![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Leiomyoma of the uterus
|
Benign tumor of the Myometrium smooth muscle
|
|
|
This is the most common Uterine tumor and also most common of all tumors in women
|
Uterine Leiomyoma
|
|
|
T or F: Leiomyomas are more common in White women than Black women
|
False = more common in Blacks
|
|
|
When are Leiomyomas more common and why?
|
During the reproductive years because the smooth muscle cells respond to Estrogen = almost never found in prepubertal girls
|
|
|
Leiomyomas
|
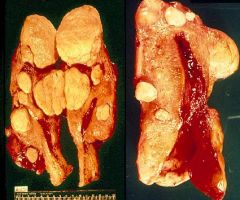
What are these?
|
|
|
Leiomyoma
|
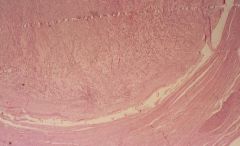
What is this?
|
|
|
What are some common clinical presentations of Leiomyomas
|
1. Menorrhagia
2. Abdominal mass 3. Pelvic pain, back pain, suprapubic discomfort 4. Infertility |
|
|
What are 2 treatments for Leiomyomas?
|
Myomectomy
Hysterectomy |
|
|
Submucosal Leiomyoma
|
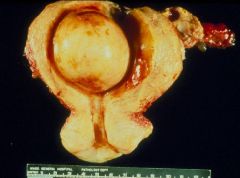
What specifically is this?
|
|
|
What are the 3 classifications of Leiomyomas?
|
Submucosal
Intramural Subserosal *from inside out |
|
|
Leiomyoma has become infected -> hemorrhage and necrosis -> pain
|
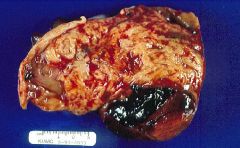
What has happened here?
|
|
|
What is a Leiomyosarcoma?
|
MALIGNANT Smooth Muscle tumor of the Myometrium of the uterus
|
|
|
How common are Leiomyosarcomas?
Do Leiomyomas transform to Leiomyosarcomas? |
Rare
No, Leiomyosarcomas originate de novo and are unrelated to preexisting Leiomyomas |
|
|
What is the gross pathology of Leiomyosarcomas?
|
Similar to Leiomyomas but with Necrosis, Hemorrhages, and Irregular borders
|
|
|
Leiomyosarcoma
|
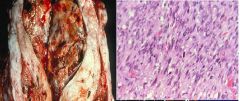
What are these showing?
|
|
|
Leiomyosarcoma
|
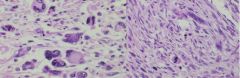
Would these be Leiomyoma or Leiomyosarcoma?
|
|
|
Describe Endometriosis
|
presence of Endometrial glands and Stroma outside the uterus
|
|
|
What are some sites for Endometriosis
|
1. Ovaries
2. Tubes 3. Round ligaments 4. Distant organs = lungs, brain, skin |
|
|
Describe the possible pathogenesis of Endometriosis
|
1. Retrograde menstruation through Fallopian Tubes
2. Hematogenous spread -> lungs, skin, brain 3. Celomic Metaplasia |
|
|
List the Clinical features of Endometriosis
|
1. Dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation) ****
2. Dyspareunia (painful sex) 3. Chronic pelvic pain 4. Dysfunctional Uterine bleeding 5. Infertility ****most common |
|
|
-Red Blue areas = Mulberry Nodules
-Powder burns secondary to hemosiderin What is the condition? |
Endometriosis
|
|
|
Endometrial glands with Stroma
Hemorrhage and fibrosis around it |
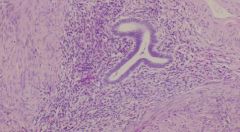
What is this?
How do you know? |
|
|
Endometriosis
-these five small areas of endometriosis have a reddish-brown to bluish appearance. Typical locations for endometriosis may include: ovaries, uterine ligaments, rectovaginal septum, pelvic peritoneum, and laparotomy scars. Endometriosis may even be found at more distant locations such as appendix and vagina. |
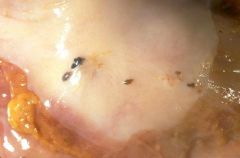
What is this?
|
|
|
Endometriosis
- Ovarian "chocolate" cyst |
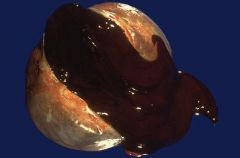
What is this?
|
|
|
Characterized by islands of Endometrium within the Myometrium
|
Adenomyosis
|
|
|
Adenomyosis
Endometrial glands and stroma in the Myometrium |
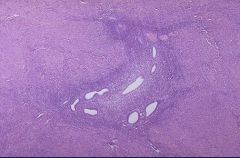
What is this?
