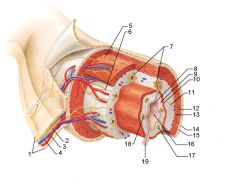
Within the stomach only, what additional layer would be found between the layers indicated by 11 and 13?
|
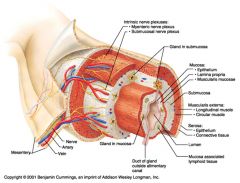
Oblique muscle (part of the muscularis externa)
|
|
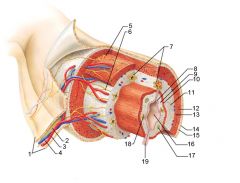
Identify 14
|
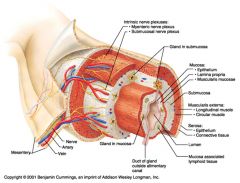
Epithelium (part of the serosa)
|
|
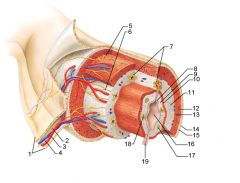
Identify 15
|
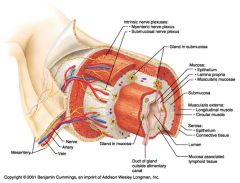
Connective tissue (part of the serosa)
|
|
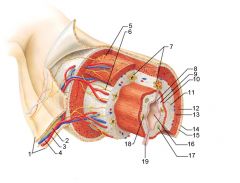
Identify 16
|
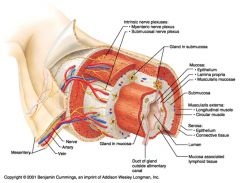
Lumen
|
|
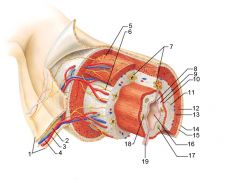
Identify 17
|
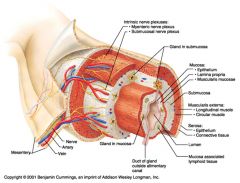
Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue
|
|
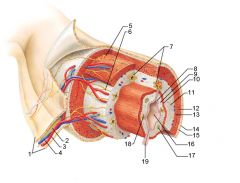
Identify 18
|
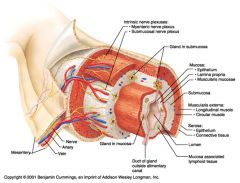
Gland in mucosa
|
|
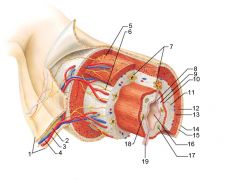
Identify 19
|
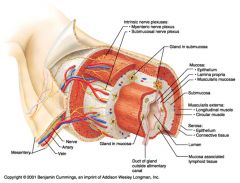
Duct of gland outside alimentary canal
|
|
What is this? What are the four areas of this picture that you should be able to identify?
|
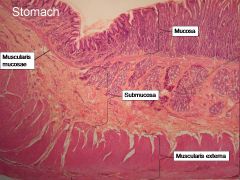
The is the stomach. Be able to identify the mucosa, the muscularis mucosae, the submucosa, and the muscularis externa.
|
|
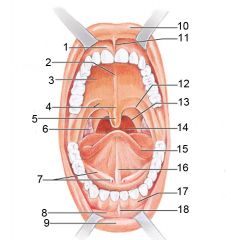
Identify 1
|
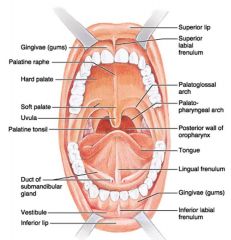
Gingivae (gums)
|
|
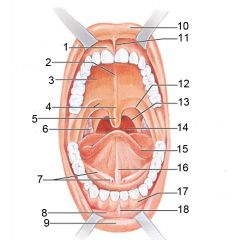
Identify 2
|
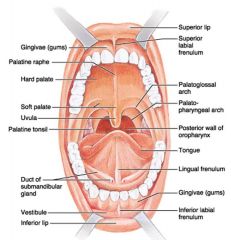
Palatine raphe
|
|
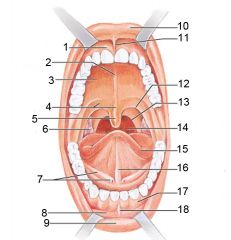
Identify 3
|
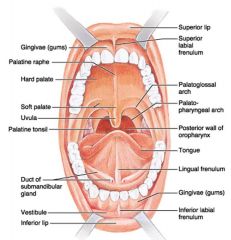
Hard palate
|
|
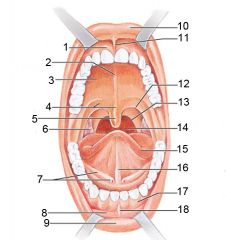
Identify 4
|
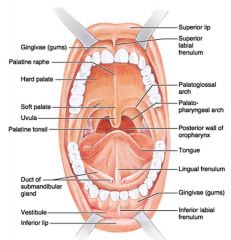
Soft palate
|
|
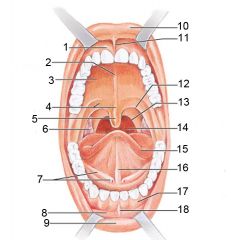
Identify 5
|
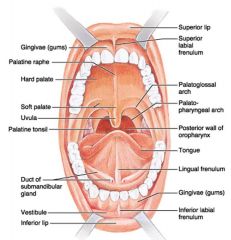
Uvula
|
|
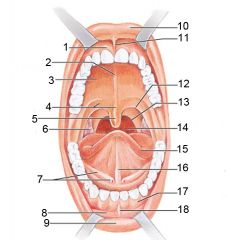
Identify 6
|
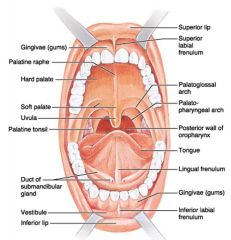
Palatine tonsil
|
|
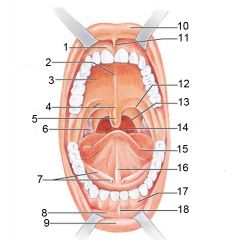
Identify 7
|
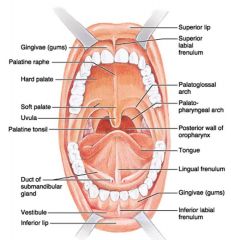
Duct of submandibular gland
|
|
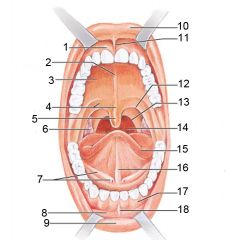
Identify 8
|
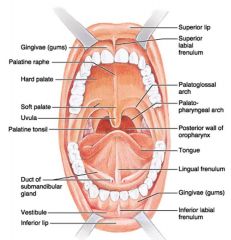
Vestibule
|
|
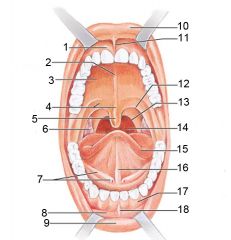
Identify 9
|
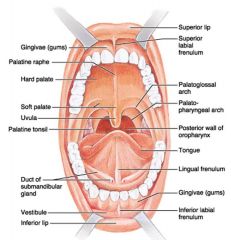
Inferior lip
|
|
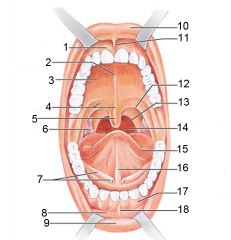
Identify 10
|
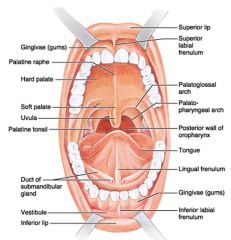
Superior lip
|
|
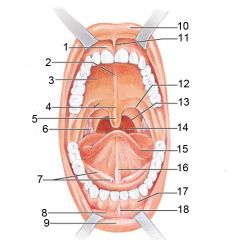
Identify 11
|
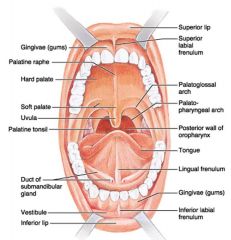
Superior labial frenulum
|
|
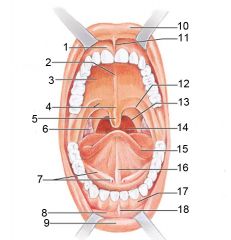
Identify 12
|
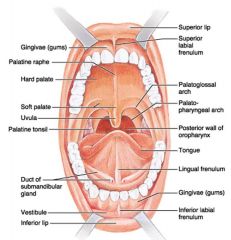
Palatoglossal arch (anterior)
|
|
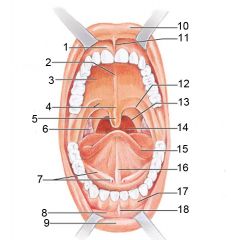
Identify 13
|
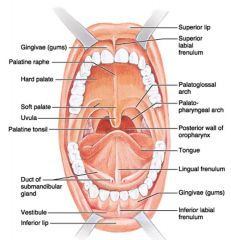
Palatopharyngeal arch (posterior)
|
|
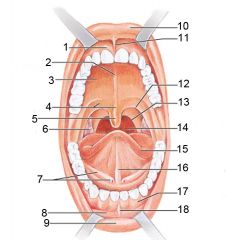
Identify 14
|
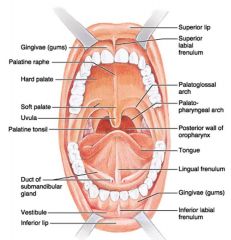
Posterior wall of oropharynx
|
|
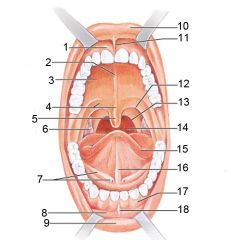
Identify 15
|
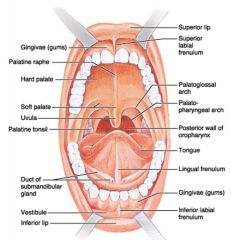
Tongue
|
|
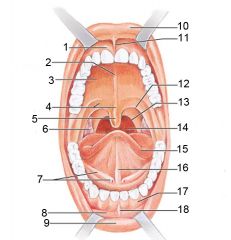
Identify 16
|
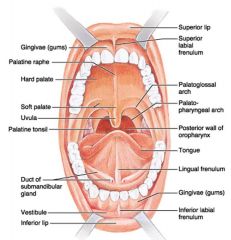
Lingual frenulum
|
|
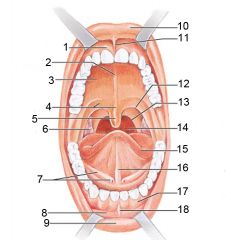
Identify 17
|
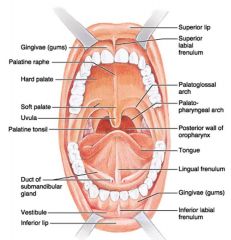
Gingivae (gums)
|
|
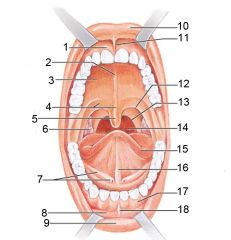
Identify 18
|
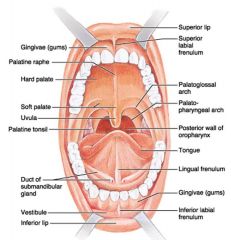
