![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How are Ovarian Tumors classified?
|
1. tumors of surface epithelium
2. Germ cell tumors 3. Sex Cord stromal tumors |
|
|
Epithelial ovarian tumor that has Fallopian Tube-like epithelium
|
Serous
|
|
|
Epithelial Ovarian tumors with Endocervical-like epithelium
|
Mucinous
|
|
|
Epithelial Ovarian tumor that is malignant and resembles Endometrium
|
Endometrioid
|
|
|
Rare, malignant Epithelial Ovarian Tumor that is composed of sheets of cells filled with Glycogen
|
Clear cell
|
|
|
Benign Epithelial Ovarian tumor with nests of cells resembling bladder Transitional Epithelium interspersed in fibrous stroma
|
Brenner tumor
|
|
|
Describe the histology of Serous Cystadenoma's
|
Single layer of Ciliated Tubal-type epithelium
|
|
|
Serous Cystadenoma = benign cysts with Fallopian Tube-like epithelium
|
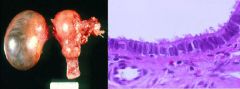
What is this showing?
|
|
|
What is the gross appearance of Mucinous Cystadenoma?
|
1. vary in size
2. Cystic, Multilocular 3. Thick mucinous fluid |
|
|
What is the histology of Mucinous Cystadenoma?
|
Tall Columnar cells filled mucin
|
|
|
Mucinous Cystadenoma
Benign |
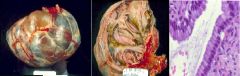
What is this showing?
Benign or Malignant? |
|
|
Brenner Tumor = benign tumor with islands of Transitional-like epithelium in a fibrous stroma
|
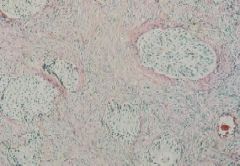
What is this showing?
|
|
|
This is the MOST COMMON MALIGNANT tumor of the Ovary
|
Serous Cystadenocarcinoma = 30% of all Ovarian CA's
|
|
|
This ovarian cancer has Psammoma bodies
|
Papillary Serous Cystadenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Papillary Serous Cystadenocarcinoma
|
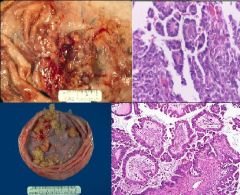
What are all these showing?
|
|
|
Papillary Serous Cystadenocarcinoma
Psammoma body |
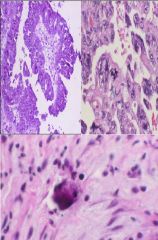
What are these showing?
What specifically is the bottom showing? |
|
|
A malignant ovarian tumor that can rupture or metastasize and produce Pseudomyxoma Peritonei with multiple peritoneal tumor implants, all producing large quantities of intraperitoneal mucinous material
|
Mucinous Cystadenocarinoma
|
|
|
Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma
|
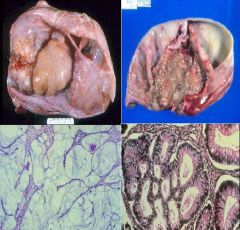
What are all of these showing?
|
|
|
Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma
Malignant |
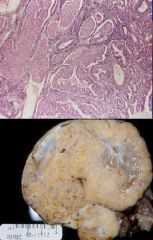
What is this showing?
Benign or Malignant? |
|
|
Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the ovary
Prognosis is even worse than the bad prognosis that we have for other ovarian cancers |
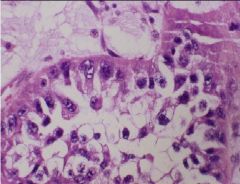
What is this showing?
What is important about it? |
|
|
What is the lab finding in Malignant Epithelial Ovarian Tumors?
|
CA-125
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of Malignant Epithelial Ovarian Tumors
|
1. BAD prognosis
2. Early metastasis 3. Peritoneal implants 4. CA-125 5. Treatment: Surgery, chemo, radiotherapy |
|
|
What are the 4 Malignant Epithelial Ovarian TUmors?
|
1. Serous Cystadenocarcinoma
2. Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma 3. Endometroid 4. Clear cell |
|
|
What are the 3 Benign Epithelial Ovarian Tumors?
|
1. Serous Cystadenoma
2. Mucinous Cystadenoma 3. Brenner tumor |
|
|
What are the key features of Borderline Epithelial Ovarian Tumors
|
1. Low malignant potential
2. worrisome histology, excellent prognosis 3. Serous or Mucinous 4. Epithelial stratification, mitosis, atypia 5. NO STROMAL INVASION |
|
|
What is the treatment for Borderline Epithelial Ovarian Tumors?
|
Surgery, even with Metastasis
|
|
|
Borderline Epithelial Ovarian tumors
-Left = Mucinous tumor -Right = Serous tumor **NO Stromal Invasion |
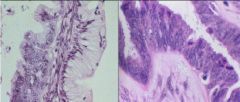
What are these showing?
