![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ddx for enteritis in neonatal cattle
|
E. coli
C. perfringens type C rotavirus calicivirus coronavirus Breda virus coccidiosis cryptosporidiosis |
|
|
Ddx for enteritis in adult cattle
|
salmonellosis
Johne's disease winter dysentery BVD |
|
|
Ddx for enteritis in nursing lambs
|
hemorrhagic enterotoxemia (C. perfringens type C)
E. coli lamb dysentery (C. perfringens type B) enterotoxemia ("pulpy kidney dz", C. perfringens type D) rotavirus cryptosporidiosis |
|
|
Ddx for enteritis in adult sheep
|
salmonellosis
coccidiosis Johne's disease |
|
|
Ddx for enteritis in neonatal pigs
|
E. coli
TGE (coronavirus) rotavirus coccidiosis C. perfringens type C |
|
|
Ddx for enteritis in adult pigs
|
swine dysentery
salmonellosis porcine intestinal adenomatosis complex adenovirus hog cholera African swine fever hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus ("vomiting & wasting disease", coronavirus) enterovirus |
|
|
Characteristics of hyperplasia
|
not excessive to needs
purposeful ceases when stimulation ceases reversible regulated |
|
|
Characteristics of neoplasia
|
excessive
purposeless persistent irreversible autonomous |
|
|
Characteristics of Benign Neoplasms
|
no metastasis
grows by uniform expansion (not invasive) resembles tissue of origin well circumscribed, often encapsulated progressive, slow growth normal mitotic figures excision usually curative adequate blood supply |
|
|
Characteristics of Malignant Neoplasms
|
metastasis
grows by expansion & infiltration (invasive) poorly differentiated (may be anaplastic) slow to rapid growth abnormal, abundant mitotic figures local recurrence frequent often outgrows blood supply & becomes necrotic |
|
|
Cytologic characteristics of malignant cells
|
unequal cell size (anisocytosis)
unequal nuclear size (anisokaryosis) hyperchromatic nuclei (abnormal DNA content) abnormal nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio enlarged & multiple nucleoli irregular clumping of chromatin high mitotic index abnormal mitoses tumor giant cells |
|
|
atresia coli
|
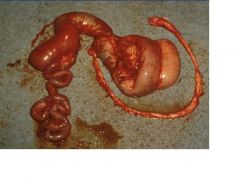
Name this condition in a calf.
|
|
|
BVD mucosal disease
|
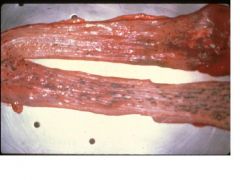
Name the disease in cattle.
|
|
|
BVD mucosal disease
|

Name the disease in cattle.
|
|
|
BVD mucosal disease
Peyer's patch necrosis |
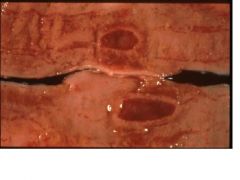
Name the disease in cattle and the lesion.
|
|
|
Edema disease
E. coli |
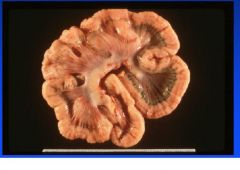
Name the disease and etiologic agent in cattle.
|
|
|
Edema disease
E. coli |
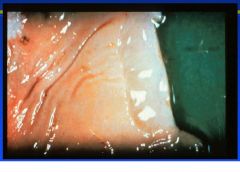
Name the disease and etiologic agent in cattle.
|
|
|
Edema disease
E. coli |
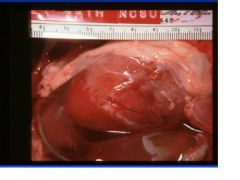
Name the disease and etiologic agent in cattle.
|
|
|
Johne's disease
|
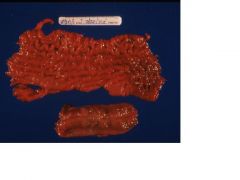
Name the disease in cattle.
|
|
|
granulomatous colitis
Mycobacterium avium paratuberculosis |
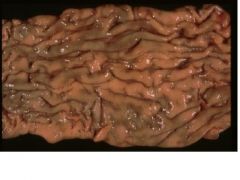
Give a morphologic diagnosis and etiologic agent in cattle.
|
|
|
Porcine intestinal adenomatosis complex
Lawsonia intracellulare |
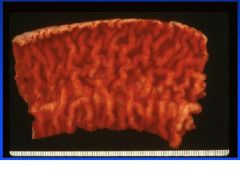
Name the disease and etiologic agent in pigs.
|
|
|
Porcine intestinal adenomatosis complex
Necrotic enteritis |
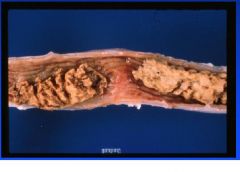
Name the disease & lesion in pigs.
|
|
|
Porcine intestinal adenomatosis complex
Proliferative hemorrhagic enteropathy |
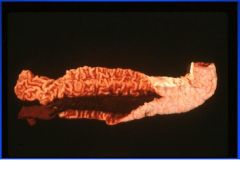
Name the disease and lesion in pigs.