Inferior labial frenulum
|
|
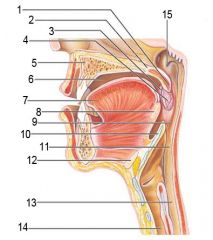
Identify 1
|
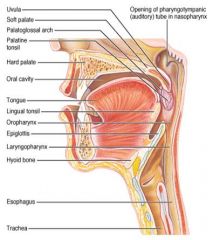
Uvula
|
|
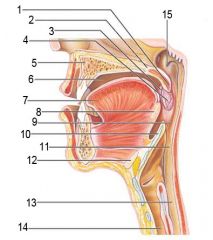
Identify 2
|
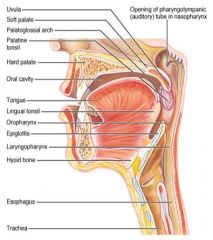
Soft palate
|
|
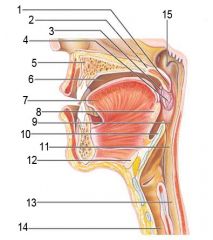
Identify 3
|
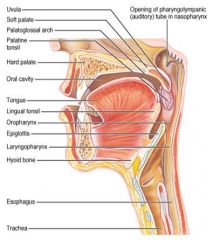
Palatoglosal arch
|
|
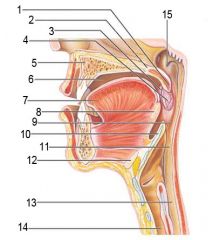
Identify 4
|
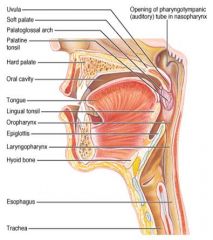
Palatine tonsil
|
|
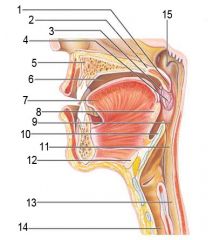
Identify 5
|
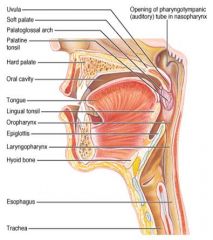
Hard palate
|
|
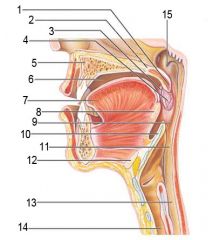
Identify 6
|
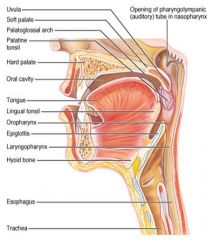
Oral cavity
|
|
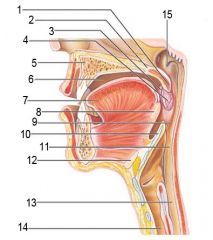
Identify 7
|
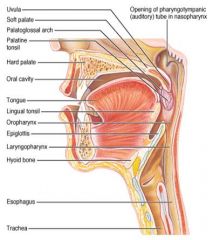
Tongue
|
|
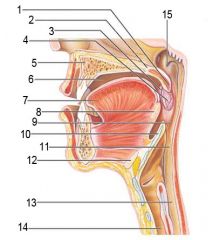
Identify 8
|
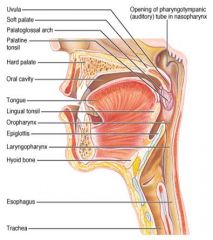
Lingual tonsil
|
|
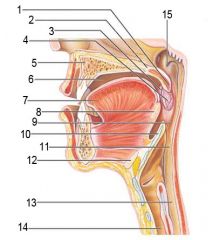
Identify 9
|
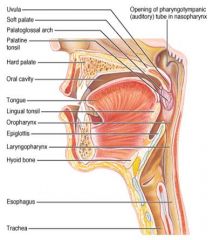
Oropharynx
|
|
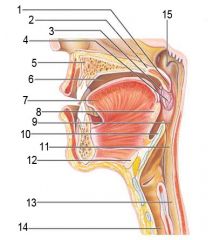
Identify 10
|
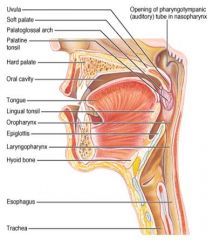
Epiglottis
|
|
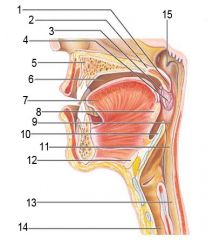
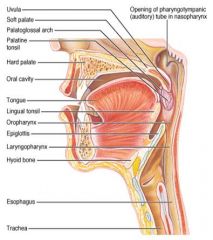
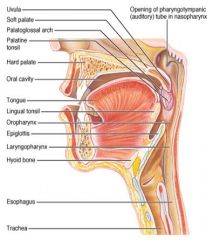
Identify 11
|
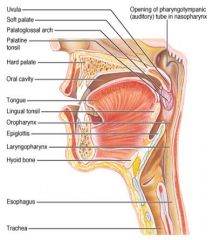
Laryngopharynx
|
|
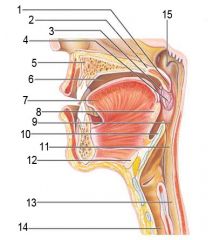
Identify 12
|
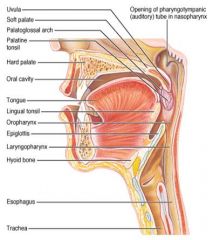
Hyoid bone
|
|
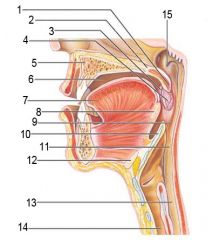
Identify 13
|
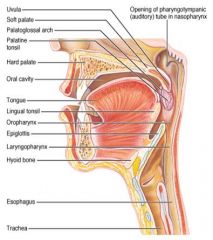
Esophagus
|
|
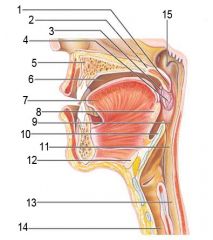
Identify 14
|
Trachea
|
|
Identify 15
|
Opening of the pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube in nasopharynx
|
|
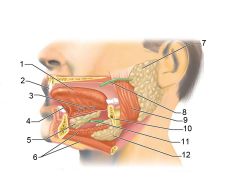
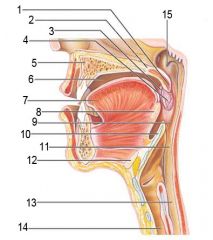
Identify 1
|
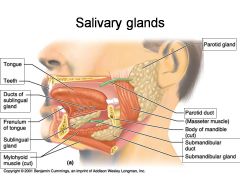
Tongue
|
|
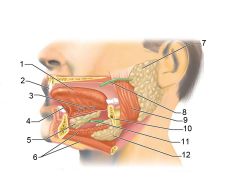
Identify 2
|
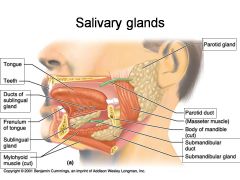
Teeth
|
|
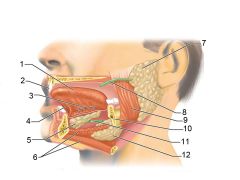
Identify 3
|
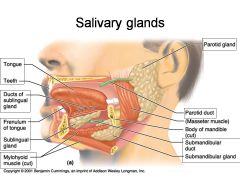
Ducts of sublingual gland
|
|
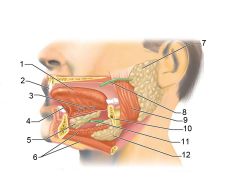
Identify 4
|
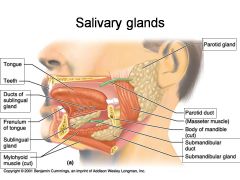
Frenulum of tongue
|
|
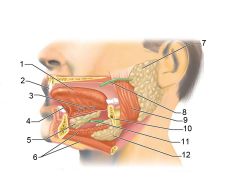
Identify 5
|
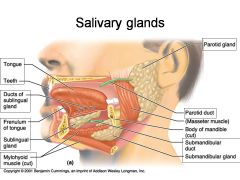
Sublingual gland
|
|
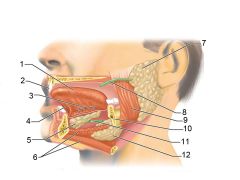
Identify 6
|
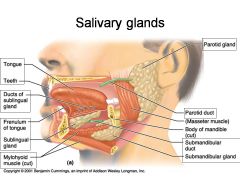
Mylohyoid muscle
|
|
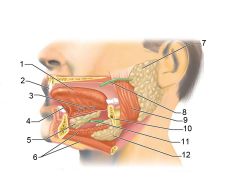
Identify 7
|
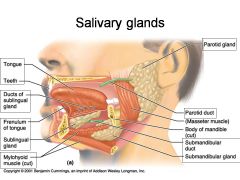
Parotid gland
|
|
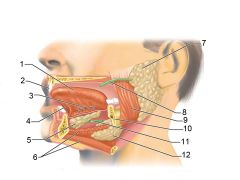
Identify 8
|
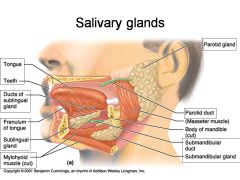
Parotid duct
|
|
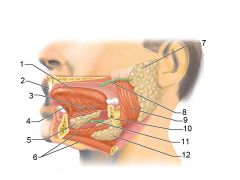
Identify 9
|
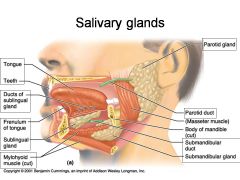
Masseter muscle
|
|
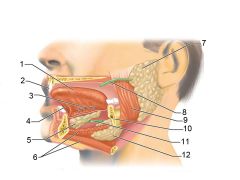
Identify 10
|
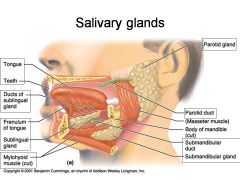
Body of mandible
|
|
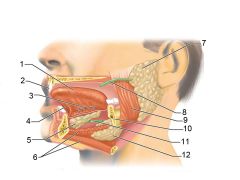
Identify 12
|
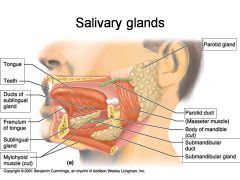
Submandibular gland
|
|
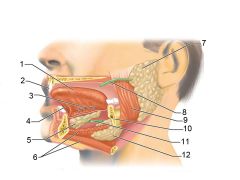
Identify 11
|
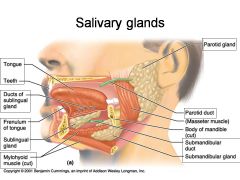
Submandibular duct
|
|
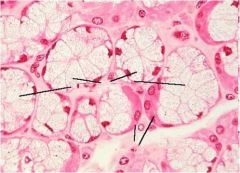
What is this? What should you be able to identify?
|
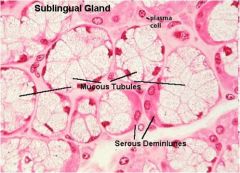
Sublingual salivary gland. Be able to identify serous demilunes and mucous tubules.
