![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the mortis collection
|
Rigor mortis - Muscle tone
Algor mortis - Cadaver(死体の) temp Livor mortis - colour of organs Smely mortis |
|
|
List four causes of tissue discolouration.
|
1.Haemoblobin imbibition(吸収)
- lysis of RBC → release of Hg → give adjacent tissue a red to pink tinge 2.Bile imbibition - occurs in tissues adjacent to the gall bladder → yellow-green discolouration 3.Putrefaction (腐敗) - production of H2S and other reactive products by putrefactive anaerobic bacteria → green, blue-green, purple and black areas of tissue discoloration & bubbles of gas 4.Autolysis - lose their vital colours - lack lustre & sheen (光沢) - become dull - paler & friable |
|
|
List postmortem changes
|
1. Rigor mortis
2. Algor mortis 3. Livor mortis 4. Tissue discolouration 5. Distention and displacement of holllow viscera 6. Softening of tissues 7. Fluid 8. Postmortem blood clots 9. Miscellaneous (種々雑多)なgross postmortem changes |
|
|
Why does postmortem autolysis occur?
|
In death, anabolic reactions cease due to circulatory failure resulting in loss of oxygen and nutrient supply to tissue while catobolic reactions continue.
|
|
|
Define fixation
|
the process of preserving tissues so that autolysis is prevented
-Denatures enzymes within tissues so that proteolysis cannot take place -Hardens tissues for processing -Kills micro-organisms |
|
|
Formalin =
|
Formaldehyde(gas) + water
*Industrial formalin is an unbuffered aqueous solution |
|
|
What is the best & most common fixative?
|
10% phosphate buffered formal saline
|
|
|
lung congestion (充血)due to an effect of barbiturates
|
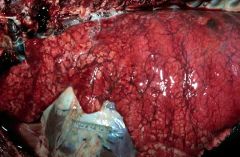
what is happening to this organ and why?
|
|
|
postmortem blood clots
*red-cell rich current jelly *plasm rich chicken fat |
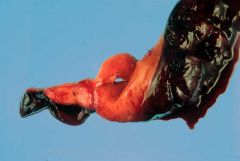
what kind of postmortem change is it?
|
|
|
focal thickening and hyperplasia of the endometrium.
The mucosa is thickened wih a bubbly appearance b/c of the development of cystic glands which contain clear watery fluid. |
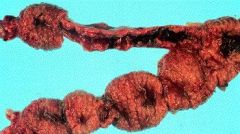
What is this gross condition?
Why does mucosa have bubbly appearance? |
|
|
hypoadrenacortism
-severe chronic diffuse adrenocortical atrophy -atrophy of zona glomerulosa leads to decrease in aldosterne secretion which regulate K+ excretion and Na retention |
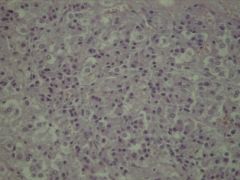
This is a histological section of adrenal cortex from the dog whose blood electrolytes indicated markedly increased K+ and decreased Na+. The dog presented for vomiting, anorexia and lethargy.
What is happening to this dog? |
|
|
Severe, chronic, diffuse adrenocortical hyperplasia & hypertrophy.
=hyperadrenocorticiism =Cushing's disease Cause:pituitary gland tumor leads to too much secretion of ACTH. Then too much cortisol secretion from adrenal cortex. |
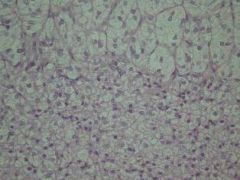
This specimen is from the dog had developed bilterally symmetrical hair loss, a pot-bellied appearance, palpable liver enlargement, polydipsia/polyurea.
What is the morphological diagnosis? |
|
|
Severe, chronic, denervation atrophy of skeletal muscle.
There are many fatty replacement. (fatty cells appeared as new cells. Not fatty change) |
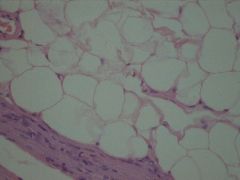
This is skeletal muscle specimen from the dog with radial nerve paralysis.
What is your morphological diagnose? |

