![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three main types of Odontogenic Tumour origins?
|
- epithelial
- mixed epithelial and mesenchymal - mesenchymal |
|
|
Which odontogenic tumours are epithelial in origin?
|
- ameloblastoma
- adenomatoid odontogenic tumour (AOT) - calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumour (CAOT) - squamous odontogenic tumour - clear cell odontogenic tumour |
|
|
Which odontogenic tumours are mixed epi and mesenchymal origin?
|
- ameloblastic fibroma
- ameloblastic fibro-odontoma - ameloblastic fibrosarcoma - odontoameloblastoma - odontoma |
|
|
Which odontogenic tumours are mesenchymal in origin?
|
- odontogenic fibroma
- granular cell odontogenic tumour - odontogenic myxoma - cementoblastoma |
|
|
What are potential etiologies of AMELOBLASTOMA?
|
- rests of dental lamina
- a developing enamel organ - epithelium lining of odontogenic cysts - basal cells of the oral mucosa |
|
|
What are the three clinico-radiologic presentations of ameloblastoma?
|
- conventional solid or multicystic (~86%)
- unicystic (~13%) - peripheral or extraosseous (~1%) |
|
|
Define "MULTICYSTIC INTRAOSSEOUS AMELOBLASTOMA:
|
- benign (but locally aggressive) neoplasm of odontogenic epithelial origin that histologically resembles the ameloblasts of the enamel organ, except no enamel is produced by lesional cells
|
|
|
Most MULTICYSTIC AMELOBLASTOMAS occur where?
|
- mandible
- molar/ramus region (80-85%) |
|
|
Approximately 20% of MULTICYSTIC AMELOBLASTOMA is associated with _______?
|
Impacted tooth - suggesting relationship to dental follicle or dentigerous cyst
|
|
|
What is the most typical radiographic feature of AMELOBLASTOMA?
|
- multilocular radiolucency (soap bubble appearance)
- well-defined borders - not sclerotic - tendency to infiltrate adjacent trabecular spaces of bone |
|
|
What is the treatment for MULTICYSTIC AMELOBLASTOMA?
|
small lesions - aggressive curettage or small en bloc resection
large lesions - large en bloc resection or segmental resection with reconstruction margin of resection should be at least 1.0 -1.5 cm past the radiographic limits of the tumour |
|
|
Define UNICYSTIC AMELOBLASTOMA:
|
- most often seen in YOUNGER patients
- 90% of cases in the posterior mandible - typically a circumscribed radiolucency that surrounds the crown of an unerupted mand. third molar resembling DENTIGEROUS CYST |
|
|
What are the three histological types of UNICYSTIC AMELOBLASTOMA?
|
- luminal ameloblastoma
- intraluminal ameloblastoma - mural ameloblastoma |
|
|
Define "plexiform unicystic ameloblastoma":
|
- nodules of tumour show plexiform pattern histologically (intraluminal ameloblastoma)
|
|
|
What is the TREATMENT of UNICYSTIC AMELOBLASTOMA?
|
LUMINAL/INTRALUMINAL: enucleation and long term follow up
MURAL: local resection as a prophylactic measure and long term follow up RECURRENCE: 30% after enucleation |
|
|
PERIPHERAL AMELOBLASTOMA probably arises from what?
|
odontogenic epithelium rest beneath the oral mucosa or from the basal epithelial cells of the surface epithelium
|
|
|
Define MALIGNANT AMELOBLASTOMA:
|
- rare lesion
- histologically appears to be routine ameloblastoma but it behaves in a malignant fashion |
|
|
Define AMELOBLASTIC CARCINOMA:
|
- rare lesion
- histologically appears malignant and clinically behaves in a malignant fashion |
|
|
Define ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR:
|
uncommon benign odontogenic tumour - probably arises from enamel organ epithelium or remnants of dental lamina
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of AOT?
|
- younger patients (70% under 20yrs)
- tendency for ANTERIOR portions of jaw - 2x as often in MAXILLA - often ASYMPTOMATIC and discovered during ROUTINE RADIOGRAPHIC EXAM to determine why tooth hasn't erupted |
|
|
What are the radiographic features of AOT?