|
|
Identify 1
|
Esophagus
|
|
Identify 2
|
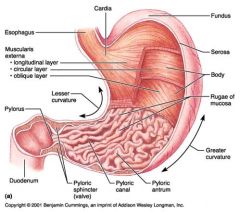
Longitudinal layer (of muscularis externa)
|
|
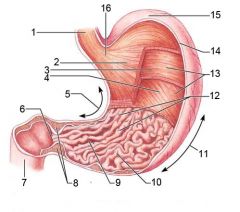
Identify 3
|
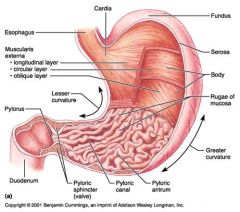
Circular layer (of muscularis externa)
|
|
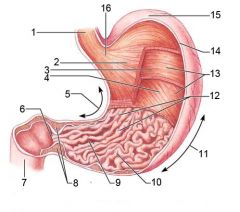
Identify 4
|
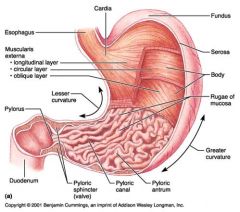
Oblique layer (of muscularis externa)
|
|
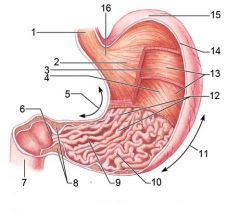
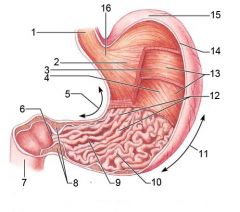
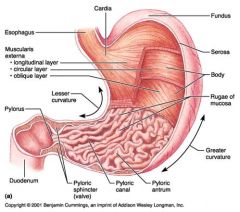
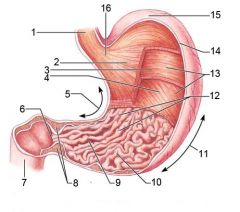
Identify 5
|
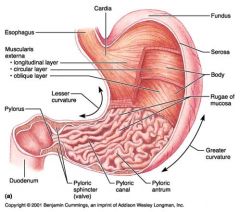
Lesser curvature
|
|
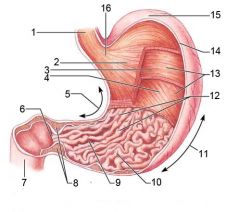
Identify 6
|
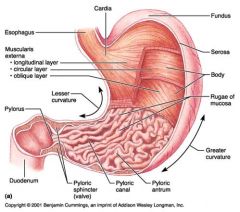
Pylorus
|
|
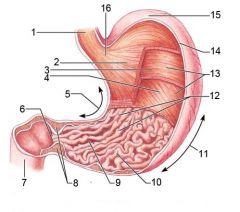
Identify 7
|
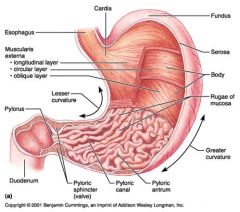
Duodenum
|
|
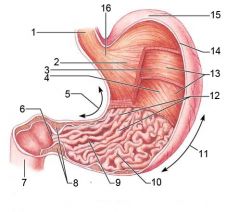
Identify 8
|
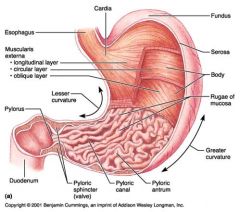
Pyloric sphincter (valve)
|
|
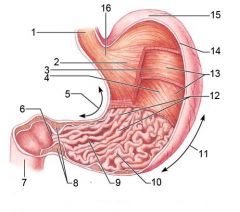
Identify 9
|
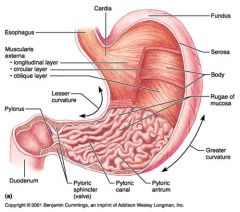
Pyloric canal
|
|
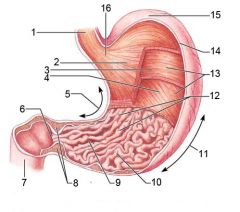
Identify 10
|
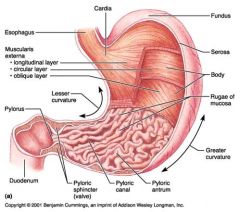
Pyloric antrum
|
|
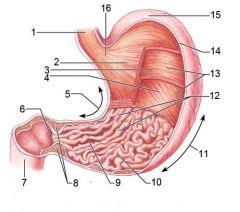
Identify 11
|
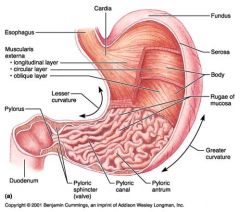
Greater curvature
|
|
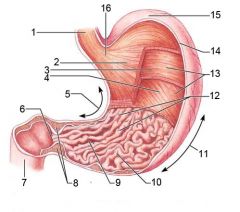
Identify 12
|
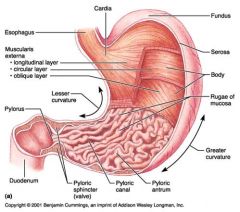
Rugae of mucosa
|
|
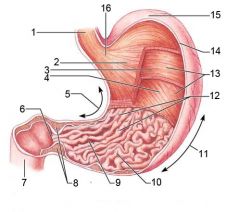
Identify 13
|
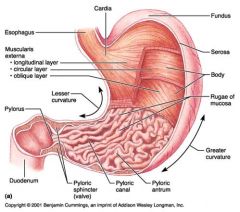
Body of stomach
|
|
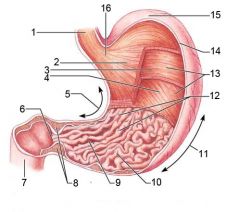
Identify 14
|
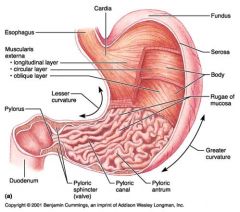
Serosa
|
|
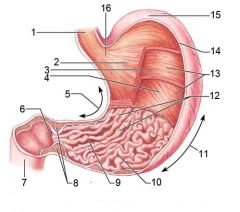
Identify 15
|
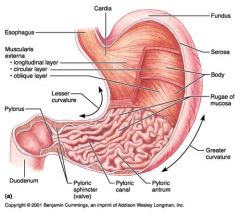
Fundus
|
|
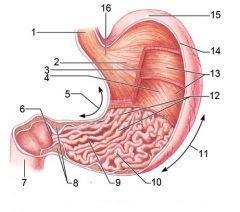
Identify 16
|
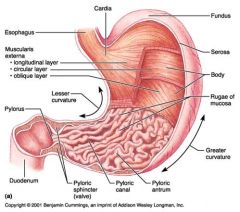
Cardiac region
|
|
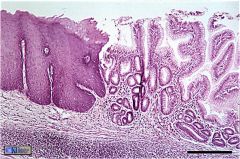
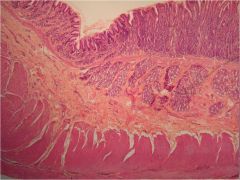
What is this? What should you know about it?
|
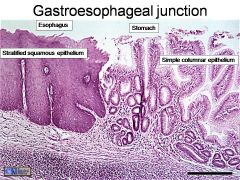
Gastroesophageal junction. The stratified squamous epithelium of the esophagus (to resist abrasion) gives way to the simple columnar epithelium of the stomach here
|
|
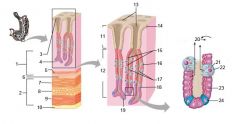
Identify 1
|
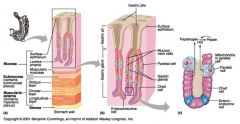
Mucosa
|
|
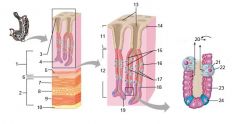
Identify 2
|
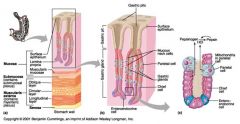
Muscularis externa
|
|
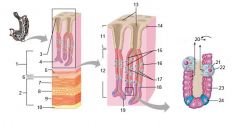
Identify 3
|
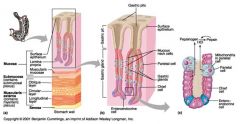
Surface epithelium (of mucosa)
|
|
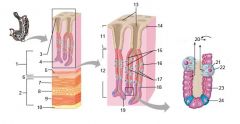
Identify 4
|
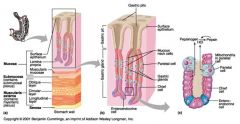
Lamina propria (of mucosa)
|
|
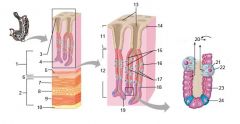
Identify 5
|
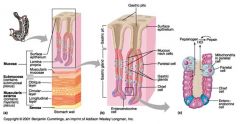
Muscularis mucosae (of mucosa)
|
|
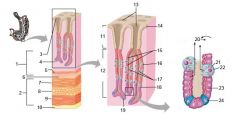
Identify 6
|
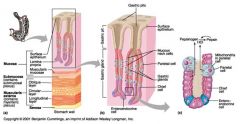
Submucosa
|
|
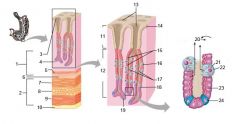
Identify 7
|
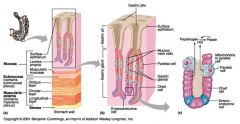
Oblique layer (of muscularis externa)
|
|
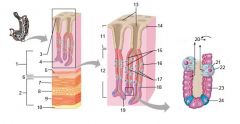
Identify 8
|
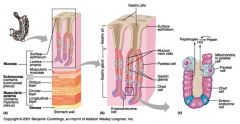
Circular layer (of muscularis externa)
|
|
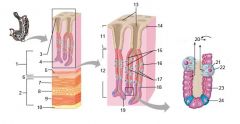
Identify 9
|
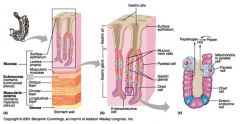
Longitudinal layer (of muscularis externa)
|
|
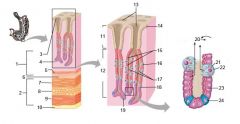
Identify 10
|
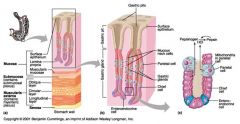
Serosa
|
|
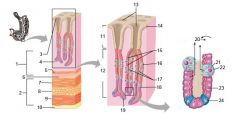
Identify 11
|
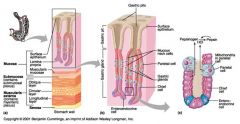
Gastric pit
|
|
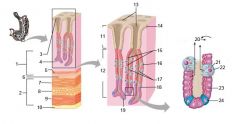
Identify 12
|
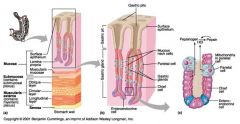
Gastric gland
|
|
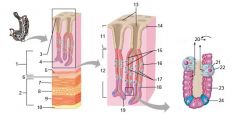
Identify 13
|
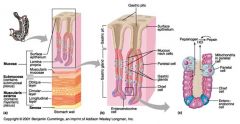
Gastric pits
|
|
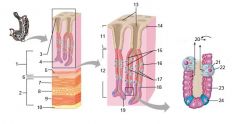
Identify 14
|
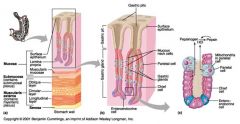
Surface epithelium
|
|
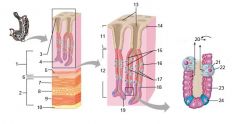
Identify 15
|
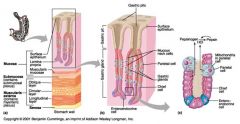
Mucous neck cells
|
|
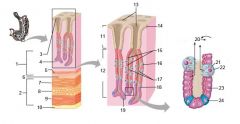
Identify 16
|
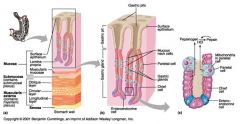
Parietal cell
|
|
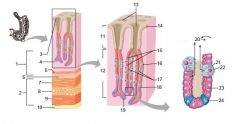
Identify 17
|
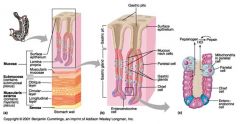
Gastric glands
|
|
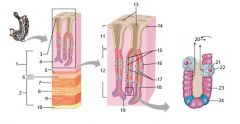
Identify 18
|
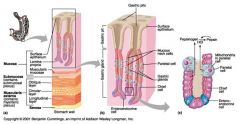
Chief cell
|
|
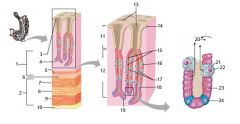
Identify 19
|
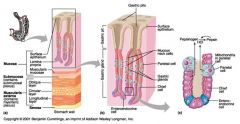
Enteroendocrine cell
|
|
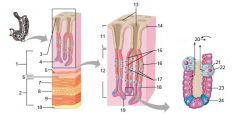
#20 is an illustration of an interaction between #22 and #23 - what is it?
