![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Autosomal recessive condition involving a mutation on Chromosome 6; associated with HLA-A3
|
Hereditary Hemochromatosis
|
|
|
Describe Hereditary Hemochromatosis
|
Mutation on chromosome 6 causing EXCESSIVE ABSORPTION OF IRON IN THE INTESTINAL MUCOSA
|
|
|
What are the causes of Secondary Hemochromatosis?
|
Iron Overload
-repeated transfusions -ineffective Erythropoiesis (thalassemia, sideroblastic anemia) -increased dietary iron uptake (Bantu in S. Africa) Chronic Liver disease in which iron can't be metabolized -Alcoholic -HCV |
|
|
What is the classic triad associated with Hereditary Hemochromatosis?
|
1. Cirrhosis w/ Hemosiderosis
2. "Bronze Diabetes" 3. Skin Hyperpigmentation *also Cardiomyopathy, Arthritis, & Hypogonadism |
|
|
What is the treatment for Hereditary Hemochromatosis?
|
Phlebotomy + Deferoxamine
|
|
|
What are the lab values in Hereditary Hemochromatosis?
|
1. increased Ferritin
2. increased Iron 3. decreased TIBC 4. increased Transferrin saturation |
|
|
Hereditary Hemochromatosis
-hepatocytes are filled with blue iron granules |
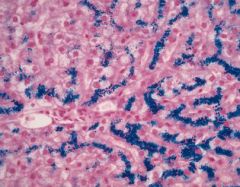
What is seen here?
|
|
|
What is the microscopic difference between Hemochromatosis & Hemosiderosis?
|
in Hemosiderosis, iron deposits are more prevalent in Kupffer cells than in parenchymal tissue (hepatocytes)
|
|
|
Disease in which the gene for ATP-dependent metal ion transporter (ATP7B) on Chromosome 13 is mutated; results in defective excretion of Copper into Bile -> Copper spills into blood
|
Wilson Disease
|
|
|
List the pathologies seen in Wilson Disease
|
1. Fatty liver -> Acute & Chronic Hepatitis -> Cirrhosis
2. Degeneration of Basal Ganglia in the brain = asterixis, Parkinsonian symptoms, choreiform movements, dementia 3. Kayser-Fleischer ring in Cornea 4. Renal tubular damage = aminoaciduria & glycosuria |
|
|
What are the lab findings are associated with Wilson Disease?
|
1. low Serum Ceruloplasmin
2. high tissue Copperl levels 3. increased urinary copper excretion |
|
|
Kayser-Fleischer ring
Wilson's disease = increased Copper accumulation |
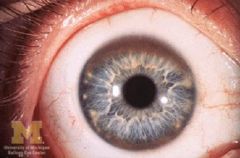
What is this lesion called?
What disease? |
|
|
Autosomal recessive mutation in which a small protease inhibitor cannot be secreted & remains in liver cells
|
Alpha-1-Antitrypsin deficiency
|
|
|
What percent of homozygotes with Alpha-1-Antitrypsin disease actually develop liver disease?
|
10-20%
|
|
|
Explain Alpha-1-Antitrypsin deficiency
|
PiZZ genotype results in 90% inhibition of hepatic secretion of AAT which results in its accumulation in the liver
|
|
|
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
-PAS with AAT granule accumulation |
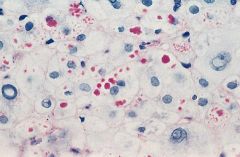
What is seen here?
|
|
|
What are the possible pathologies seen in AAT deficiency?
|
1. Micronodular Cirrhosis & increased risk of HCC
2. Panacinar Emphysema |
|
|
Chronic Hepatitis that occurs in the association with other autoimmune disorders (Thyroiditis, Sjogren, SLE)
|
Autoimmune Hepatitis
|
|
|
What is the gender preference for Autoimmune Hepatitis? What HLA's are associated with it?
|
F:M = 7:3
HLA-B8 & HLA-DRw3 |
|
|
What autoantibodies are associated with Autoimmune Hepatitis?
|
1. Anti-nuclear Antibody (ANA)
2. Anti-Smooth Muscle Antibody (ASM) |
|
|
What is the treatment for Autoimmune Hepatitis?
|
Corticosteroid therapy
-decreases the incidence of cirrhosis to only 5% |
|
|
Chronic autoimmune progressive disease due to destruction of the Bile Ducts from non-suppurative Granulomas in Portal Triads
|
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
|
|
|
Autoimmune destruction of Bile Ducts in Portal Triads
|
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
|
|
|
What is the gender preference for Primary Biliary Cirrhosis?
