![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In order to maximize gas transport rates across the respiratory epithelia, what evolutionary trend would you expect to see in the respiratory epithelia structure?
A: Increased surface area and increased thickness B: Increased surface area and decreased thickness C: Decreased surface area and increased thickness D: Decreased surface area and decreased thickness |
B: Increased surface area and decreased thickness
|
|
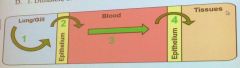
What modes of transport are used to transport oxygen at each of these four locations in the body?
A: 1. Convection, 2. active transport, 3. convection, 4. active transport. B: 1. Convection, 2. diffusion, 3. convection, 4. diffusion C: 1. Diffusion, 2. active transport, 3. convection, 4. diffusion. D: 1. Diffusion, 2. convection, 3. diffusion, 4. convection |
B: 1. Convection, 2. diffusion, 3. convection, 4. diffusion
|
|
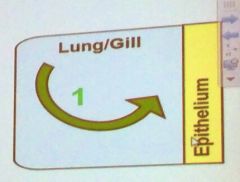
What is a major benefit of the convection inn the lung/gill that applies to both respiratory gasses?
A: Maintain the concentration gradient of gasses across the respiratory epithelium B: moves the respiratory gasses away from the respiratory epithelium C: Moves the respiratory gasses toward the respiratory epithelium D: Keeps some air in the lung from the previous inspiration |
A: Maintain the concentration gradient of gasses across the respiratory epithelium
|
|
|
What is it rare to find aquatic organisms use tidal flow (in/out of a lung) to ventilate their respiratory epithelia?
A: Water is more viscous than air B: Water holds more oxygen than air C: It is easier to eliminate CO2 in water D: The diffusion rate of gasses in water is lower |
A: Water is more viscous than air
|
|
|
How do fish ventilate the respiratory epithelia?
A: Swallowing water and pushing it across their gill B: Swallow water, wait for diffusion of gasses into the blood stream, then expel the water C: Forcing water across their gills by swimming with their mouths open D: A or C E: A, B, or C |
D: A or C
|
|
|
In humans which represents the greatest volume of air?
A: The amount of air that is pushed in and out of the lungs in each breath during resting breathing B: The amount of air that is left in the lungs after exhalation during resting breathing C: The amount of air that is expelled from the lung during maximal expiration effort at rest D: The amount of air that can enter the lungs during maximal inspiration effort at rest |
D: The amount of air that can enter the lungs during maximal inspiration effort at rest
|
|
|
In humans, which tissue generates most of the force required to fill the lungs during relaxed breathing?
A: The alveoli B: The intercostal muscles C: The diaphragm D: The throat muscles E: This action requires no active force |
C: The diaphragm
|
|
|
In humans, which tissue generates most of the force required to expel the air from the lungs during relaxed breathing?
A: The alveoli B: The intercostal muscles C: The diaphragm D: The throat muscles E: This action requires no active force |
E: This action requires no active force
|
|
|
In humans, which tissue generates most of the force required to inspire/expel the air from the lungs during exercise?
A: The alveoli B: The intercostal muscles C: The diaphragm D: The throat muscles E: This action requires no active force |
B: The intercostal muscles
|
|
|
What is the most remarkable feature of the avian respiratory system?
A: Bird lungs are external B: Birds have an extremely large inspirational reserve volume per body size C: Fresh air moves over the bird respiratory epithelia during inhalation and exhalation D: The respiratory epithelia is located all over the body in birds E: That birds can breathe through those tiny nose holes |
C: Fresh air moves over the bird respiratory epithelia during inhalation and exhalation
|
|
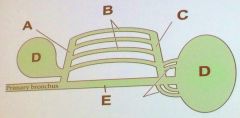
In this figure of the avian respiratory system, where is the respiratory exchange epithelia?
|
B.
|
|
|
If 1mL of air holds 0.10mL of O2, and 1mL of blood can array about 0.2mL of O2, what is the proper ratio of alveolar ventilation to perfusion?
A: 1:1 B: 2:1 C: 1:2 D: 3:1 E: 1:5:1 |
B: 2:1
|
|
|
If you are swimming underwater, your body will begin to signal you that you need to come up for air. What was least likely the stimulus that your body sensed to recognize that you weren't breathing?
A: Low blood pH B: Low blood O2 C: Low blood CO2 |
C: Low blood CO2
|
|
|
When running really fast, what is least likely the stimulus that your body sensed to recognize that you need to increase ventilation?
A: Low blood pH B: Low blood O2 C: High blood CO2 |
C: High blood CO2
|
|
|
When slowly walking up stairs at high altitude, you surprisingly start to breathe heavily. What is most likely the stimulus that your body sensed to recognize that you need to increase ventilation?
A: Low blood pH B: Low blood O2 C: High blood CO2 |
B: Low blood O2
|

