![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Most common cause of Rhinitis...
|
Adenovirus
|
|
|
|
Repeated bouts of Rhinitis is A/w
|
Nasal polyps
|
|
|
|
Nasal polyps A/w
|
Cystic Fibrosis(child), Aspirin intolerant asthma(adult)
|
|
|
|
Aspirin intolerant asthma clinical triad
|
Asthma
Aspirin Induced Bronchospasm Nasal Polyps |
|
|
|
adolescent males with profuse bleeding of the nose...
|
Angiofibroma
|
|
|
|
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma A/w?
Classic presentation? |
A/w EBV and classically seen in African children, chinese adults
Classically presents with enlarged cervical lymph nodes. |
|
|
|
Pleiomorphic keratin positive epithelial cells in the background of lymphocytes
|
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Keratin = epithelial cells IMF, thus it must be carcinoma |
|
|
|
Most common cause of epiglottitis
|
H. Flu type B in BOTH immunized and non-immunized children
|
|
|
|
hoarse, barking cough and inspiratory stridor
|
Laryngotracheobronchitis(croup)
commonly caused by Parainfluenza virus(paramyxovirus) |
|
|
|
Vocal cord nodules
|
nodules that arise due to excessive use.
|
|
|
|
Laryngeal Papilloma is caused by?
|
HPV 6 and 11.
Generally single in adults and multiple in children. |
|
|
|
Second most common cause of lobar pneumonia?
|
Klebsiella(First is strep. pneumo)
Klebsiella hits malnourished and debilitated. Currant jelly sputum often complicated by abscess |
|
|
|
Four classic phases of lobar pneumonia
|
1.) congestion
2.) red hepatization 3.) gray hepatization 4.) Resolution Resolution occurs via Type II pneumocyte. |
|
|
|
COPD superimposed pneumonia caused by?
|
H. Flu or Moraxella Catarrhalis
|
|
|
|
empyema
|
pus in the pleural space
caused by? |
Staph Aureus
|
|
|
Most common cause of secondary pneumonia after viral infection
|
Staph. Aureus.
Often will cause abscess/empyema Virus will disrupt mucociliary elevator which allows other organisms to superinfect. |
|
|
|
Pneumonia in CF
|
Pseudomonas
|
|
|
|
Aspiration is most common to cause infection in the...
|
Right lower lobe
|
|
|
|
Atypical pneumonia presentation
|
Classic pneumonia presents with high fever, chills, productive cough, elevated white count, etc.
Atypical pneumonia usually presents with low fever and minimal symptoms. |
|
|
|
Mycoplasma pneumonia a/w
|
autoimmune hemolytic anemia - cold agluttinins(IgM)
|
|
|
|
Military recruit or college student with pneumonia
|
Mycoplasma Pneumonia
|
|
|
|
Atypical pneumonia in infants...
|
RSV
|
|
|
|
Second most common cause of atypica pneumonia
|
Chlamydia pneumonia
|
|
|
|
Atypical pneumonia post-transplant
|
CMV
|
|
|
|
Atypical pneumonia in elderly, immunocompromised, those with pre-existing lung disease
|

Influenza.
Patients are then susceptible to bacterial superinfection by Staph. Aureus or H.flu |
|
|
|
seen in farmers and veterinarians with high fever and atypical pneumonia
|
Coxiella Burnetti
Atypical pneumonia with high fever(Q fever) --rickettsial organism. Coxiella spores deposited on cattle by ticks or present on cattle placentas. |
|
|
|
How Coxiella varies from normal Rickettsial organisms
|
1.) causes pneumonia
2.) doesn't cause skin rash 3.) does not require arthropod vector(surives as heat resistant endospore) |
|
|
|
Aspiration pneumonia a/w what organisms...
|
anaerobic bacteria in oropharynx -
Bacteroides, Fusobacterium and peptococcus |
|
|
|
Sterile pyuria
|
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis that spread to kidney
|
|
|
|
Where does Myc. TB affect meninges?
|
At the base of the brain...
|
|
|
|
Describe primary Myc. TB infection...