|
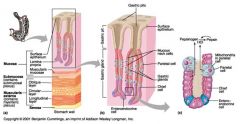
Pepsinogen (from chief cells) turns into pepsin in the presence of HCl, which is released by parietal cells
|
|
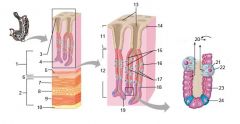
Identify 21
|
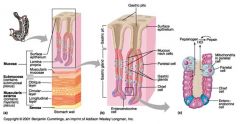
Mitochondria in parietal cell
|
|
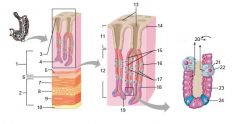
Identify 22
|
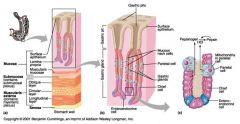
Parietal cell
|
|
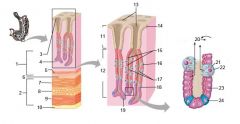
Identify 23
|
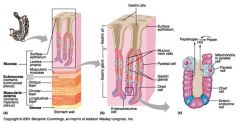
Chief cell
|
|
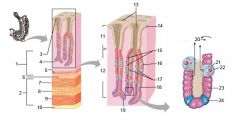
Identify 24
|
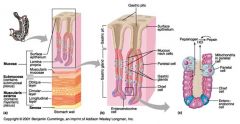
Enteroendocrine cell
|
|
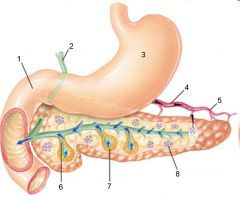
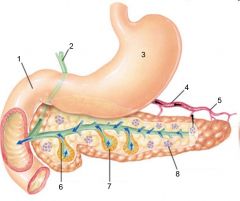
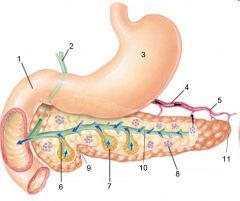
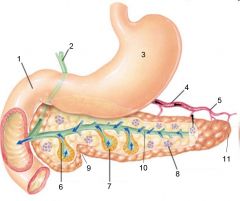
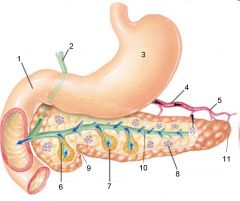
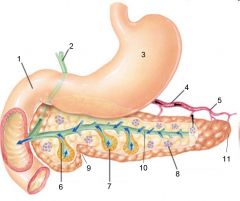
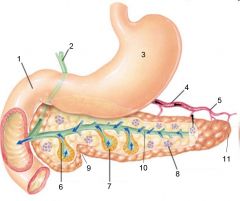
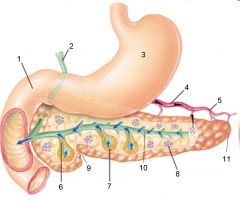
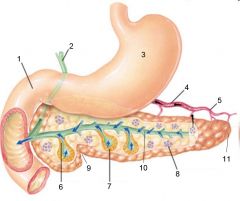
Identify 1
|
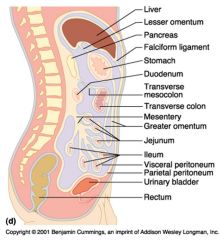
Liver
|
|
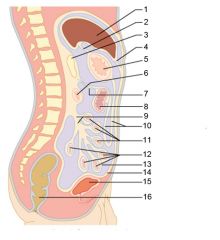
Identify 2
|
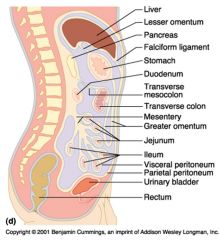
Lesser omentum
|
|
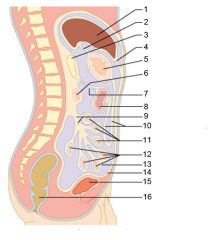
Identify 3
|
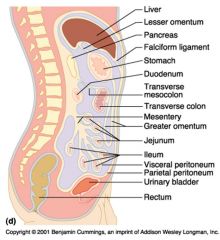
Pancreas
|
|
Identify 4
|
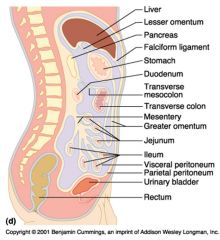
Falciform ligament
|
|
Identify 5
|
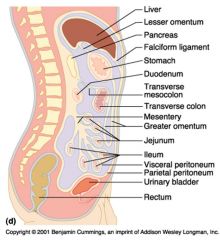
Stomach
|
|
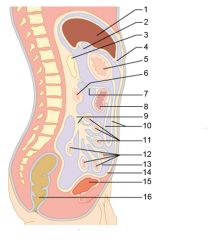
Identify 6
|
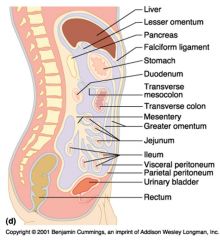
Duodenum
|
|
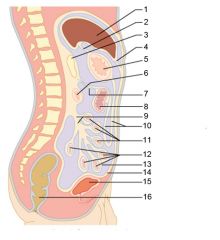
Identify 7
|
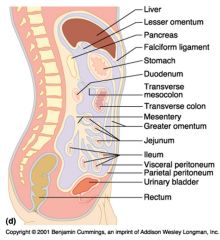
Transverse mesocolon
|
|
Identify 8
|
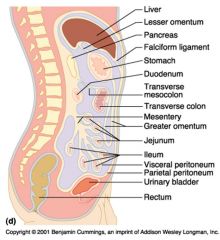
Transverse colon
|
|
Identify 9
|
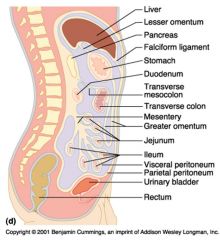
Mesentery
|
|
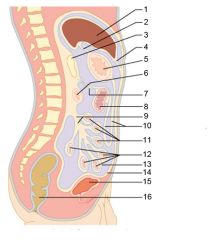
Identify 10
|
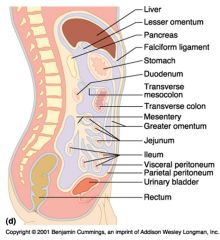
Greater omentum
|
|
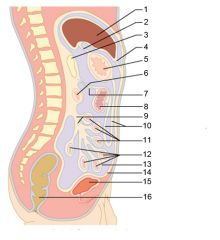
Identify 11
|
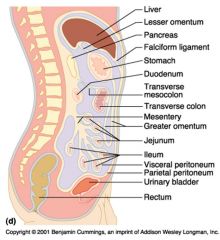
Jejunum
|
|
Identify 12
|
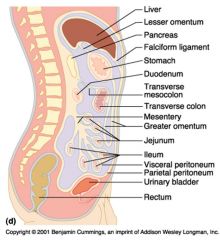
Ileum
|
|
Identify 13
|
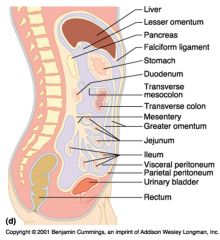
Visceral peritoneum
|
|
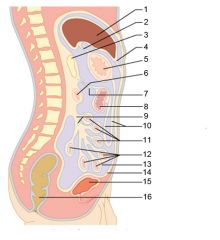
Identify 14
|
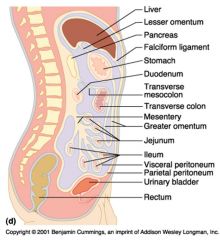
Parietal peritoneum
|
|
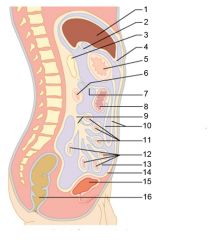
Identify 15
|
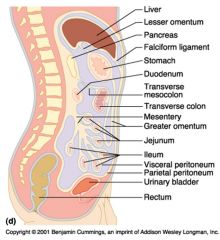
Urinary bladder
|
|
Identify 16
|
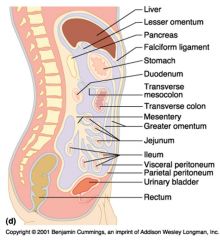
Rectum
|
|
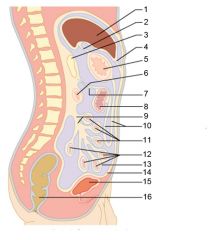
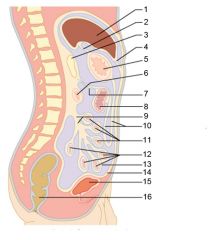
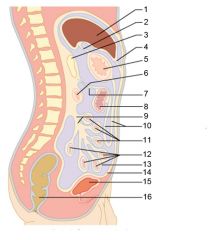
Identify 1
|
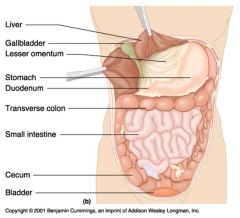
Liver
|
|
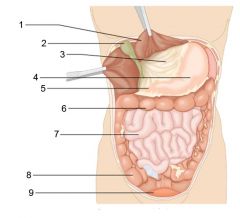
Identify 2
|
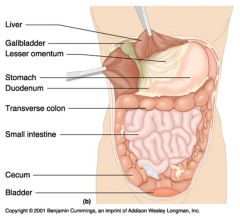
Gallbladder
|
|
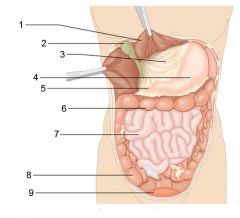
Identify 3
|
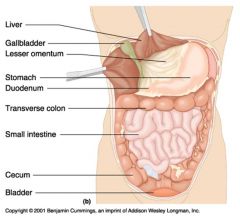
Lesser omentum
|
|
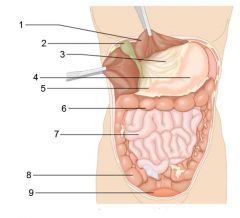
Identify 4
|
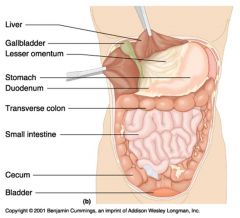
Stomach
|
|
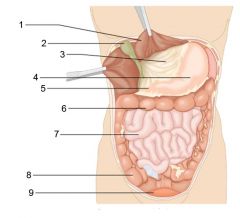
Identify 5
|
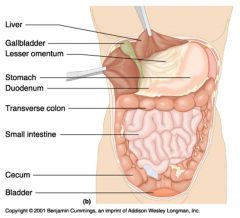
Duodenum
|
|
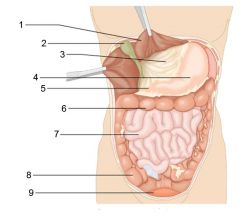
Identify 6
|
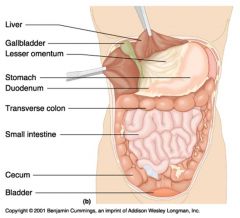
Transverse colon
|
|
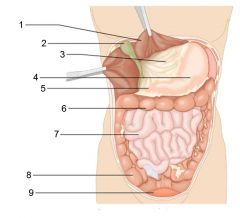
Identify 7
|