-Left? -Right? |
|
|
Jelly-belly = Numerous Peritoneal implants of Mucus-secreting cells
|
Pseudomyxoma Peritonei
|
|
|
What are the possible sources of Pseudomyxoma Peritonei?
|
1. Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma
2. Mucinous Cystadenoma 3. Carcinomatous mucocele of the appendix 4. Bowel |
|
|
What is the treatment for Pseudomyxoma Peritonei?
|
-repeated debulking
- Chemotherapy |
|
|
This is the most Malignant Germ Cell tumor of the Ovary
|
Dysgerminoma = Ovarian Seminoma
|
|
|
What is Dysgerminoma analogous to in the male?
|
Testicular Seminoma
|
|
|
Germ cell ovarian tumor with glycogen-filled tumor cells
|
Dysgerminoma
-similar to Seminoma cells of Testicular germ cell tumors |
|
|
What age group does Dysgerminoma commonly occur at?
|
10-30 years
|
|
|
What is the prognosis of Dysgerminoma?
|
Excellent prognosis
|
|
|
Most common Germ Cell Tumor
|
Mature Teratoma = Dermoid cyst
|
|
|
Describe the key properties of Mature Teratomas
|
1. Benign
2. 3 germ cell layers 3. Cystic |
|
|
What is Struma Ovarii?
|
Mature Teratoma comprised of almost all Thyroid tissue = can show high Thyroid levels in a patient with normal Thyroids
|
|
|
Mature Teratoma
Benign |
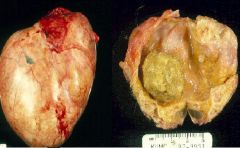
What are these showing?
Benign or Malignant? |
|
|
Mature Teratoma
|
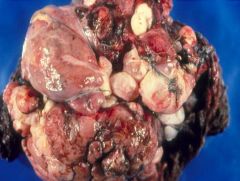
What is this?
|
|
|
Dermoid cysts of Mature Teratomas
|
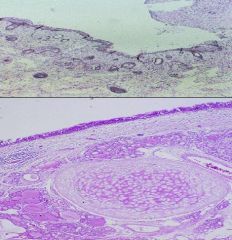
What are these?
|
|
|
Mature Teratoma
Several different tissues present |
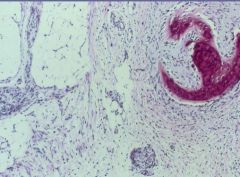
What is this?
How do you know? |
|
|
Germ cell tumor that has 3 Germ Cell layers, is Malignant, has embroyonal tissue that is usually neural
|
Immature Teratoma
|
|
|
Immature Teratoma
|
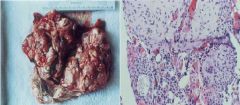
What are these?
|
|
|
Another name for Endodermal Sinus Tumor
|
Yolk Sac Tumor
|
|
|
-Highly malignant
-affects a young age group -tumor is hemorrhagic and necrotic -Schiller-Duval bodies |
Endodermal Sinus Tumor = Yolk Sac tumor
|
|
|
Germ cell tumor that secretes AFP
|
Endodermal Sinus Tumor = Yolk Sac tumor
|
|
|
A girl with ovarian cancer at the age of 3
|
Yolk Sac tumor
|
|
|
Yolk Sac Tumor
Schiller-duval bodies |
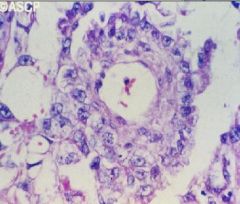
What ovarian tumor?
|
|
|
Agressive and malignant ovarian tumor with areas of necrosis and hemorrhage composed of neoplastic Syncytiotrophoblasts and Cytotrophoblasts
|
Choriocarcinoma of the ovary
|
|
|
A young girl presents with precocious sexual development. She yields a + pregnancy test with the presence of hCG. She swears she is a virgin
|
Choriocarcinoma
|
|
|
Choriocarcinoma of the Ovary
Syncytiotroph's and Cytotroph's with areas of necrosis and hemorrhage |
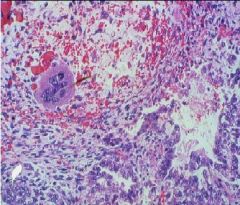
What tumor is this?