|
Primary TB is generally ASYMPTOMATIC aside from the formation of the ghon complex
Focal caseating necrosis in the subpleural lower lobe of lung and hilar lymph nodes. These foci undergo fibrosis and calcification forming a Ghon Complex. |
|
|
|
Secondary reactivation of TB manifests as...
|
1.) cavitary foci of caseous necrosis
2.) miliary pulmonary TB 3.) Tuberculous bronchopnuemonia Fever/night sweats, cough with weight loss, biopsy of caseating granulomas, AFB reveals acid fast bacilli |
|
|
|
Histology of respiratory tract
|
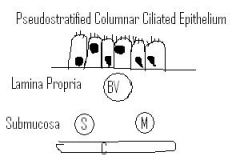
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Lamina Propria contains large blood vessels(venules) to warm the air. Submucosa contains serous and mucinous glands. Serous to humidify the air, and mucinous to protect against irritants. |
|
|
|
Spirometry of COPD
|
FEV1 goes down A LOT
FVC goes down FEV1/FVC goes DOWN. This DEFINES COPD. FVC is the total air you can breathe out after taking a deep breath. FVC1 is the air you breathe out in one second. |
|
|
|
What does the Reed index measure?
|

It measures the thickness of the mucinous glands relative to the thickness of the bronchial wall.
>50% indicates COPD. <40% normal |
|
|
|
Cor pulmonale
|
Global lung arteriole vasoconstriction in an attempt to shunt blood to a more oxygenated portion of the lung(that doesn't exist). This causes pulmonary hypertension leading to right ventricular hypertrophy and eventually failure.
|
|
|
|
Smoking causes
|
centriacinar emphysema that tends to affect the upper lobes most
|
|
|
|
alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency causes
|
panacinar emphysema that tends to affect the lower lobes most
A1AT is misfolded and accumulated within the ER of hepatocytes causing liver cirrhosis. |
|
|
|
Pink, PAS-positive globules in hepatocytes
|
these are the accumulation of A1AT in the ER of hepatocytes
|
|
|
|
Genotyping of A1AT Deficiency
|
PiMM -- normal
PiMZ --- heterozygote, usually asymptomatic but have less circulating A1AT PiZZ --- disease state, panacinar emphysema and liver cirrhosis |
|
|
|
"prolongued expiration with pursed lips"
|
improves expiration of emphysema patients.
|
|
|
|
discuss FRC. How fibrosis changes it. How emphysema changes it.
|
fibrosis decreases FRC.
Emphysema increases FRC(increase A-P diameter) |
|
|
|
the elastic recoil forces of the lungs and chest wall are equal but opposite at this spirometrical measure...
|
Functional Residual Capacity
|
|
|
|
Phases of Eosinophil mediated Asthma attack
|
1.) Histamine release due to cross linking of IgE receptors
2.) Leukotriene C4,D4,E4 release causing vasoconstriction, vascular permeability and bronchiolar smooth muscle constriction 3.) Inflammatory mediators like major basic protein perpetuate bronchoconstriction |
|
|
|
Curschmann spirals
|
found within mucus of asthmatics
|
|
|
|
Charcot-Leyden crystals
|
crystalline aggregates of eosinophils with major basic protein that show up in the mucus of asthmatics
|
|
|
|
Bronchiectasis
|

Permanent dilatation of bronchioles and bronchi; loss of airway tone results in air trapping
|
|
|
|
Kartagener Syndrome
A/w? |
inherited defect of the DYNEIN arm, which is necessary for ciliary movement. Can cause bronchiectasis
A/w Situs Inversitus |
|
|
|
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosus
|
Bronchopulmonary - "larger airways"
hypersensitivity to Aspergillus causing chronic inflammatory damage and bronchiectasis classically seen in? |
Seen in asthmatics and CF patients
|
|
|
Bronchiectasis can have what important complication?
|
Secondary Amyloidosis
Primary amyloidosis is when light chain is overproduced remember? But SECONDARY amyloidosis arises from chronic inflammatory process creating excess "SAA" protein which then causes AA amyloid crap to be deposited in tissues. |
|
|
|
What chemokine induces fibrosis in the lungs from injured pneumocytes?