|
- well-circumscribed
- unilocular radiolucency that may contain radiopaque flecks - separation of roots or displacement of adjacent teeth occur frequently - when associated with unerupted tooth (most often CANINE) lesion extends apical to CEJ - less often AOT presents as well-delinated radiolucent lesion located between the roots of erupted teeth |
|
|
What is the treatment of AOT?
|
- enucleation is easy because of capsule
- good prognosis |
|
|
What is another name for PINDBORG TUMOUR?
|
Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumour (CEOT)
|
|
|
Define CEOT?
|
- rare locally aggressive uncommon odontogenic tumour consisting of strands of polyhedral epithelial cells, amyloid staining hyaline deposits, and spherical calcifications (Liesengang rings).
|
|
|
What is the histogenesis of CEOT?
|
- unknown
- may be stratum intermedium or dental lamina |
|
|
What are the clinical features of CEOT?
|
- painless
- slow growing swelling is most common presenting sign - POSTERIOR MANDIBLE favored - rarely may occur peripherally as gingival mass, most often anterior gingiva |
|
|
What are the radiographic features of CEOT?
|
- unilocular or multilocular radiolucency
- margins often scalloped and usually relatively well defined - some may have ill-defined periphery or exhibit a cortical border - may be entirely radiolucent but may contain calcified structures of varying sizes - occasionally a "driven snow " pattern - often associated with impacted teeth (most often mand molar) |
|
|
What is the treatment of CEOT?
|
- conservative local resection to include narrow rim of surrounding bone
- overall prognosis is good - rare cases of malignant or borderline CEOT with metastasis to regional lymph nodes or lung have been reported |
|
|
Define SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR (SOT)
|
- rare benign odontogenic neoplasm consisting of islands of bland-appearing squamous epithelium in a fibrous stroma.
- may arise from rest of dental lamina or perhaps from the epithelial rest of Malassez |
|
|
What are the clinical features of SOT?
|
- asymptomatic but tooth mobility and pain may be present
- mean age 37 years - no preferred site - several cases have had multiple sites of involvement |
|
|
What are the radiographic features of SOT?
|
- semicircular / triangular radiolucency between two tooth roots
- may or may not be well defined - vertical periodontal bone loss in some instances |
|
|
What is the treatment of SOT?
|
conservative local excision or curettage
- prognosis good - multicentric lesions are less aggressive than solitary |
|
|
What are the clinical features of AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA?
|
- Younger patients (first two decades)
- posterior mandible most common site - small lesions (ASYMPTO), large lesions painless swelling - 75% associated with UNERUPTED TOOTH |
|
|
What are the radiographic features of AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA?
|
- unilocular when small
- multilocular when large - well-defined or sclerotic |
|
|
What is the treatment of AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA?
|
- aggressive curettage
- followup |
|
|
Define AMELOBLASTIC FIBRO-ODONTOMA:
|
tumour with general features of an ameloblastic fibroma but that also contains enamel and dentin.
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of AMELOBLASTIC FIBRO-ODONTOMA?
|
- usually in children
- most freq in posterior regions of jaws - commonly asymptomatic - in most cases an unerupted tooth is present at the margin of the lesion, or the crown of an unerupted tooth may be included in the lesion |
|
|
What are the radiographic features of AMELOBLASTIC FIBRO-ODONTOMA?
|
- well circumscribed
- unilocular or, rarely, multilocular - radiolucent - variable amount of calcified material within radiolucency |
|
|
WHat is the treatment of AMELOBLASTIC FIBRO-ODONTOMA?
|
- curettage
- good prognosis |
|
|
What is an AMELOBLASTIC FIBROSARCOMA?
|
Rare malignant counterpart of the ameloblastic fibroma in which ONLY the mesenchymal portion of the lesion shows malignancy
- may arise de novo or from recurrence of a previously diagnosed ameloblastic fibroma or ameloblastic fibroma-odontoma - more common in mandible - RADICAL SURGICAL EXCISION treatment of choice |
|
|
Define ODONTOMA:
|
Developmental anomalies rather than true neoplasms
|
|
|
Define: HAMARTOMA
|
Developmental anomaly
|
|
|
Describe a COMPOUND ODONTOMA:
|
- multiple, small tooth like structures
- anterior maxilla |
|
|
Describe a COMPLEX ODONTOMA:
|
- amorphous radiopaque conglomerations
- posterior regions of either jaw - irregular |
|
|
How are odontomas treated?