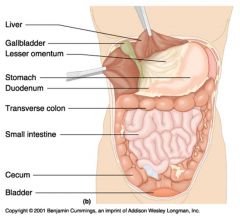
Small intestine
|
|
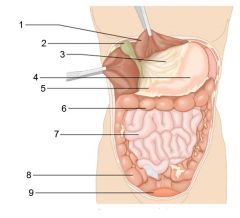
Identify 8
|
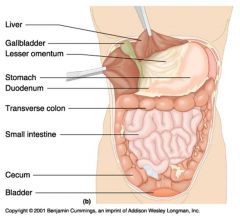
Cecum
|
|
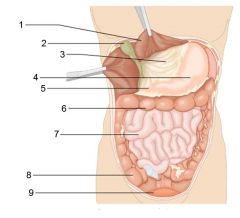
Identify 9
|
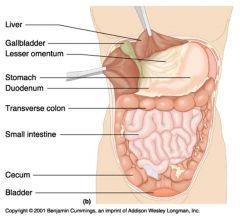
Bladder
|
|
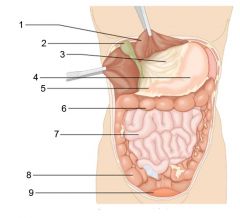
Identify 1
|
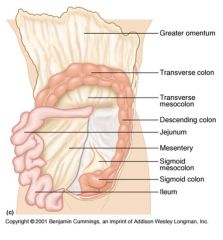
Greater omentum
|
|
Identify 2
|
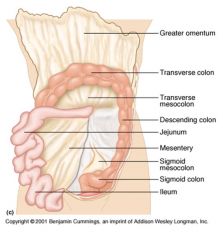
Transverse colon
|
|
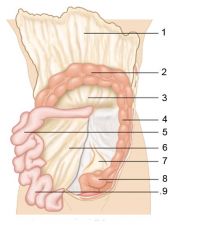
Identify 3
|
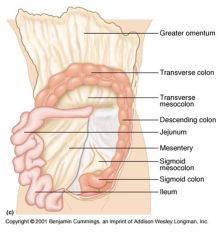
Transverse mesocolon
|
|
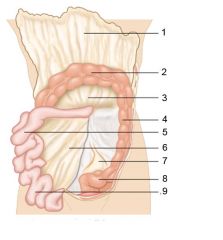
Identify 4
|
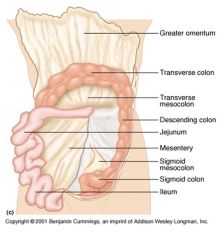
Descending colon
|
|
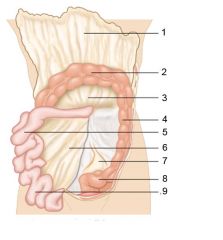
Identify 5
|
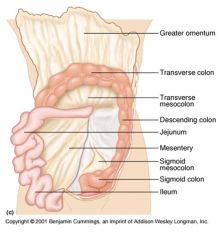
Jejunum
|
|
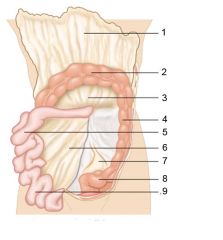
Identify 6
|
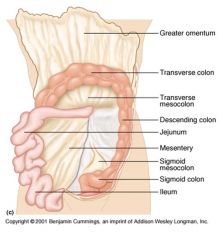
Mesentery
|
|
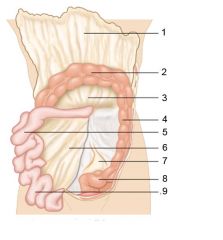
Identify 7
|
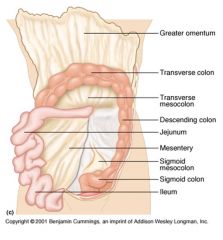
Sigmoid mesocolon
|
|
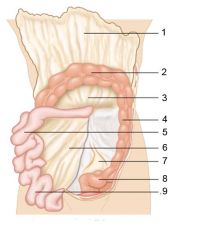
Identify 8
|
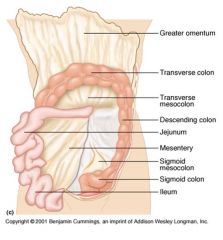
Sigmoid colon
|
|
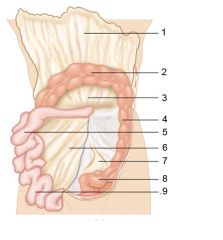
Identify 9
|
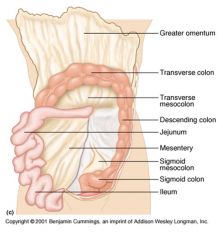
Ileum
|
|
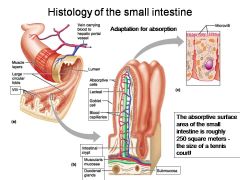
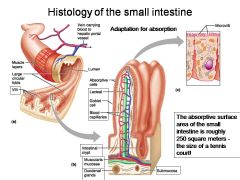
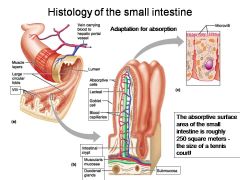
How large is the absorptive surface area of the small intestine, roughly?
|
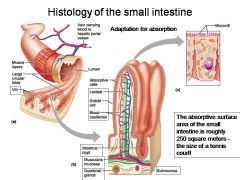
Approximately 250 square meters - the size of a tennis court!
|
|
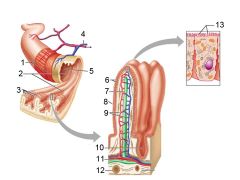
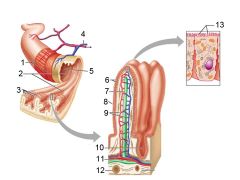
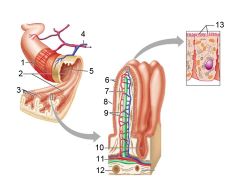
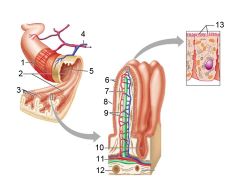
Identify 1
|
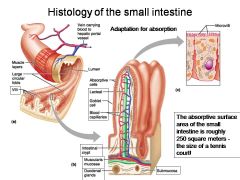
Muscle layers
|
|
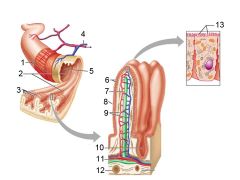
Identify 2
|
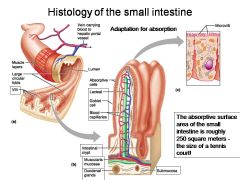
Large circular folds
|
|
Identify 3
|
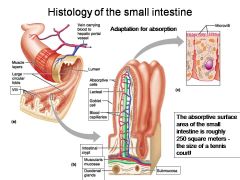
Villi
|
|
Identify 4
|
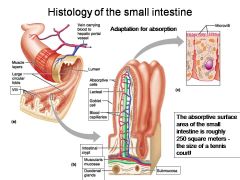
Vein carrying blood to hepatic portal vessel
|
|
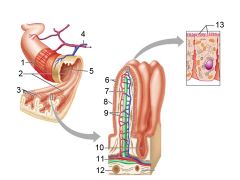
Identify 5
|
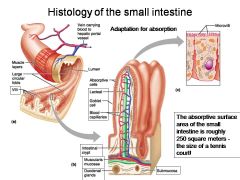
Lumen
|
|
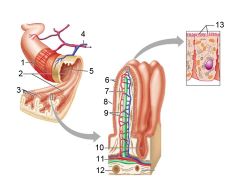
Identify 6
|
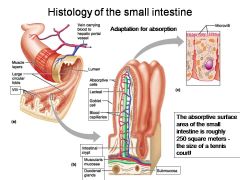
Absorptive cells
|
|
Identify 7
|
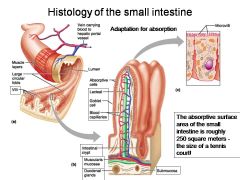
Lacteal
|
|
Identify 8
|
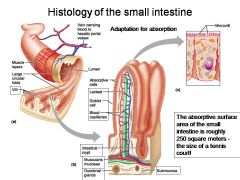
Goblet cell
|
|
Identify 9
|
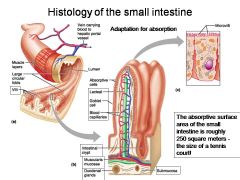
Blood capillaries
|
|
Identify 10
|
Intestinal crypt
|
|
Identify 11
|
Muscularis mucosae
|
|
Identify 12
|
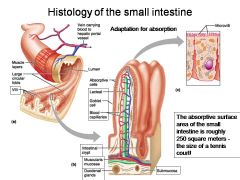
Duodenal glands
|
|
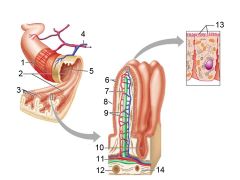
Identify 13
|
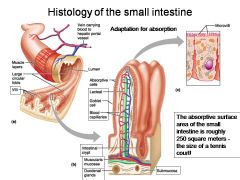
Microvilli
|
|
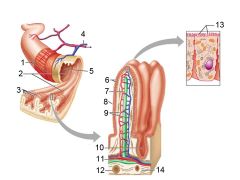
Identify 14
|
Submucosa
|
|
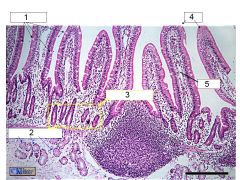
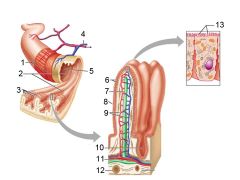
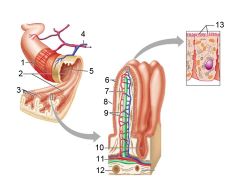
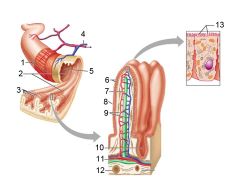
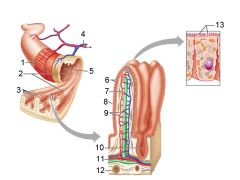
What is this? Identify the numbered areas
|
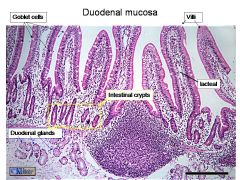
Duodenal mucosa. 1. Goblet cells. 2. Duodenal glands. 3. Intestinal crypts. 4. Villi. 5. Lacteal
|
|
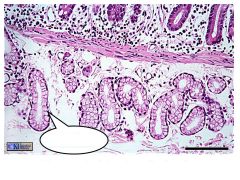
What are these?