|
TGF-Beta
|
|
|
|
Common drugs that cause pulmonary fibrosis
|
Bleomycin and Amiodarone
Radiation therapy |
|
|
|
Fibrosis begins in which part of the lung in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
|
Initially it begins in subpleural patches
|
|
|
|
Coal Worker's Pneumoconiosis
|
Carbon dust, seen in coal miners. Massive exposure leads to diffuse fibrosis('black lung')
A/w? |
Rheumatoid Arthritis(Caplan syndrome)
|
|
|
Caplan Syndrome
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis A/w Coal Worker's Pneumoconiosis
|
|
|
|
Anthracosis
|
carbon laden macrophages - not clinically significant
|
|
|
|
fibrotic nodules in upper lobes of lung
|
Silicosis
Increased risk for TB due to impairment of phagolysosome formation by macrophages |
|
|
|
Non-caseating granulomas in the lung, hilar lymph nodes and systemic organs
increases risk for? |
SOUNDS LIKE sarcoidosis but is driven by Beryllium. Seen in beryllium miners and workers in the aerospace industry.
INCREASES risk for lung cancer |
|
|
|
Works in aerospace industry
|
Berylliosis
|
|
|
|
Asbestosis
|
fibrosis in the lung, fibrosis in the pleura, cancer in the lung, cancer it the pleura
Cancer of the pleura = mesothelioma |
|
|
|
Ferruginous body
|
Asbestos related
|
|
|
|
African American female with noncaseating granulomas in multiple organs(lung, hilar lymph nodes)
|
Sarcoidosis
|
|
|
|
Dry eyes, dry mouth with non-caseating granulomas
|
Sarcoidosis
|
|
|
|
Clinical features of Sarcoidosis
|
Elevated Serum ACE
NOTABLY Hypercalcemia - due to 1 alpha hydroxylase activity of epithelioid histiocytes of granulomas convert vitamin D to active form) |
|
|
|
Presents with fever, cough, dyspnea hours after going to the zoo.
|
(Pigeon breeder's lung)
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis a/w granulomatous reaction to inhaled organic particles/antigens. Causes granulomatous reaction that resolves with removal of exposure but can progress to interstitial fibrosis in chronic exposure. |
|
|
|
Severe long standing pulmonary hypertension can lead to...
|
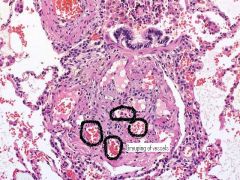
Plexiform lesions, group of capillaries that travel together.
|
|
|
|
young woman with exertional dyspnea
|
pulmonary hypertension
|
|
|
|
causes excess proliferation of smooth muscle leading to pulmonary hypertension. A/w young adult women
|
BMPR2 inactivating.
Think plexiform lesions. |
|
|
|
BMPR2 inactivating mutation
|
causes excess proliferation of smooth muscle leading to pulmonary hypertension. A/w young adult women
Think plexiform lesions. |
|
|
|
Secondary Pulmonary HTN
|
Due to hypoxemia(COPD, interstitial lung diseasea)
or increased volume in pulmonary circuit(congenital heart disease leading to Eisenmenger Syndrome) |
|
|
|
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
|
formation of hyaline membrane due to leakage of protein rich fluid into alveoli
Diffuse damage to the alveolar-capillary interface(diffuse alveolar damage) Activation of neutrophils induces protease-mediated and free radical damage to type I and type II pneumocytes |
|
|
|
What does the hyaline membranization of alveoli cause?
|
This causes inability to exchange gas and an increase in alveolar surface tension
use PEEP to keep alveoli open despite the increased surface tension of alveoli |
|
|
|
Notable complication of ARDS
|
Interstitial fibrosis due to the destruction of type II pneumocytes by neutrophils leading to inability to regenerate.
|
|
|
|
indicates lung maturity
|
lecithin(phosphatidylcholine):sphingomyelin ratio greater than 2
|
|
|
|
C-section a/w
|
Neonatal RDS due to lack of stress induced steroids. Steroids increase surfactant production.