|
|
|
Salmonella typhimurium, S. cholerasuis
rectal stricture |
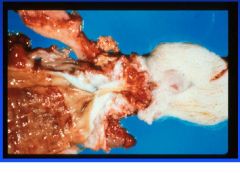
Give the etiologic agent and resulting pathology in pigs.
|
|
|
Multifocal granulomatous enteritis
|

Give a morphologic diagnosis in sheep.
|
|
|
Eimeria sp.
|
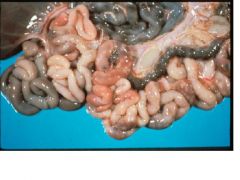
Name the etiologic agent in sheep.
|
|
|
coccidiosis
|
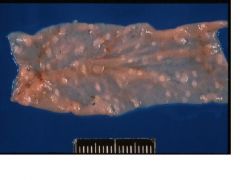
Name the disease in sheep.
|
|
|
feline infectious peritonitis
|
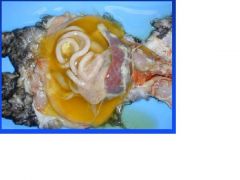
Name the disease in cats.
|
|
|
hemorrhagic enterocolitis
|
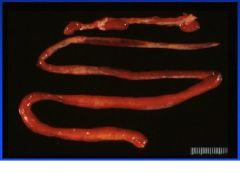
Give a morphologic diagnosis in a lamb.
|
|
|
hemorrhagic enterotoxemia
Clostridium perfringens type C |
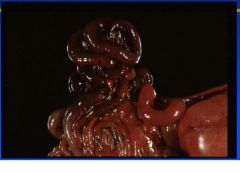
Name the disease and etiologic agent in a lamb.
|
|
|
Johne's disease
|
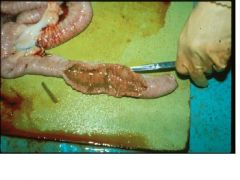
Name the disease in sheep.
|
|
|
granulomatous lymphadenitis
Johne's disease |
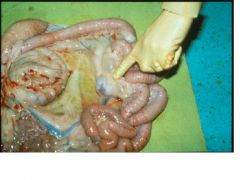
Give a morphologic diagnosis & disease in sheep.
|
|
|
Oesophagostomum (nodular worm)
|
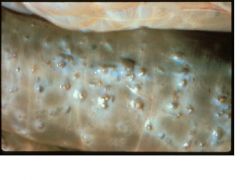
Name the etiologic agent in sheep.
|
|
|
granulamtous lymphadenitis
Oesophagostomum |
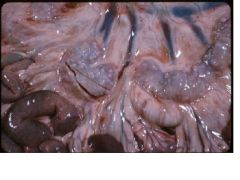
Give a morphologic diagnosis and etiologic agent in sheep.
|
|
|
Peyer's patch necrosis
parvovirus |
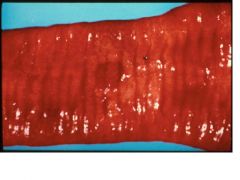
Give a morphologic diagnosis & disease in dog.
|
|
|
parvovirus
|
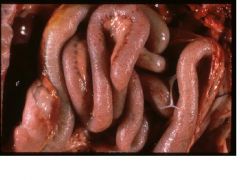
Name the disease in dogs.
|
|
|
cryptosporidiosis
|
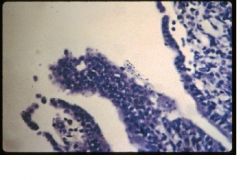
Name the disease in calves.
|
|
|
polyserositis
E. coli |
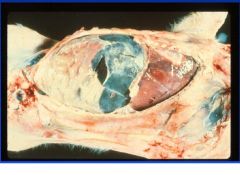
Give a morphologic diagnosis and etiologic agent in pigs.
|
|
|
glandular hyperplasia
porcine intestinal adenomatosis complex |
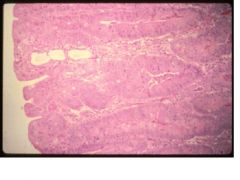
Give a morphological diagnosis and disease in pigs.
|
|
|
shiga-like toxin II damages small blood vessels
|
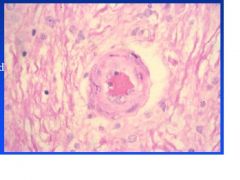
How does E. coli cause edema disease in pigs?
|
|
|
villous atrophy
transmissible gastroenteritis, coccidiosis |
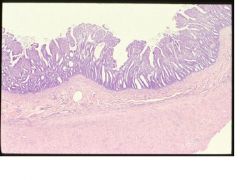
Name the lesion and give 2 differetial diagnoses in neonatal pigs.
|
|
|
intestinal crypt necrosis
parvovirus |
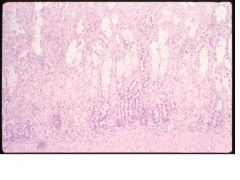
Name the lesion & the etiologic agent in dogs.
|
|
|
lymphoid necrosis
parvovirus |
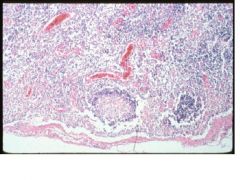
Name the lesion & etiologic agent in dogs.
|

