![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
ID
|
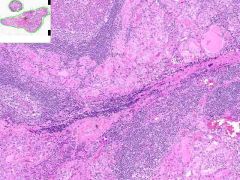
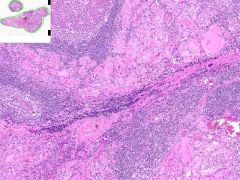
HASHIMOTO'S THYROIDITIS:
Thyoid is diffusely enlarged with an in-tact capsule and on gross exam, a cut surface that is grey-tan and nodular. Much of the thyroid is infiltrated by mononuclear inflammation containing plasma cells, small lymphocytes and well developed lymphoid germinal centers. Increased inter-follicular CT. |
|
ID
|
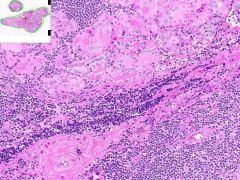
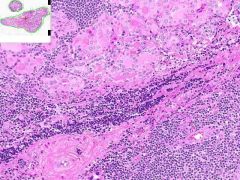
HASHIMOTO'S THYROIDITIS:
Much of the thyroid is infiltrated by mononuclear inflammation containing plasma cells, small lymphocytes and well developed lymphoid germinal centers. Increased interfollicular CT. |
|
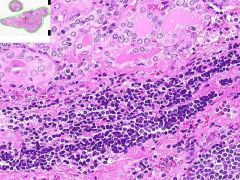
ID
|
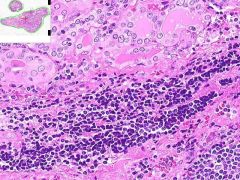
HASHIMOTO'S THYROIDITIS:
Much of the thyroid is infiltrated by mononuclear inflammation containing plasma cells, small lymphocytes and well developed lymphoid germinal centers. Increased inter-follicular CT. |
|
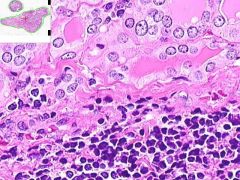
ID
|
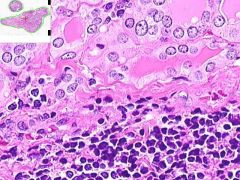
HASHIMOTO'S THYROIDITIS:
Infiltrate of lymphocytes, plasma cells and cell-developed germinal centers. Thyroid follicles that remain are small and atrophic. Some have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm in follicular epithelial cells (Hurthle cells). |
|
ID
|
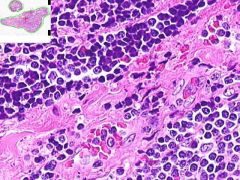
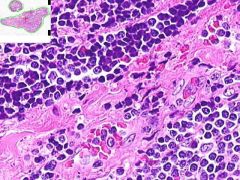
HASHIMOTO'S THYROIDITIS:
Infiltrate of lymphocytes, plasma cells and cell-developed germinal centers. Thyroid follicles that remain are small and atrophic. Some have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm in follicular epithelial cells (Hurthle cells). |
|
ID
|
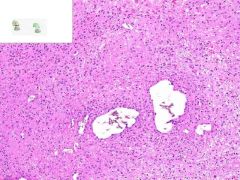
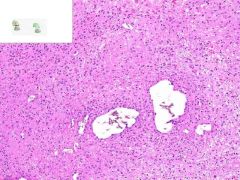
LEUKOCLASTIC VASCULITIS:
Dermis from slide where surface epithelia has been removed. Surrounding the capillaries is a perivascular infiltrate of neutrophils. Swollen gross appearance would be due to blood vessel dilation. |
|
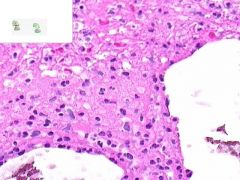
ID
|
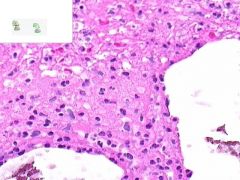
LEUKOCLASTIC VASCULITIS:
Perivascular infltration of neutrophils. Some neutrophils in the walls of vessels are undergoing cellular fragmentation (leukocytoCLAST). Fibrinoid necrosis of vessel media may be present (not shown). |
|
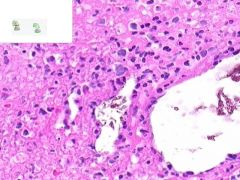
ID
|
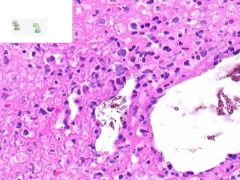
LEUKOCLASTIC VASCULITIS:
Perivascular infltration of neutrophils. Some neutrophils in the walls of vessels are undergoing cellular fragmentation (leukocytoCLAST). Fibrinoid necrosis of vessel media may be present (not shown). |
|
ID
|
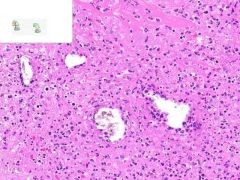
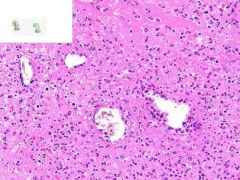