|
|
|
|
Maternal Diabetes a/w
|
Neonatal RDS due to increased insulin production. Insulin inhibits surfactant production
|
|
|
|
Neonatal ARDS risks
|
Patent PDA, and necrotizing enterocolitis
|
|
|
|
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
|
free radical damage to lung early in life before lungs are mature enough to handle pure oxygen
|
|
|
|
Supplemental oxygen complication in neonate
|
Free radical damage to retina causing blindness. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
|
|
|
|
Imaging reveals 'coin-lesion'. What do you do BIATCH!?
|
Check for past x-rays to see if it has been stable. if it has, it's likely benign. If it's new, CUT THAT SHIT UP AND BIOPSY IT.
|
|
|
|
Most likely coin lesions in younger gentlepeoplez?
|
Granuloma -- often due to TB or fungus(especially Histoplasma in the midwest)
Bronchial Hamartoma - benign tumor composed of lung tissue AND cartilage often calcified on imaging |
|
|
|
Mode of treatment for lung cancer
|
Small cell -- chemo
Non-Small Cell -- surgical resection(doesn't respond well to chemo) |
|
|
|
Non-Small Cell Subtypes
|
Adenocarcinoma(40%)
Squamous Cell Carcinoma(30%) Large Cell Carcinoma(10%) Carcinoid Tumor(5%) - neuroendocrine origin |
|
|
|
Male Smokers
|
Small Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
|
Small Cell Carcinoma associations
|
Smokers, Central, Paraneoplastic Syndromes(ADH, ACTH or Eaton-Lambert Syndrome)
|
|
|
|
Eaton-Lambert Syndrome
|
Antibodies formed against presynaptic calcium channels STRONGLY associated with Small Cell Carcinoma and Smokers
|
|
|
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|
Keratin pearls or intercellular bridges(desmosomal connections).
Associated with male smokers. May produce PTHrP |
|
|
|
PTHrP
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
|
What unique site does lung cancer like to metastasize to?
|
Adrenal glands
|
|
|
|
Metastasis to lung
|
Most common sources are breast and colon carcinoma. Presents with multiple 'cannon-ball' nodules on imaging. More common than primary tumors.
|
|
|
|
Central Tumors
|
Small Cell, Squamous Cell, Large Cell(central or periphery), Carcinoid Tumor(central or periphery)
|
|
|
|
female smoker lung cancer
|
Adenocarcinoma
Presents peripherally |
|
|
|
non-smoker lung cancer
|
adenocarcinoma
Presents peripherally |
|
|
|
Large Cell Carcinoma
|
Poorly differentiated large cells that lack karatin pearls, intercellulary bridges, glands or mucin.
Associated with smoking |
|
|
|
Associated with smoking
|
Small Cell Carcinoma(male), Squamous Cell Carcinoma(male), Large Cell Carcinoma, Adenocarcinoma(female)
|
|
|
|
Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma arises from what cell?
|
Clara Cells - main function is to protect bronchiolar epithelium, perhaps by secreting GAGS
|
|
|
|
Neuroendocrine Tumors
|
Chromogranin POSITIVE
Small Cell Carcinoma(poorly differentiated, arises from Kulchitsky Cells) Carcinoid Tumor(Well differentiated) |
|
|
|
What cell line does Small Cell Carcinoma arise from?
|
Kulchitsky cells(AKA enterochromaffin cells) which derive from the neural crest
|
|
|
|
polyp like mass in the bronchus
|
Carcinoid Tumor
|
|
|
|
Lung cancers not related to smoking
|
Bronchioalveolar Carcinoma
Carcinoid Tumor |
|
|
|
asteroid body
|
sarcoidosis
|
|
|
|
granulomas with eosinophils in lungs
|
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
presents acutely with fever, cough and dyspnea |
|
|
|
fever, cough, dyspnea hours after exposure
|
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
|
|
|
|
pigeon breeder's lung
|
HYPERSENSITIVITY pneumonitis
a/w granulomas and eosinophils. |
|

