![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gametes |
Sperm and egg cells |
|
|
Zygote |
The cells formed by the Union of sperm and eggs |
|
|
Monoploid |
Also known as haploid, meaning it contains half the normal complement of chromosomes |
|
|
Diploid |
Meaning it contains the full complement of chromosome |
|
|
Seminiferous tubules |
Located inside the testes where sperm is formed, as well as interstitial cells such as testosterone |
|
|
Interstitial cells (leydig) |
Cells that produce testosterone |
|
|
Epididymis |
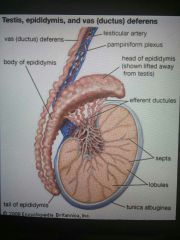
Made up of coiled tubes that store sperm while they mature |
|
|
How does the sperm travel from the epididymus? |
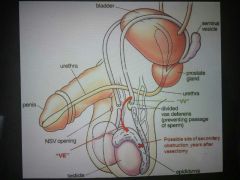
The sperm is sent through the epididymus during ejaculation through vas deferens, then to the ejaculatory duct, then to the urethra. |
|
|
What is the primary reproductive organ in females? |
The ovaries |
|
|
Ovaries |
Produce eggs and the hormones progesterone and estrogen. |
|
|
Oocyte |
Immature egg contained inside the ovaries |
|
|
Ovulation |
The process in which a mature cell is released into the fallopian tubes |
|
|
Fallopian tubes |
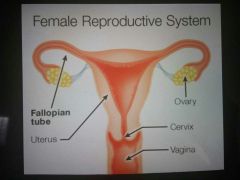
A tube that connected to the ovaries where a mature egg travels through and can be fertilized. |
|
|
Uterus |
"The womb" it is where fertilized eggs travel to |
|
|
Endometrium |
A lining of the uterus that a fertilized egg travels to and rests on if she becomes pregnant. |
|
|
Menstruation |
The shedding of the endometeium when the egg is not fertilized. |
|
|
Placenta |
A tissue that the mother and embryo form together. |

