![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What's responsible for the BBB?
|
The tight jxns of overlapping capillary endothelial cells are responsible for the blood brain barrier
|
|
|
What maintains the endothelial cells of the BBB?
|
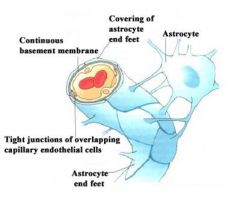
Structures labled in this pictures
|
|
|
why are there many mitochondria surrounding the brain capillary
|
There are many mitochondria b/c there are a lot transport mechanisms occurring and therefore need lots of energy
|
|
|
Because the CNS vascular endothelium have little transcytotic activity, what 2 things do they lack?
|
lack both fluid-phase and receptor-mediated endocytosis.
|
|
|
what is found in the CNS- Vascular Endothelial?
a. specific transporters b. catabolic enzymes c. R mediated endocytosis d. only a & b e. all of th above |
D only A & B
|
|
|
the specific transporters in the CNS vascular endothelium are to carry what?
|
1. glucose
2. amino acids 3.vitamins 4. metals 5. nucleosides |
|
|
what Catabolic enzymes are found in the CNS vascular endothelium
|
neurotransmitters and peptidases
|
|
|
What transporter is used for glucose in the brain?
|
Glucose - Glut1 –glucose transporter isotype-1
Glucose transported down its concentration gradient |
|
|
what transporters are used for amino acids in the brain?
|
Amino acids -3 carrier systems
A System ASC System L System |
|
|
which aa are carried by A system?
|
A system
Glycine and neutral AA with short linear side chains Alanine or serine |
|
|
the A system for aa transport is dependent on what?
|
Energy dependent, Na+dependent
|
|
|
Which 2 aa transporters of the brain are Na dependent & energy dependent?
|
A system
ASC system |
|
|
ASC system transports which aa?
|
Transports alanine, serine and cysteine
|
|
|
This aa transporter is located at the abluminal endothelial cell surface
|
ASC system
|
|
|
which aa system of the brain is Na independent
|
L system is Na+-independent
|
|
|
which aa are transported by the L system? their [ ] gradient?
|
large neutral AA with branched or ringed side chains (leucine and valine)
AA are transported down their concentration gradient |
|
|
This a precursor for dopamine
|
L-DOPA
|
|
|
How is L-DOPA administered? given for Tx of what?
|
systemically for treatment of Parkinson's
|
|
|
2 fxns of the Na-K ATPase in the brain?
|
1. Na,K-ATPase provides the energy and Na+ exchange.
2.Removal of K+ that accumulate in brain in response to intense neuronal activity |
|
|
Fxn of Multiple Drug Resistant - MDR
downside of this fxn? |
Protects brain from circulating neurotoxins
any chemotherapy drug is kicked out b/c the body thinks it's a toxin |
|
|
what are some experimental inhibitors of
a. L system b. A system |
a. 2-aminobicycloheptane-2-carboxylic acid (BCH)
b. a-methylaminoisobutyric acid (MeAIB) |
|
|
4 things that disrupt the BBB?
|
1. Tumors – lack BBB
2. Hypertension – opens BBB 3. Ischemic events (stroke) 4. Head injury |
|
|
what 5 things may circumvent the BBB?
|
1. Direct injection – emergent needs
2. Injection of hypertonic solutions (glucose, mannose, sucrose, urea, etc) – shrink cells 3. Bradykinin analogues – pulls cells apart 4. Enhanced lipid solubility – pro drug approach 5. Chemical delivery systems |
|
|
areas within the CNS that lack BBB? (5) what is ech of their fxns and how are they regulated
|
1. Median eminence – hormone/ANS regulation
2. Organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis – BP 3. Subfornical organ –water balance/BP 4. Subcommissural organ – BP 5. Area postrema : vomiting regulated by angiotensin II |
|
|
The lining of the ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord is called the _________.
|
ependyma
|
|
|
T/F: The ependyma lining have special cells called panycytes that form tight junction.
|
FALSE: they're called tanycytes
|
|
|
What is the fxn of the tanycytes?
|
These tight junctions prevent the entry of molecules from the blood supply of the circumventricular organs from entering the CSF.
|
|
|
Tight barriers are in _______ _______ which is the area that produces CSF.
|
choroid plexus
|
|
|
In the choroid plexus, there are _______ _______that also form tight jxns & preventing substances from entering the __________ .
|
epithelial cells
ventricles |
|
|
Fxn of the dura venous? why can it have this fxn?
|
Dura venous sinuses allow for exit of toxins from the brain since they connect with venous system
|
|
|
the 4 barriers in the brain?
|
1. BBB
Blood /CSF barrier 2. Choroid plexus 3. Circumventricular organs 4.Arachnoid villi |
|
|
Which of the statements is FALSE?
a. The BBB is formed primarily from tight jxns of overlapping capillary endothelial cells b. L-DOPA is broken down by AADC and monamine oxidase in the capillary endothelial cells; therefore treatment for Parkinson’s dz includes L-DOPA and an inhibitor for AADC. c. Substances that are not lipid soluble utilize specialized transporters to cross the BBB d. None of the above e. All of the above |
D: none of the above
|
|
|
T/F: Special cells on arachnoid villi to protect the CSF from blood in the dura venous sinuses
|
TRUE
|
|
|
Connective tissue sheaths in the brain
|
meninges
|
|
|
Composition of the meninges
|
Comprised of three membranous layers from the inner surface of the skull and vertebral column
|
|
|
what are the 3 layers of the meninges?
