![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Free radicals are chemical species with an _____________ in their __________.
|
unpaired electron; outer orbit
|
|
|
Physiologic generation of ___________ occur during oxidative phosphorylation. How does it occur?
|
free radicals
Partial reduction of yields superoxide (O2*-, hydrogen peroxide (H202), and hydroxyl radicals (*OH). |
|
|
Complex IV in the ETC is the enzyme ___________.
|
cytochrome c oxidase
|
|
|
Cytochrome c transfers _________ to ___________.
|
electrons; oxygen
|
|
|
Oxygen accepts ___ electrons before becoming water.
|
4
|
|
|
What ROS are made when oxygen is partially reduced by 1, 2, 3 and 4 electrons respectively?
|
O2 --> O2*- --> H2O2 --> OH* --> H2O
|
|
|
Free radicals can be generated pathologically. How? What ROSes are produced in each case?
|
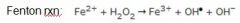
(1) Ionizing radiation (e.g. X-ray and gamma radiation). Hydroxyl ion (radiation hits water within tissues and knocks off an electron)
(2) Inflammation (respiratory burst) (3) By interaction with metals (e.g., copper and iron) via the fenton reaction. (4) Drugs and chemicals (e.g., acetaminophen is metabolized in liver causing free radicals in the process, causes massive liver necrosis, a chemical is CCl4) |
|
|
This free radical is the most damaging one. What vitamin is the best neutralizer of this free radical?
|
Hydroxyl ion.
Vitamin C |
|
|
In the first step of oxidative burst in neutrophils, the enzyme ___________ converts oxygen to _________.
|
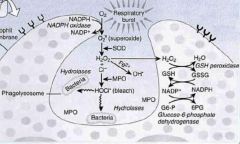
NADPH oxidase; superoxide
|
|
|
The second step of oxidative burst in neutrophils is mediated by _______________, producing ___________.
|
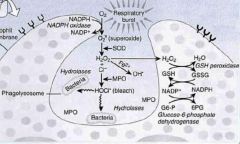
superoxide dismutase; hydrogen peroxide
|
|
|
____________ is a copper-transport plasma protein.
|
Ceruloplasmin
|
|
|
Ceruloplasmin contains ____ atoms of copper in its structure.
|
6
|
|
|
Ceruloplasmin represents ____ to ____ & of the total serum copper concentration.
|
90%; 95%
|
|
|
The inheritance pattern of Wilson's disease is ________.
|
AR
|
|
|
What is Wilson's disease?
|
An autosomal recessive disease associated with a defect in secreting copper into bile and in incorporating copper into ceruloplasmin.
|
|
|
Provide three examples of enzymes that require copper to function.
|
(1) SOD
(2) Cytochrome c oxidase (3) Tyrosinase |
|
|
__________, a soluble iron-protein complex, is the storage form of iron in the ____________, ______, _______, and ________.
|
ferritin; intestinal mucosa; liver; spleen; marrow
|
|
|
Ferritin is synthesized (in/by) ________.
|
macrophages
|
|
|
Serum ferritin levels reflect ____________ in the bone marrow.
|
iron stores
|
|
|
What is the best screening test for iron deficiency and iron overload disorders?
|
Serum ferritin is the best screening test for iron deficiency and iron overload disorders (e.g., hemochromatosis).
|
|
|
Hemosiderin is a ___________ degradation product.
|
ferritin
|
|
|
Patients who require ongoing transfusions are at risk for ____________.
|
hemosiderosis
|
|
|
___________ is the primary binding protein for iron (transport).
|
Transferrin
|
|
|
When iron stores in the bone marrow macrophages are decreased (e.g., iron deficiency), liver synthesis of transferrin __________ (increases/decreases), which increases ___________.
|
increases; total iron-binding capacity (TIBC)
|
|
|
What is the most common AR disorder?
|
Hemochromatosis
|
|
|
Alcohol __________ (increases/decreases) ________ absorption.
|
increases; iron
|
|
|
What's the real problem with free radicals? What do they do?
|
(1) Peroxidation of lipids
(2) Oxidation of DNA and proteins • ROS are implicated in oncogenesis. |
|
|
How do antioxidants prevent FR damage?
|
They neutralize them by DONATING one of their own electrons, thereby preventing the "electron stealing" of FRs. Antioxidants remain stable and do not become and FR.
|
|
|
Vitamin C neutralizes FRs produced by ___________ and ___________.
|
pollutants; cigarette smoke
|
|
|
Smokers have decreased levels of ____________ because they are used up in neutralizing FRs derived from cigarette smoke.
|
vitamin C
|
|
|
Vitamin E prevents ____________
|
lipid peroxidation in cell membranes.
|
|
|
Vitamin E neutralizes what lipoprotein?
|
Oxidized LDL
|
|
|
In what cell compartment do selenium neutralize FRs?
|
cytosol
|
|
|
Glutathione is located in the __________________ pathway.
|
pentose phosphate
|
|
|
Catalase, present within ________ degrades _________ into water and oxygen.
|
peroxisomes; peroxide
|
|
|
One treatment of acetaminophen FR injury?
|
N-acetylcysteine. It increases synthesis of glutathione for neutralization of drug FRs.
|
|
|
Acetaminophen may cause _______________.
|
diffuse chemical hepatitis (liver cell necrosis initially occurring around the central veins (zone III)
|
|
|
Acetaminophen induced liver cell necrosis can occur at nontoxic levels in _________.
|
alcoholics
|
|
|
In the cytosol, retinol is irreversibly _________ to ____________, in a similar fashion to __________ and __________.
|
oxidized; retinoic acid; steroids; vitamin D
|
|
|
What three major enzymes are important in elimination of FRs?
|
(1) SOD
(2) Glutathione peroxidase (3) Catalase Fit them in here: O2 --> O2*- --> H2O2 --> OH* --> H2O |
|
|
CCl4 might show up in a clinical vignette as a person in the ____________ industry.
|
dry cleaning
|
|
|
What happens when CCl4 gets into your body?
|
It gets into the blood, gets converted into CCl3 (P-450 system of the liver). CCl3 is now a free radical. Reversible injury occurs, with cellular swelling. RER ribosomes detach, protein synthesis is reduced. This diminishes apolipoprotein synthesis. Fat can then enter the liver but not go out. Fatty change in the liver is seen.
|
|
|
What is reperfusion injury?
|
Restoration of blood flow has consequences:
(1) Hypoxic endothelium increases adhesion molecules, recruiting circulating neutrophils (2) Superoxide FRs are generated (3) Calcium influx irreversibly damages injured cells |
|
|
A patient has an MI. The cardiac enzymes are increasing. After the artery is relieved of stenosis, the cardiac enzymes continue to rise. What is happening?
|
Reperfusion injury
|
|
|
A baby is treated for RDS with 60% oxygen. What may happen?
|
Retinopathy of prematurity. Blindness may occur in the treatment of RDS with an O2 concentration > 50%.
|