|
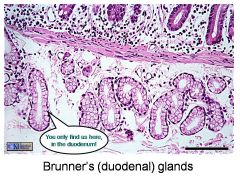
Brunner's (duodenal) glands
|
|
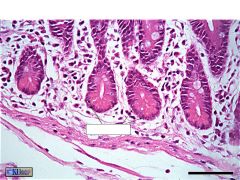
What are these? What is the labeled bit?
|
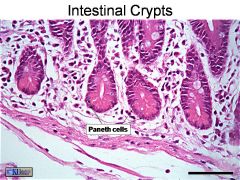
Intestinal crypts. Paneth cells
|
|
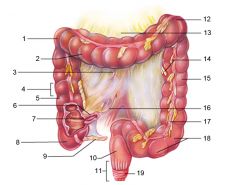
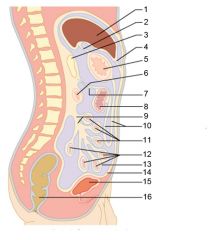
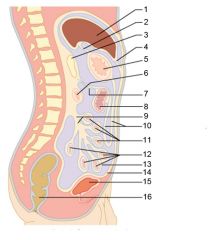
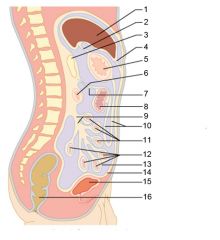
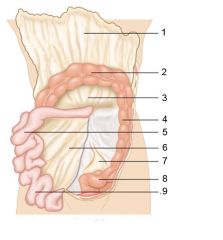
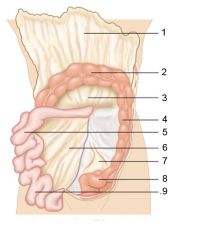
Identify 1
|
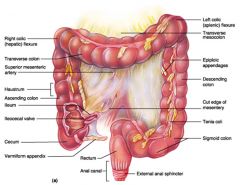
Right colic (hepatic) flexure
|
|
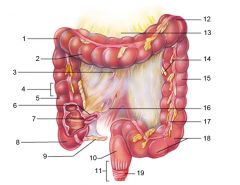
Identify 2
|
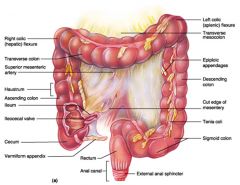
Transverse colon
|
|
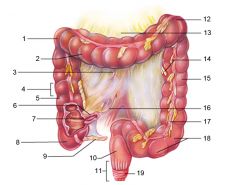
Identify 3
|
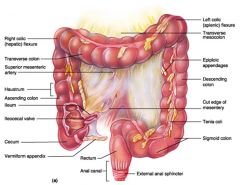
Superior mesenteric artery
|
|
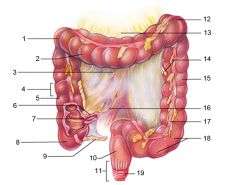
Identify 4
|
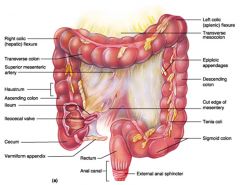
Haustrum
|
|
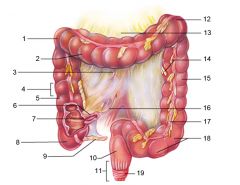
Identify 5
|
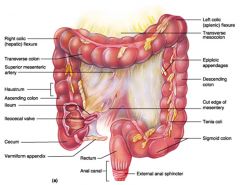
Ascending colon
|
|
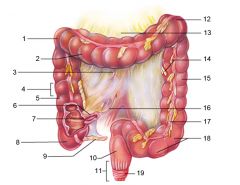
Identify 6
|
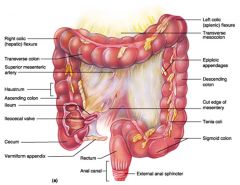
Ileum
|
|
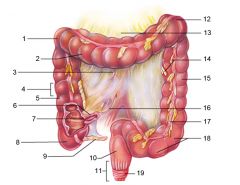
Identify 7
|
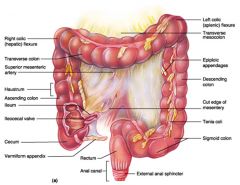
Ileocecal valve
|
|
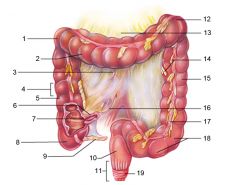
Identify 8
|
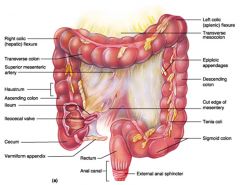
Cecum
|
|
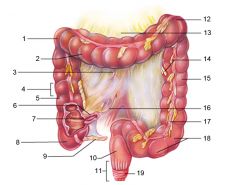
Identify 9
|
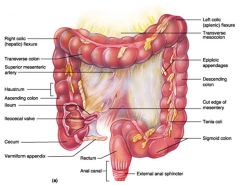
Vermiform appendix
|
|
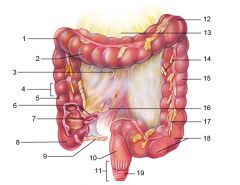
Identify 10
|
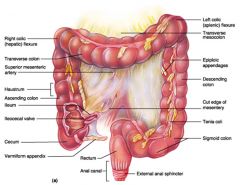
Rectum
|
|
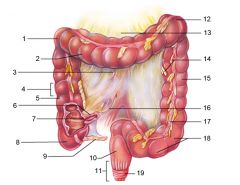
Identify 11
|
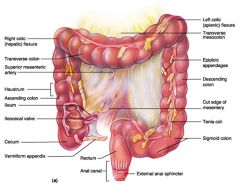
Anal canal
|
|
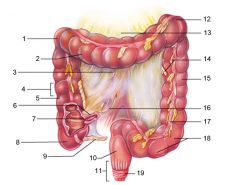
Identify 12
|
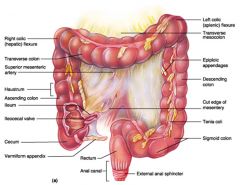
Left colic (splenic) flexure
|
|
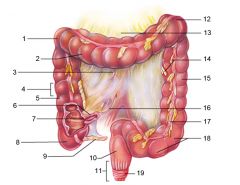
Identify 13
|
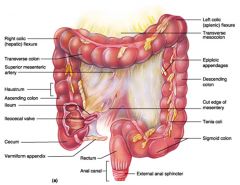
Transverse mesocolon
|
|
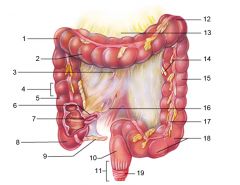
Identify 14
|
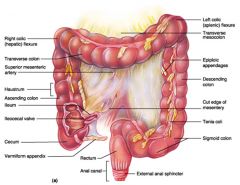
Epiploic appendages
|
|
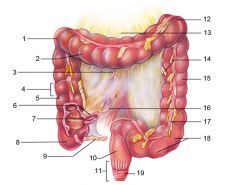
Identify 15
|
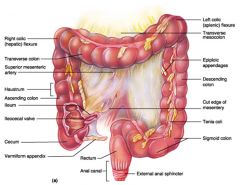
Descending colon
|
|
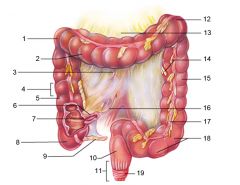
Identify 16
|
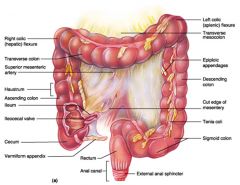
Cut edge of mesentery
|
|
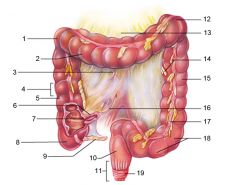
Identify 17
|
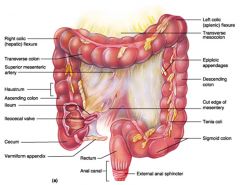
Tenia coli
|
|
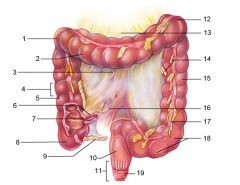
Identify 18
|
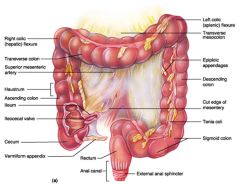
Sigmoid colon
|
|
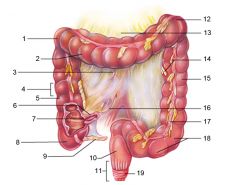
Identify 19
|
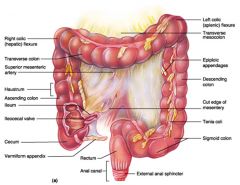
External anal sphincter
|
|
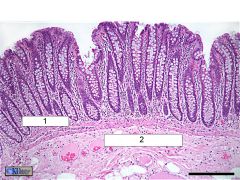
What is this? What are the numbered areas?
|
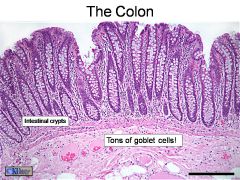
The colon. 1. Intestinal crypts. 2. Goblet cells.
|
|
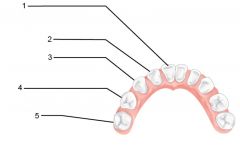
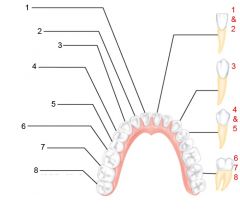
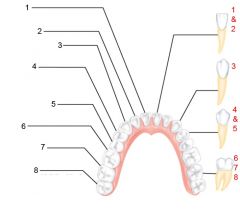
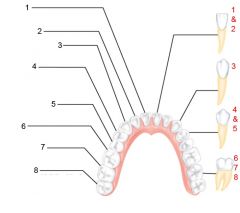
What is an alternate name for "baby" teeth?
|
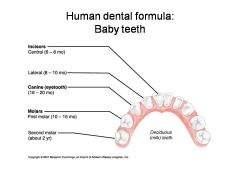
Deciduous (milk) teeth
|
|
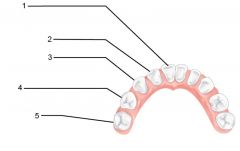
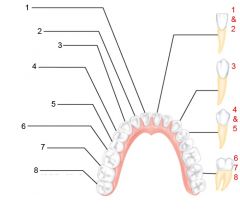
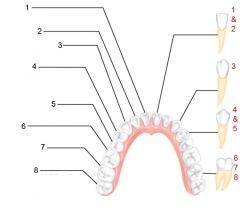
Identify 1 - approximately when would this kind of tooth come in?
|
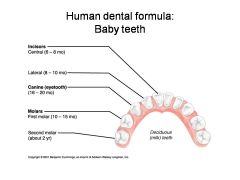
Incisors (central) (6-8 mo)
|
|
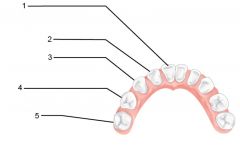
Identify 2 - approximately when would this kind of tooth come in?