How do you know? |
|
|
What syndrome is associated with an increased risk for Dysgerminoma?
|
Turner's syndrome
|
|
|
What are the 3 Ovarian Sex Cord Stromal tumors
|
1. Fibroma-Thecoma
2. Granulosa Cell tumor 3. Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor |
|
|
Most common Sex Cord / Stromal tumor
|
Fibroma
|
|
|
When do most Ovarian Fibroma's occur?
|
around Menopause
|
|
|
A woman presents with Ascitis (distended stomach) and Pleural effusions (hydrothorax). What tumor does she most likely have? What syndrome is this?
|
Ovary Fibroma (Sex cord tumor)
Meig's Syndrome |
|
|
What is the clinical triad in Meig's Syndrome?
|
1. Ovarian Fibroma
2. Ascites = distended stomach 3. Pleural effusion |
|
|
Ovarian Fibroma
Benign |
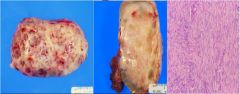
What is this tumor?
Benign or Malignant? |
|
|
Benign, POSTMENOPAUSAL Ovarian tumor that has round lipid-containing cells in addition to fibroblasts. Also secretes Estrogen
|
Ovarian Thecoma
|
|
|
What are Thecomas associated with increasing the risk of? Why?
|
Endometrial Hyperplasia and Endometrial Cancer
Because they secrete Estrogen |
|
|
Thecoma
|
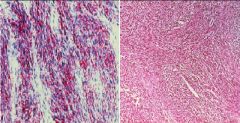
This was shown to secrete Estrogen, what is it?
|
|
|
Ovarian tumor:
-secretes Estrogen -Call-Exner bodies -associated with Endometrial Hyperplasia/Cancer |
Granulosa Cell Tumor
|
|
|
Granulosa Cell Tumor
Call-Exner bodies = follicles filled with Eosinophilic secretions |
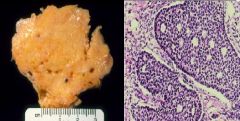
What is this tumor?
What are the characteristic features on the right? |
|
|
Granulosa Cell Tumor
|
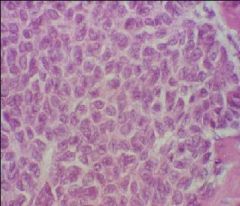
A girl with this tumor (Coffee-bean nuclei) came in and was found to have Precocious Puberty. She was also at an increased risk of Endometrial Hyperplasia/Cancer
|
|
|
Ovarian tumor that secretes Androgen
|
Sertoli-Leydig Cell tumors = Androblastoma = Arrhenoblastoma
|
|
|
A 25 year old woman presented with facial and chest hair. She was found to have what ovarian tumor?
|
Sertoli-Leydig Cell tumor
|
|
|
Androgens
Sertoli-Leydig Cell tumor |
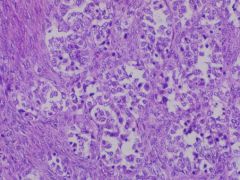
What do these cells secrete?
What tumor? |
|
|
What are the properties of Metastatic Ovarian cancer? Where do they commonly come from?
|
Usually BILATERAL
Breast, Colon, Stomach |
|
|
What are Krukenburg Tumors?
|
1. Adenocarcimona mucin-producing
2. Contains Signet Ring Cells from the Stomach |
|
|
Krukenberg tumors = bilateral
Gastric Adenocarcinoma |
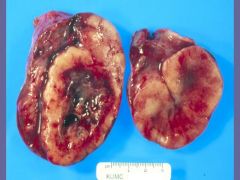
After histologic examination, there appeared to be Signet Ring Cells in the specimen.
-What is the name of this tumor? -Where did it likely come from? |

