![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
During gastrulation where does theendoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm end up? |
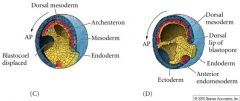
Inside: endoderm and mesoderm Outside: ectoderm (incl. future neural ectoderm) |
|
|
What is the organiser |
Dorsal lip of blastopore Bit of mesoderm |
|
|
What becomes epidermis (skin) cells? |
Ectoderm that secretes and recieves BMP |
|
|
What is the diffusible factor made by the organiser, and what does it do? |
BMP antagonist Diffuse into ectoderm close to it - cells acquire neural ID Form neural plate |
|
|
What was the Spemann and Mangold expt in 1920’s and what did it provide evidence of? |
Ectopic transplantation of 2nd organiser into host embryo. Developed with 2 organisers => twinned embryo with secondary neural axis. Only tissue derived from 2nd organiser was axial. Proved: organiser induces surrounding cells to form neural tissue |
|
|
What is meant by‘neural induction’ |
Organiser cells induce cells to become neural plate Dorsal mesoderm involutes and undergoes convergent extension and self-differentiates into notochord (most of it) and prechordal mesoderm (right at front). (axial mesoderm) The process of convergent extension (gastrulation) alters the shape of the developing embryo, creating the anterior-posterior and dorso-ventral axis |
|
|
What happens during neuralation? |
Neural plate rolls up Border region fuses to form neural tube Neural tube drops down (underneath ectoderm) Rod of axial mesoderm cells on ventral side of tube |
|
|
Features of neural inducers in organiser |
BMP antagonist Molecule must be expressed in organiser Over expression of molecule in ectopic site should lead to induction of secondary axis Inhibition of activity of molecule should prevent axis formation |
|
|
So what are the neural inducing molecules (i.e. theBMP antagonists), what is their method of action and where do they come from? |
e.g.Noggin, - interact with R chordin, - binds BMP preventing it binding R follistatin, cerberus Foundto be expressed in organiser, and differentiated derivatives (prechordalmesoderm and notochord). |
|
|
How do ectoderm cells acquire neural ID? |
BMP is blocked from signalling via its receptor. Inhibits Smad from inhibiting Sox (transcription factor) Sox allows expression of pro-neural bHLH genes |
|
|
What happens if BMP binds its R? |
Phosphorylates Smad Smad enters nucleus Binds to enhancers (eg Gata 1 and Msx) Inhibits Sox Epidermis cell fate |
|
|
What body axis does the BMP dictate? |
DV (broadly) |