|
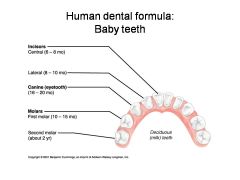
Incisors (lateral) (8-10 mo)
|
|
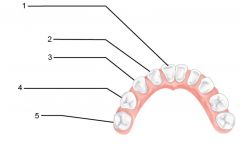
Identify 3 - approximately when would this kind of tooth come in?
|
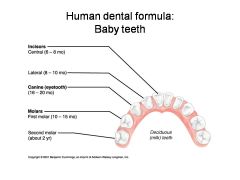
Canine (eyetooth) (16-20 mo)
|
|
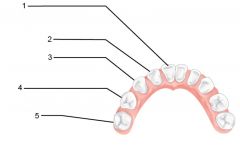
Identify 4 - approximately when would this kind of tooth come in?
|
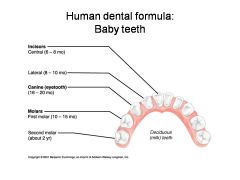
First molar (10-15 mo)
|
|
Identify 5 - approximately when would this kind of tooth come in?
|
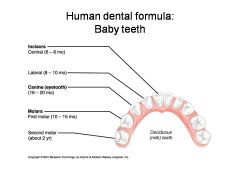
Second molar (2 yr)
|
|
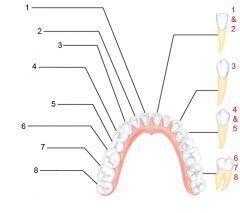
Identify 1 - approximately when would this tooth come in?
|
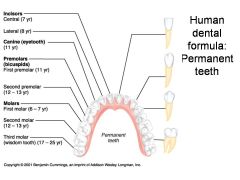
Incisors (central) (7 yr) - ID: thin, flattish top.
|
|
Identify 2 - approximately when would this tooth come in?
|
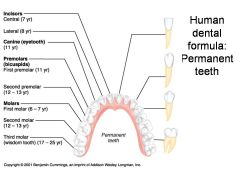
Incisors (lateral) (8 yr) - ID: thin, flattish top.
|
|
Identify 3 - approximately when would this tooth come in?
|
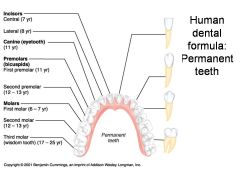
Canine (eyetooth) (11 yr) - ID: Comes to single point
|
|
Identify 4 - approximately when would this tooth come in?
|
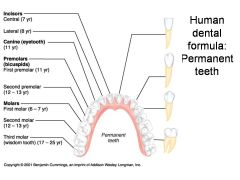
First premolar (bicuspid) (11 yr) - ID: Two points or bumps
|
|
Identify 5 - approximately when would this tooth come in?
|
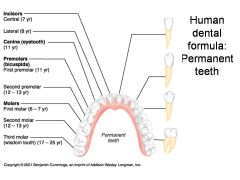
Second premolar (bicuspid) (12-13 yr) - ID: Two points or bumps
|
|
Identify 6 - approximately when would this tooth come in?
|
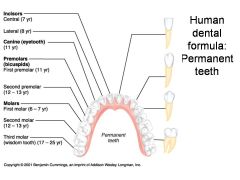
First molar (6-7 yr) - ID: Multiple roots
|
|
Identify 7 - approximately when would this tooth come in?
|
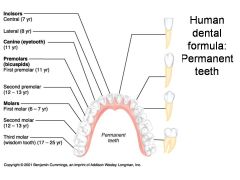
Second molar (12-13 yr) - ID: Multiple roots
|
|
Identify 8 - approximately when would this tooth come in?
|
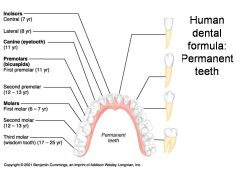
Third molar (wisdom tooth) (17-25 yr) - ID: Multiple roots
|
|
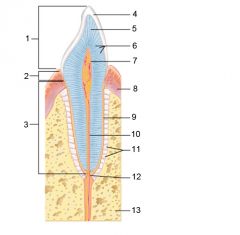
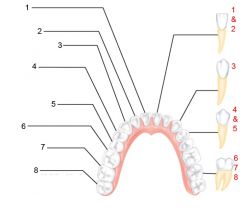
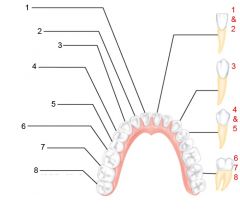
Identify 1
|
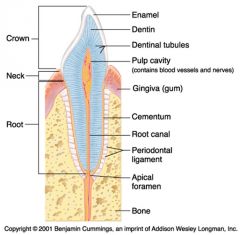
Crown
|
|
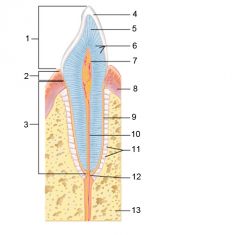
Identify 2
|
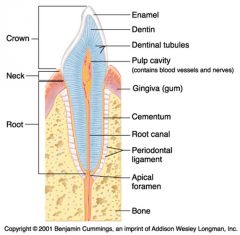
Neck
|
|
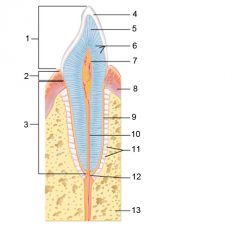
Identify 3
|
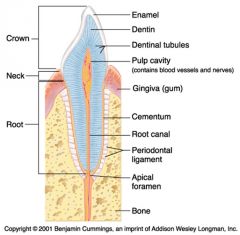
Root
|
|
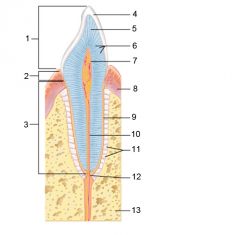
Identify 4
|
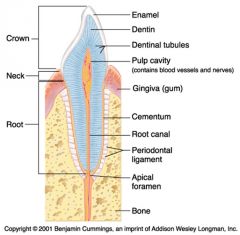
Enamel
|
|
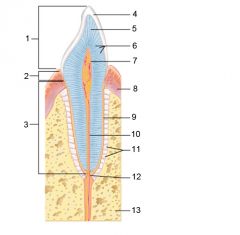
Identify 5
|
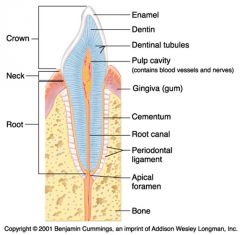
Dentin
|
|
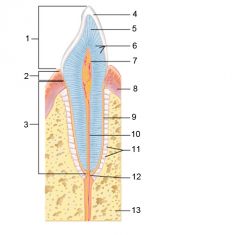
Identify 6
|
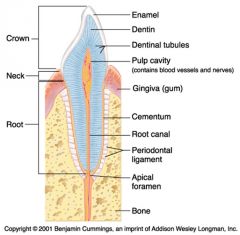
Dentinal tubules
|
|
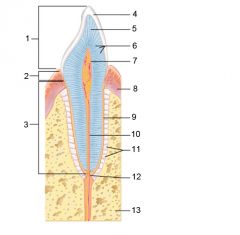
Identify 7
|
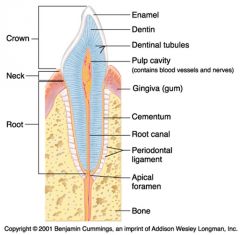
Pulp cavity (contains blood vessels and nerves)
|
|
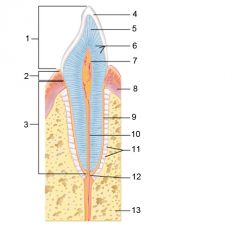
Identify 8
|
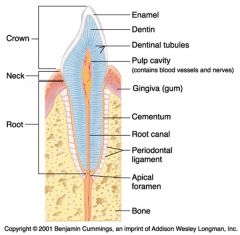
Gingiva (gum)
|
|
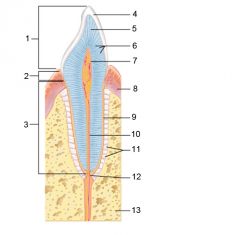
Identify 9
|
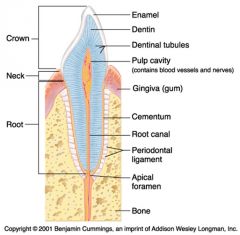
Cementum
|
|
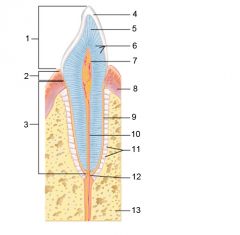
Identify 10
|
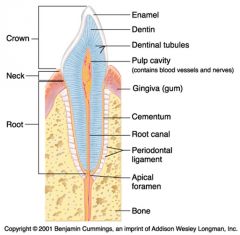
Root canal
|
|
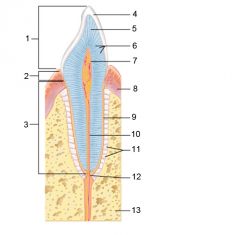
Identify 11
|
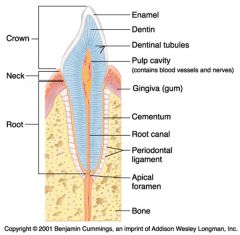
Periodontal ligament
|
|
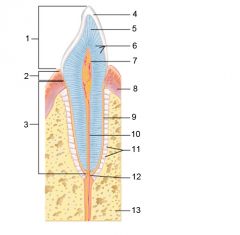
Identify 12
|
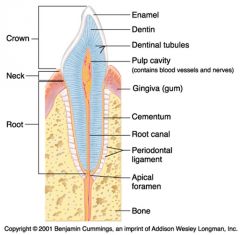
Apical foramen
|
|
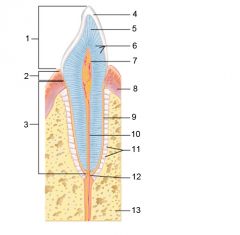
Identify 13
|
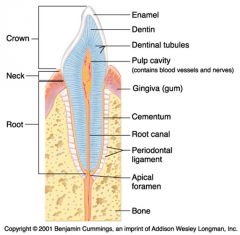
Bone
|
|
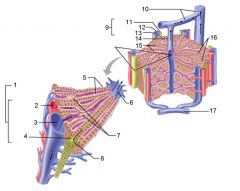
Identify 1
|
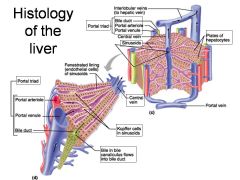
Portal triad
|
|
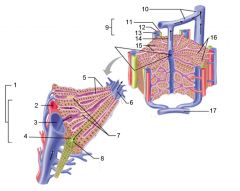
Identify 2
|
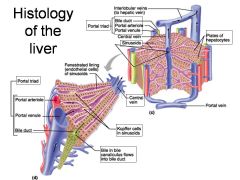
Portal arteriole
|
|
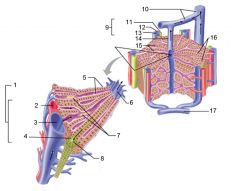
Identify 3
|
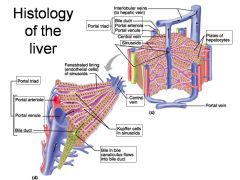
Portal venule
|
|
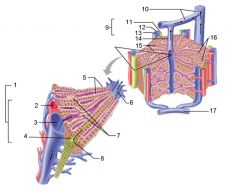
Identify 4
|
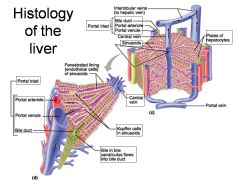
Bile duct
|
|
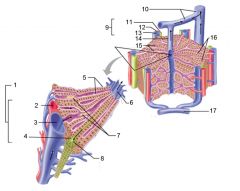
Identify 5
|
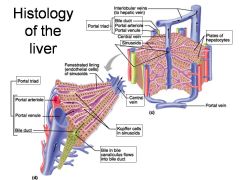
Fenestrated lining (endothelial cells) of sinusoids
|
|
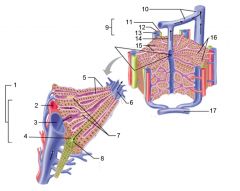
Identify 6
|
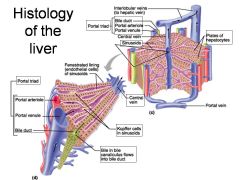
Central vein
|
|
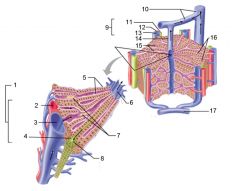
Identify 7
|
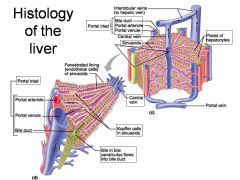
Kupffer cells in sinusoids