LEUKOCLASTIC VASCULITIS:
Dermis from slide where surface epithelia has been removed. Surrounding the capillaries is a perivascular infiltrate of neutrophils. Swollen gross appearance would be due to blood vessel dilation. |
|
ID
|
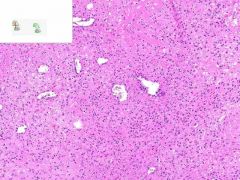
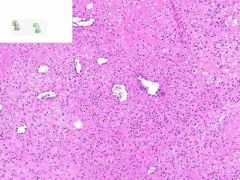
LEUKOCLASTIC VASCULITIS:
Dermis from slide where surface epithelia has been removed. Surrounding the capillaries is a perivascular infiltrate of neutrophils. Swollen gross appearance would be due to blood vessel dilation. |
|
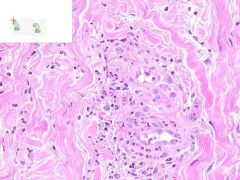
ID
|
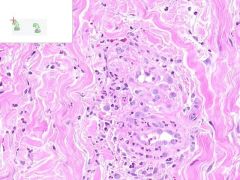
LEUKOCLASTIC VASCULITIS:
Perivascular infltration of neutrophils. Some neutrophils in the walls of vessels are undergoing cellular fragmentation (leukocytoCLAST). Fibrinoid necrosis of vessel media may be present (not shown). |
|
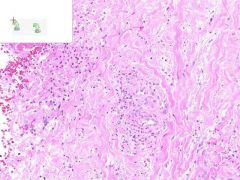
ID
|
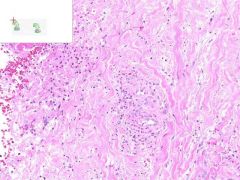
LEUKOCLASTIC VASCULITIS:
Dermis from slide where surface epithelia has been removed. Surrounding the capillaries is a perivascular infiltrate of neutrophils. Swollen gross appearance would be due to blood vessel dilation. |
|
ID
|
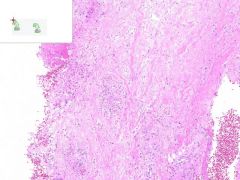
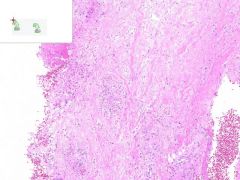
LEUKOCLASTIC VASCULITIS:
Dermis from slide where surface epithelia has been removed. Surrounding the capillaries is a perivascular infiltrate of neutrophils. Swollen gross appearance would be due to blood vessel dilation. |
|
ID
|
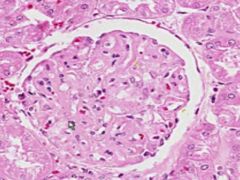
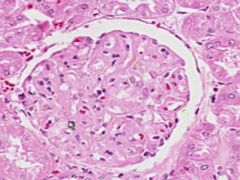
SLE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS:
Note the increased number of glomerular cells + thickened capillary membranes (wire loops). Some of the parietal glomerular epithelia form crescent-shaped foci. Immunoflourescene would show immune complex deposition in subendothelial and subepithelial areas, with antibodies to DNA. |
|
ID
|
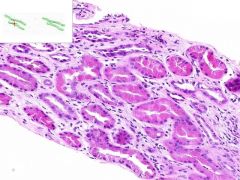
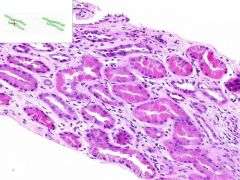
SLE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS:
SLE causing immune complex deposition in the kidney leads to MEMBRANOPROLIFORATIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS: 1) proliforation of epithelia in glomeruli and Bowman's capsule (proliforative glomerulonephritis) 2) thickening of glomerular capillary walls (membranous glomerulonephritis). This biopsy also has a focal interstitial inflammation surounding some renal tubules (lymphocytes and plasma cells). |
|
ID
|
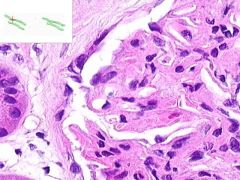
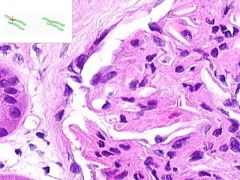
SLE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS:
Note the increased number of glomerular cells + thickened capillary membranes (wire loops). Some of the parietal glomerular epithelia form crescent-shaped foci. Immunoflourescene would show immune complex deposition in subendothelial and subepithelial areas, with antibodies to DNA. |