|
simple local excision
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of CENTRAL ODONTOGENIC FIBROMA?
|
- female predilection
- Maxilla - ant to first molar - Mandible - post to first molar - SOME lesions associated with unerupted tooth - |
|
|
What is the treatment of CENTRAL ODONTOGENIC FIBROMA?
|
- enucleation / curettage: few recurrences, good prog
- surgical excision for peripheral lesions |
|
|
Define ODONTOGENIC MYXOMA:
|
- benign neoplasm assumed to be of odontogenic origin because it only affects the jaw bones as a central lesion - no other bones
|
|
|
What is the recurrence rate of UNICYSTIC AMELOBLASTOMA after enucleation?
|
30%
|
|
|
What is the treatment of MURAL AMELOBLASTOMA?
|
local resection
|
|
|
How does SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR present radiographically?
|
- semicircular or triangular radiolucency between two tooth roots
- may or may not be well defined - vertical periodontal bone loss sometimes |
|
|
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA occurs most commonly where?
|
posterior mandible
|
|
|
Which odontogenic tumours are associated with an unerupted tooth?
|
- ameloblastoma
- ameloblastic fibroma - ameloblastic fibro-odontoma - adenomatoid odontogenic tumour |
|
|
What are the "virtually pathognomonic" radiographic features of a cemento blastoma?
|
- well circumscribed radiopaque mass
- fine radiolucent border - fused to the root of a tooth - usually MAND FIRST MOLAR - resorption of tooth is typically noted |
|
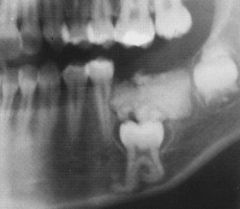
|
AMELOBLASTIC FIBRO-ODONTOMA
|
|

|
AMELOBLASTIC FIBRO-ODONTOMA
|
|
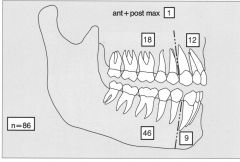
DISTRIBUTION AMELOBLASTIC FIBRO-ODONTOMA
|
AMELOBLASTIC FIBRO-ODONTOMA
|
|
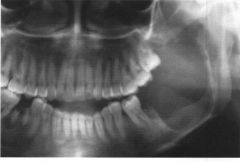
What is this lesion?
|
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA
|
|
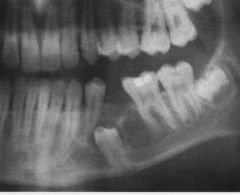
What is this lesion?
|
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA
|
|
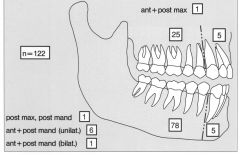
DISTRIBUTION AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA
|
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA
|
|
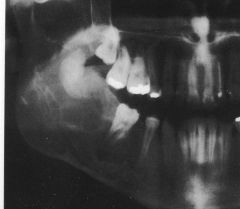
What is this lesion?
|
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA
|
|
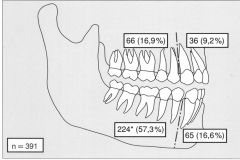
AMELOBLASTOMA DISTRIBUTION
|
AMELOBLASTOMA
|
|
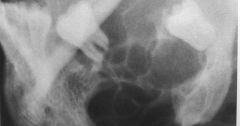
What is this lesion?
|
AMELOBLASTOMA
|
|
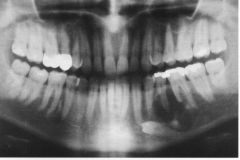
What is this lesion?
|
AMELOBLASTOMA
|
|
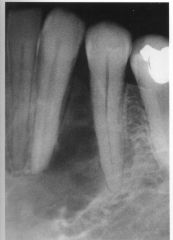
What is this lesion?
|
AMELOBLASTOMA
|