|
|
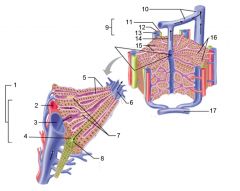
Identify 8
|
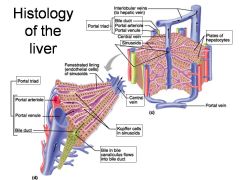
Bile in bile canaliculus flows into bile duct
|
|
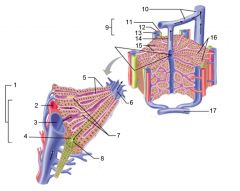
Identify 9
|
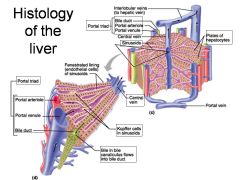
Portal triad
|
|
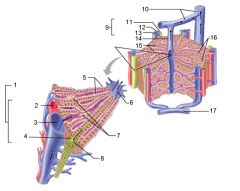
Identify 10
|
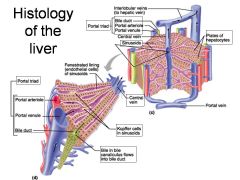
Interlobular veins (to hepatic vein)
|
|
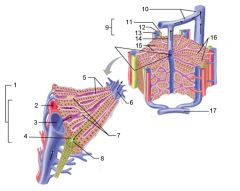
Identify 11
|
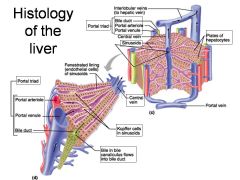
Bile duct
|
|
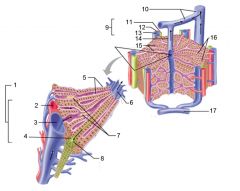
Identify 12
|
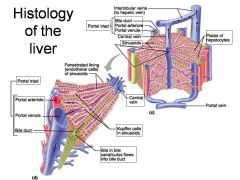
Portal arteriole
|
|
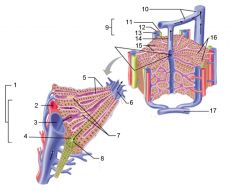
Identify 13
|
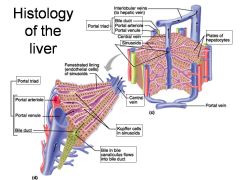
Portal venule
|
|
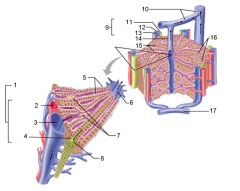
Identify 14
|
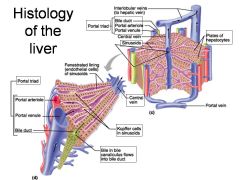
Central vein
|
|
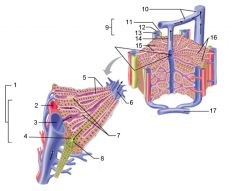
Identify 15
|
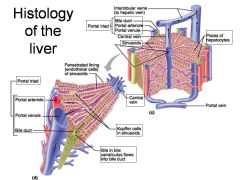
Sinusoids
|
|
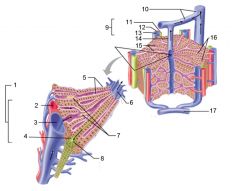
Identify 16
|
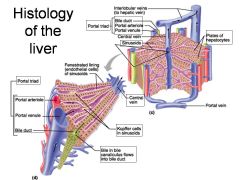
Plates of hepatocytes
|
|
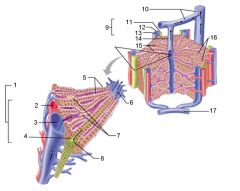
Identify 17
|
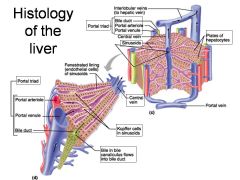
Portal vein
|
|
What is this? What should you be able to identify?
|
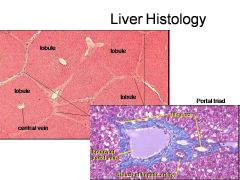
Liver. Be able to identify lobules and central veins, and to identify parts of portal triad
|
|
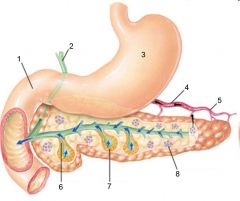
Identify 1
|
Duodenum
|
|
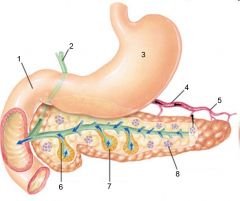
Identify 2
|
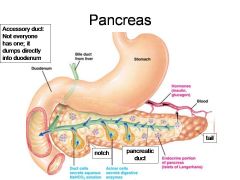
Bile duct from liver
|
|
Identify 3
|
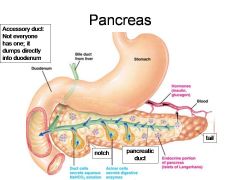
Stomach
|
|
Identify 4
|
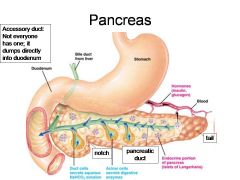
Hormones (insulin, glucagon)
|
|
Identify 5
|
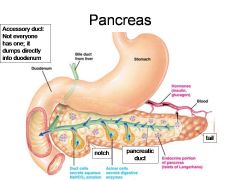
Blood
|
|
Identify 6
|
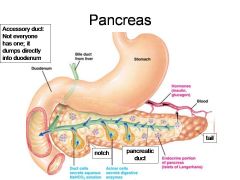
Duct cells (secrete aqueous NaHCO3 solution)
|
|
Identify 7
|
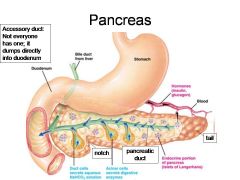
Acinar cells (secrete digestive enzymes)
|
|
Identify 8
|
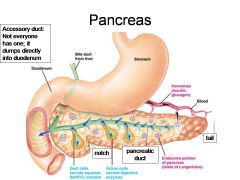
Endocrine portion of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
|
|
Identify 9
|
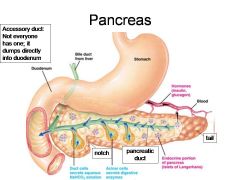
Notch
|
|
Identify 10
|
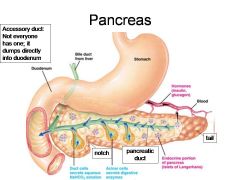
Pancreatic duct
|
|
Identify 11
|
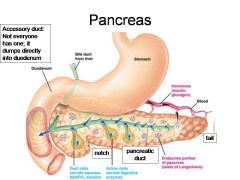
Tail
|
|
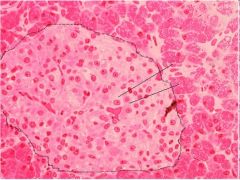
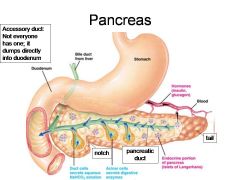
What is this? What should you be able to identify?
|
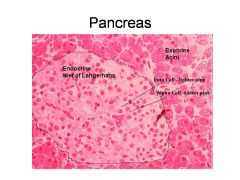
Pancreas. Islets of Langerhans, Acini, Alpha and Beta cells
|
|
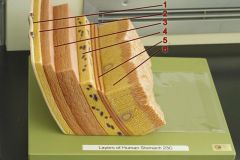
Identify 1
|
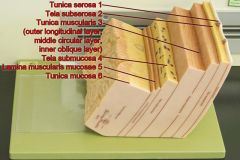
Tunica serosa
|
|
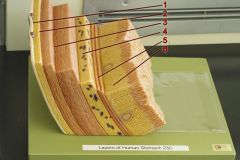
Identify 2
|
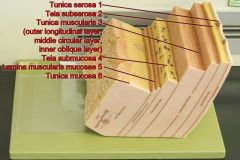
Tela subserosa
|
|
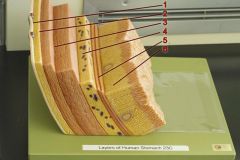
Identify 3
|
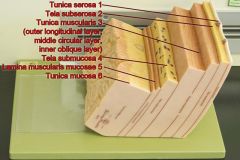
Tunica muscularis (outer longitudinal layer, middle circular layer, inner oblique layer)
|
|
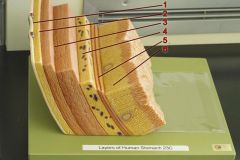
Identify 4
|
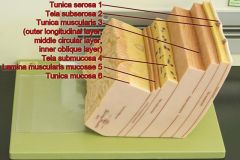
Tela submucosa
|
|
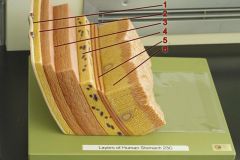
Identify 5
|
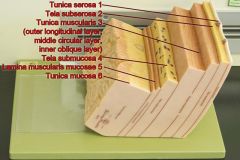
Lamina muscularis mucosae
|
|
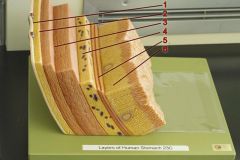
Identify 6
|
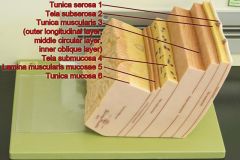
Tunica mucosa
|
|
|
When a substance is added to Lugol's solution, what are you testing for? What is a positive indicator?
|
You are testing for starch. The solution turns blue/black in the presence of starch.
|
|
|
When a substance is added to Benedict's solution, what are you testing for? What is a positive indicator?
|
You are testing for sugar. The solution (originally blue) will turn green, yellow, or red, depending on the amount of sugar present, or remain blue if none is present.
|
|
|
When a substance is added to a BAPNA solution, what are you testing for? What is a positive indicator?
|
You are testing for Tripsyn, which breaks down proteins. The solution will turn yellow if Tripsyn is present.
|
|
|
When you test as substance using litmus blue, what are you testing for? What is a positive indicator?
|
You are testing acidity. Litmus blue changes from blue to pink as the tested substance becomes more acidic.
|