How do you know? |
|
|
How do you distinguish Acute Salpingitis from Chronic?
|
Acute = PMN's
Chronic = Lymphocytes |
|
|
What is the usual cause of Salingitis?
|
Ascending infections
-N. gonorrhoeae -E. coli -Chlamydia -Mycoplasma |
|
|
Normal Fallopian Tube
|
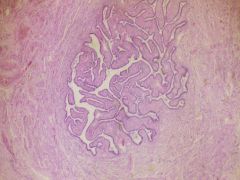
What is this?
|
|
|
Fallopian tube filled with watery fluid
|
Hydrosalpinx
|
|
|
Fallopian tube filled with pus
|
Pyosalpinx
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of Salpingitis?
|
1. Fibrosis, adhesions -> can close the lumen -> fertility problems
2. Ectopic pregnancy 3. Pain |
|
|
Acute Salpingitis
|
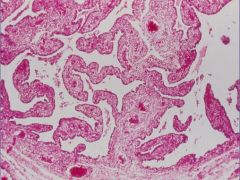
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Hydrosalpinx
|
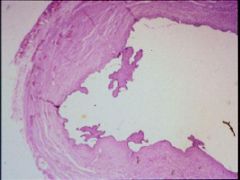
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Tubo-ovarian mass
|
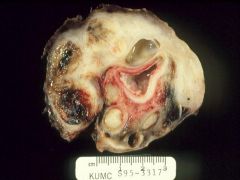
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Tubo-ovarian abscess due to N. gonorrhoeae
|
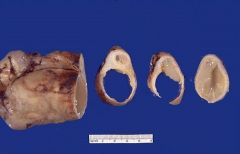
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Ovarian cyst due to distention of the unruptured graafian follicle
|
Follicular cyst
|
|
|
Follicular cyst
|
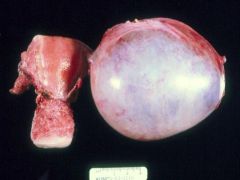
What is this?
|
|
|
Normal Follicular follicle
|
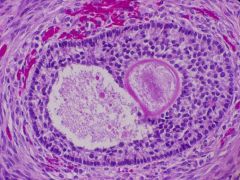
What is this?
|
|
|
Follicular cyst lined by Granulosa cells
|
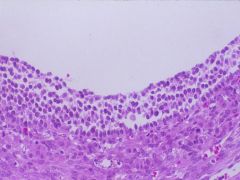
What is this?
|
|
|
What 2 things are Follicular cysts associated with?
|
Hyperestrinism
Endometrial Hyperplasia |
|
|
Corpus Luteum cysts
- yellow on the outside and hemorrhage on the inside |
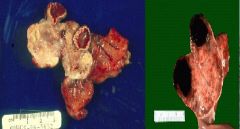
What are these?
|
|
|
Para-ovarian/Para-tubal cyst that got twisted, cutting off blood supply, and became necrotic
|
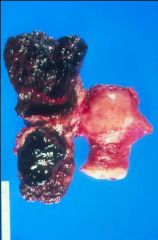
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Para-tubal/Para-ovarian cyst
|
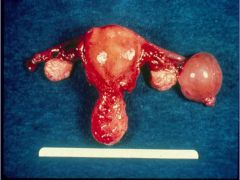
What is this?
|
|
|
Para-tubal cyst
|
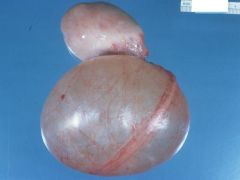
What is this?
|
|
|
Another name for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
|
Stein-Leventhal Syndrome
|
|
|
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome characterized by clinically?
|
1. Amenorrhea / Anovulation
2. Infertility 3. Obesity 4. Hirsutism |
|
|
What is the cause of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
|
Hormonal disturbance:
1. elevated LH 2. low FSH 3. elevated Testosterone |
|
|
What characterizes Polycystic Ovary Syndrome morphologically?
|
1. thickened ovarian capsule
2. multiple small cortical Follicular Cysts 3. Absence of Corpora Lutea or Albicans |
|
|
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
-follicular cysts |
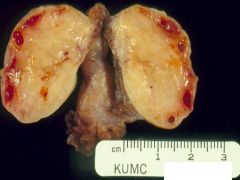
What is this showing?
|
|
|
Polycystis Ovary Syndrome
|
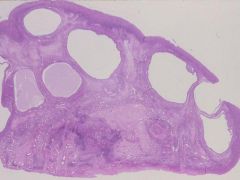
What is this showing?
|