|
ID
|
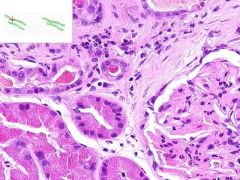
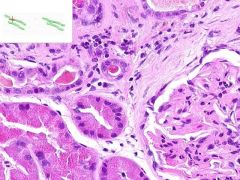
SLE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Focal interstitial inflammatory infiltrate surrounding some renal tubules? Lymphocytes and plasma cells. |
|
ID
|
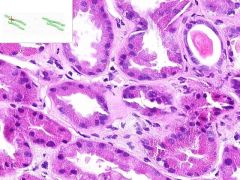
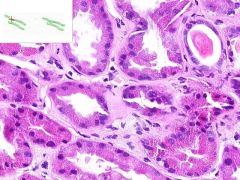
SLE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS:
Focal interstitial inflammatory infiltrate surrounding some renal tubules, composed of lumphocytes and plasma cells. |
|
ID
|
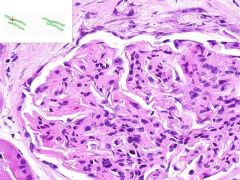
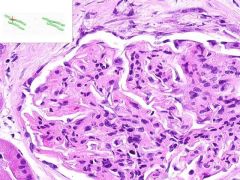
SLE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS:
Note the increased number of glomerular cells + thickened capillary membranes (wire loops). Some of the parietal glomerular epithelia form crescent-shaped foci. Immunoflourescene would show immune complex deposition in subendothelial and subepithelial areas, with antibodies to DNA. |
|
ID
|
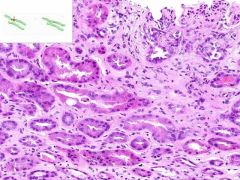
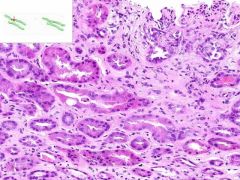
SLE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS:
SLE causing immune complex deposition in the kidney leads to MEMBRANOPROLIFORATIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS: 1) proliforation of epithelia in glomeruli and Bowman's capsule (proliforative glomerulonephritis) 2) thickening of glomerular capillary walls (membranous glomerulonephritis). This biopsy also has a focal interstitial inflammation surounding some renal tubules (lymphocytes and plasma cells). |
|
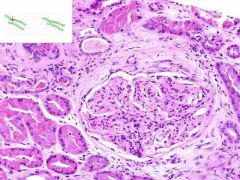
ID
|
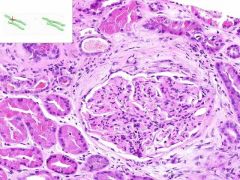
SLE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
proliferative glomerulonephritis - A proliferative response of the glomerular endothelial cells as well as the parietal epithelium lining Bowman's capsule. membranous glomerulonephritis - A thickening of the glomerular capillary walls. membranousproliferative - When both major components are present. Wire loops - Thickened walls of capillaries Crescent shaped foci - parietal epithelium proliferation |
|
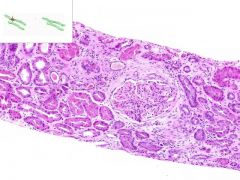
ID
|
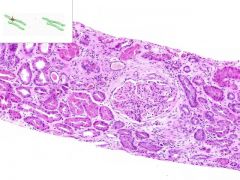
SLE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS:
SLE causing immune complex deposition in the kidney leads to MEMBRANOPROLIFORATIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS: 1) proliforation of epithelia in glomeruli and Bowman's capsule (proliforative glomerulonephritis) 2) thickening of glomerular capillary walls (membranous glomerulonephritis). This biopsy also has a focal interstitial inflammation surounding some renal tubules (lymphocytes and plasma cells). |