What autoantibodies are present 90% of the time? |
F:M = 10:1
Anti-mitochondrial (Mitochondrial Pyruvate Kinase) |
|
|
What are the clinical findings in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis?
|
1. Middle-aged women with other autoimmune diseases
2. Progressive Jaundice 3. Skin itching = due to bile salts in skin 4. Xanthomas = cholesterol uptaken by macrophages |
|
|
What lab findings are associated with Primary Biliary Cirrhosis?
|
1. increased Bilirubin
2. increased Alk. Phos. 3. increased Cholesterol 4. Anti-mitochondrial Ab |
|
|
What would a biopsy show in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis?
|
Granulomatous destruction of Bile ducts in portal triads
|
|
|
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
-destruction of Bile Ducts by periportal granuloma formation -lymphocyte infiltration into portal tract |
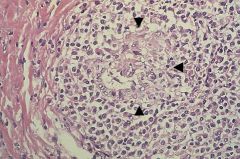
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Chronic progressive pericholangitis of intrahepatic & extrahepatic Bile Ducts with concentric fibrosis -> obstruction of bile flow -> cirrhosis
|
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
|
|
|
What is the gender preference in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? What is it associated with?
|
M:F = 2:1
Ulcerative Colitis |
|
|
What autoantibody is present in 80% of cases with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis?
|
P-ANCA
|
|
|
Cholangiography shows "Beading Strictures" in this Liver disease
|
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
|
|
|
Liver disease associated with Ulcerative Colitis
|
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
|
|
|
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
|

What schematic does this represent?
|
|
|
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis = fibrosing destruction of INTRAHEPATIC BILE DUCTS
Males = 2:1 Ulcerative Colitis |
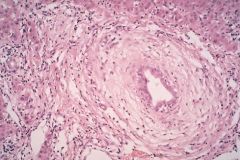
What liver disease is this?
Gender preference? Associated disease? |
|
|
Occlusion of the Hepatin Vein by a thrombus, often resulting in death
|
Budd-Chiari Syndrome
|
|
|
What is Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis associated with an increased incidence of ?
|
Cholangiocarcinoma
|
|
|
What possible etiologies could cause Budd-Chiari Syndrome?
|
1. Polycythemia vera
2. Pregnancy 3. Oral Contraceptives 4. Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria 5. Hepatocellular CA 6. Idiopathic |
|
|
Budd-Chiari Syndrome
-Centrilobular congestion & necrosis with sinusoidal dilation |
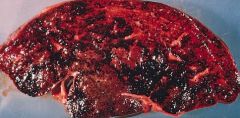
What is this showing?
|
|
|
List the 3 Benign Tumors of the liver
|
1. Hemangioma
2. Liver Cell Adenoma 3. Focal Nodular Hyperplasia |
|
|
Benign tumor of the liver associated with oral contraceptive use & can rupture causing Hematoperitoneum
|
Liver Cell Adenoma = Hepatic Adenoma
|
|
|
Most common Benign tumor of the Liver
|
Hemangioma
|
|
|
Circumscribed nodule found in an otherwise normal liver; represents a hamartoma composed of liver cells arranged around a central fibrotic scar containing thick-walled vessels
|
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia
|
|
|
Liver Cell Adenoma
|
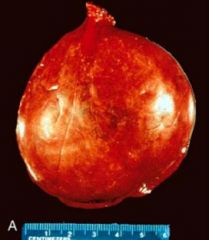
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Liver Cell Adenoma
-resembles normal liver except for the lack of Portal Tracts |
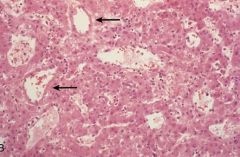
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia
|
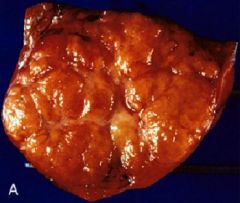
What Benign Liver tumor is seen here?
|
|
|
List the Malignant tumors of the liver
|
1. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
2. Cholangiocarcinoma 3. Angiosarcoma (rare) 4. Metastases to the Liver |
|
|
What is Hepatocellular Carcinoma associated with?
|
HBV
HCV Cirrhosis Alcohol consumption Aflatoxin B1 |
|
|
What is the gender ratio for Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
|
Male:Female = 4:1
also more common in African-Americans |
|
|
What lab finding is associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
|
serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP)
|
|
|
What is the most common malignant tumor of the liver?
|
Metasteses to the liver
|
|
|
What are the most common primary sites of Metastases of the liver?
|
1. Lung (most common)
2. GI tract 3. Breast |
|
|
What are Angiosarcomas associated with?
|
Vinyl chloride, throtrast, arsenic exposures
|
|
|
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
|
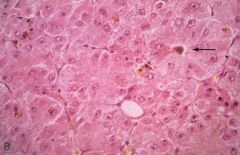
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
|
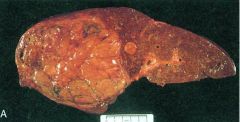
What is seen here?
|
|
|
Cholangiocellular Carcinoma = adenocarcinoma arising from bile duct epithelium
Clonorchis Sinensis |
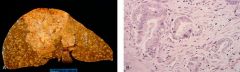
What is shown here? What is an associated cause?
|
|
|
Def: Adenocarcinoma arising from bile duct epithelium
|
Cholangiocarcinoma
|
|
|
Metastatic Carcinoma
-Lung -Colon -Breast |
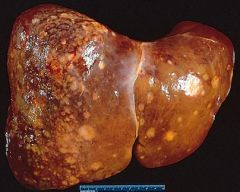
What is seen here?
|