|
1. dura mater
2. arachonoid mater 3. pia mater |
|
|
Dense firm layer consisting of collagenous connective tissue
|
dura mater
|
|
|
The internal surfaces of the bones enclosing the cranial cavity are clothed by ________
|
periosteum
|
|
|
blood for the dura mater comes from where?
|
periosteum
|
|
|
Waste material from brain would enter the _______ ________ _______that’s imbedded in the dura mater.
|
superior sagittal sinus
|
|
|
The veins draining the brain empty into the ________ ________of the dura mater and then into the ________ ________ veins.
|
venous sinuses
internal jugular |
|
|
3 features of the arachnoid mater
|
1. collagenous and elastic fibers
2. both sides covered in squamous epithelial cells 3. avascular |
|
|
4 features of the pia mater?
|
1. connective tissue- collagenous and elastic fibers
2. external surface covered in squamous epithelial cells 3. contains fine blood vessels 4. covers all surfaces of the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
This liquid flows through subarachnoid space
|
CSF
|
|
|
These are "fluid-filled" spaces in the brain where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is produced and circulates
|
ventricles
|
|
|
This Interventrucilar foramen helps the lateral and third ventricles to communicate with each other.
|
foramen of Monroe
|
|
|
3rd & 4th ventricle communicate with each other via ________ _________
|
cerebral aqueduct
|
|
|
CSF leaves 4th ventricle to enter the subarachnoid spaces through these foramens
|
foramens of Magende & Luschka
|
|
|
Fxns of the CSF?
|
1. Cushioning of CNS structures.
2. Dispersion of nutrients/mode of communication between various brain regions. 3. Removal of CNS metabolic wastes. |
|
|
specialized highly vascularized epithelial structures found on the inner lining of all brain cerebral ventricles.
|
Choroid Plexus
|
|
|
CSF is enriched with
|
Enriched with Na,K-ATPase and other transporters
|
|
|
CSF is filtrate of ________
|
Plasma
|
|
|
Choose the correct answer. CSF is produced in the ventricles at a rate of 400-500 ml/day. However, the amount of CSF in the ventricles and arachnoid is only 100-150ml. What accounts for the differences in the amount produced on a given day and the amounts localized in the spaces?
a.The production rate b. The components of CSF vs Plasma c. The osmolarity d. All of the above e. None of the above |
E. none of the above b/c it’s d/t turn over and absorption of arachnoid villi
|
|
|
compare the protein and glucose in CSF vs plasma?
|
both protein and glucose are more abundant in plasma
|
|
|
Inflammation of the meningeal layers -
|
meningitis
|
|
|
which layers are most affected by meninigitis
|
Pial and arachnoid layers most often affected
|
|
|
Route of entry for meningitis
|
ears or nasal sinuses or vascular system
|
|
|
symptoms of meningitis
|
headache
neck stiffness fever nausea/vomiting photophobia lethargy |
|
|
what is seen in the CSF of viral meningitis?
|
1. Lymphocytes increase
2. increase in protein (moderate) 3. sugar content (normal) |
|
|
viral meningitis presents after what viral disorders?
|
presents following other viral disorders (mumps, West Nile, Epstein-Barr etc).
|
|
|
which meningitis has a worse prognosis? which has a higher incidence?
|
bacterial
viral |
|
|
mortality rate of bacterial meningitis?
|
20%
|
|
|
Tx for bacterial meningitis?
|
immediate antiobotic therapy of Penicillins and cephalosporins are current therapeutic choices
|
|
|
three manin causes of bacterial meningitis?
|
--Neisseria meningitidis – (meningococcal meningitis)
--Haemophilus influenzae – (type b) --Streptococcus pneumoniae – (pneumococcal meningitis) |
|
|
which is the most common cause of bacterial meningitis
|
Neisseria meningitidis – (meningococcal meningitis)
|
|
|
increase in ventricular volume of CSF is d/t what 3 reasons?
|
1. decreased absorption
2. overproduction 3. obstruction |
|
|
what may cause over secretion of CSF?
|
Choroid Plexus tumor
|
|
|
4 features of normal pressure hydrocephalus?
|
1. increase in ventricular volume, normal ICP
2. unknown etiology 3. difficult to diagnose – dementia, incontinence, motor errors 4. treat with ventricular shunts (atrial or peritoneal) |
|
|
3 causes of communicationg hydrochephalus?
|
1. any increase in venous pressure
2. subarachnoid hemorrhage 3. post-meningitis state |
|
|
2 causes of communicationg hydrochephalus
|
1. Impaired Absorption of CSF – “clogged” arachnoid villi 2. Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
|
|
|
cause of noncommunicationg hydrocephalus
|
Obstruction of CSF Flow
|
|
|
cause of obstruction of CSF flow in noncommunicationg hydrocephalus
|
1. obstruction in ventricular system
2. Brain tumors, congenital malformations |
|
|
Most likely location of tumor leading to noncommunicationg hydrocephalus is where?
|
clogging is in Aqueduct of Silvius/cerebral aqueduct
|
|
|
which group of people are likely to be affected in noncommunicating hydrocephalus?
|
children
|
|
|
this syndrome has narrowing of ventricular/subarachnoid interface which leads to obstruction flow and a noncommunicationg hydrocephalus
|
Dandy-Walker Syndrome
|

