![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the processes that give rise to 1. transudates, and 2. exudates. Mention why they happen in their typical clinical settings.
|
1- Clear salt like fluid in edema
1. Increased total body fluid 2. Vascular problems 3. Decreased plasma protein content/albumin content 4. Lymphatic obstruction 2- "pus" protein rich in salt water formed from damaged lymphatics 4. Lymphatic obstruction |
|
|
Describe edema as seen in inflammation in...
a. Cardiac b. renal c. liver |
a. appearing first in the feet after standing and in sacral area for bedridden
b. appears first around the eyes c. appears as access fluid in abdomen |
|
|
Describe the special cases of cerebral edema and "angioedema". Explain how and when lymphedema develops
|
cerebral- from injury, poisoning or variety of other causes is problematic due to pushing brainstem out of bottom of skull
angiodema- blood vessels suddenly becoming extra permeable (C1-esterase deficiency) lymphedema- most often due to cancer also a filarial disease that causes epidemic elephantiasis |
|
|
Describe in general terms the causes and consequences of hemorrhages.
|
a. Blood cells that have escaped from a vessel
b. Causes- i. Blood vessel diseases- (petechiae of scurvy and syphilitic aortic aneurysm into throat) ii. Around blood vessels- infections and cancers iii. Lack of clotting factors- (congentinal, acquired, DIC) iv. Lack of platalets, v. High blood pressure Consequences- depends on where and how much |
|
|
Cite Virchow's triad for the causes of thrombosis, and recognize and give examples in each category.
|
Three preconditions that make risk for thrombosi development greater
1. injured endothelium- myocardial infarcts, radiation injuries, high blood pressure, cigarette smoke, electrical injury, invasion of vessel by tumor, 2. altered blood flow (turbulence/stasis)- bed rest, sickle cell, 3. Hypercoagulable blood- hereditary |
|
|
Describe the possible fates, good and bad, of a thrombus.
a. Good- body needs blood to coagulate and form a thrombus otherwise we lose too much blood b. Bad- When thrombus breaks off (embolizes) it can eventually travel to area that causes infarction |
9. Describe the possible fates, good and bad, of a thrombus.
a. Good- body needs blood to coagulate and form a thrombus otherwise we lose too much blood b. Bad- When thrombus breaks off (embolizes) it can eventually travel to area that causes infarction |
|
|
Describe the nature, causes and effects of disseminated intravascular coagulation, and give its synonyms.
|
when too much clotting and too much bleeding problem occurs... aka- consumption coagulopathy, defibrination syndrome- "death is coming"
Causes 1.Things that release thromboplastin into blood a. Large infarcts b. Massive intravascular hemolysis (malaria) c. Snakebite d. Decompression sickness (scuba diving) e. Plague 2. Things that Damage endothelium a. Rickettsial diseases b. Meningococcemia c. Other infections d. Toxemia 3. Things that do both a. Shock b. Gram- negative sepsis c. Massive trauma 2. |
|
|
Describe things that embolize.
Briefly discuss each of the following... a. classic pulmonary thromboemboli, b. paradoxical emboli c. systemic thromboemboli. |
any liquid, solid or gasseous thing other than liquid blood and solutes that travel along blood stream
a. majority come from deep leg veins, one of greatest killers of hospitalized patients, b. from systemic vein that passes through a right to left intracardiac shunt to occlude systemic artery c. embolism down systemic artery... always produce infaracts |
|
|
Give accounts of the causes and consequences of the following emboli...
a. amniotic fluid b. air c. fat d. arthrosclerotic |
a. amniotic fluid has baby's debris and somehow entered circulation
b. air- gas in circulation from decompression injury- gas blocks blood flow c. fat- after fractures globules of fat are released into circulation.. sometimes fat embolization syndrome resulting in pulmonary edema d. "trash foot" bits of grumous debris from inside atheroslerotic placques embolize in kidneys, toes, and male genitals |
|
|
Give accounts of the causes and consequences of the following emboli...
a. marrow b. tumor c. therapeutic |
a. occur after vigorous CPR that fractures ribs
b. bits of cancer that invaded a vein and then broke off c. "gel-foam", silicones from surgery |
|
|
Give a brief definition and full account of the red and white infarcts. Tell about their causes and appearances in all the major organs
|
- localized area of necrosis due to ischemia
a. White- (spleen, kidney, brain and heart) arterials are occluded in solid organs and not reperfused and single blood supply b. Red- vein occlusion, (arteries in bowel) or dual blood supply or reperfused |
|
|
Define and Mention two factors contributing to reperfusion injury
|
tissue damage that occurs when already damaged tissue gets its circulation back
1. Calcium, enters damaged cells and stiffens sarcomeres and preciptates with phosphates 2. oxygen generates free radicals 3. fresh blood components meeting damaged biomolecules generates neutrophil entry, complement activation and etc |
|
|
Define shock and mention major causes...
|
Whenever there is widespread underperfusion of the body
causes- heart not pumping, water loss, vascular tone lost |
|
|
Describe how whole-body hypoperfusion causes problems...
|
a. lactic acidosis develops and lowers pH
b. variety of secondary mediators make problem worse |
|
|
Describe the stages of shock...
a. compensated b. progressive/decompensated c. irreversible |
a. Head and heart receive available blood, BP normal, but kidney/gut-liver/skin are underperfused ("pale/cold") elevated pulse
b. kidneys/ liver cells mostly dead, pH down lactate up, still savable c. no intervention can save |
|
|
What are the anatomic pathology that results from shock
|
Anatomic findings...
a. diffuse hypoxic injury to braid b. "watershed" infarcts subendocardial necrosis c. widespread contraction band necrosis in heart d. acute tubular necrosis of kidneys e. bleeding kidneys f. leaked fibrin in air space |
|
|
Define the following terms...
a. anasarca b. congestion c. effusion (types) d. empyema |
a. anasarca- bad generalized edema
b. congestion- decreased blood flow from an organ that results in increased blood content. Occurs when something interferes with venous drainage c. effusion (types)- excess fluid in specific areas i. Pleural ii. Pericardial iii. Loculated d. empyema- - when there is excess pus like fluid in pleural cavity |
|
|
Define the following terms...
a. hematemesis b. hemoptysis c. hydrocele d. hydrosalpinx |
a. hematemesis- when you have blood in throwup
b. hemoptysis- bleeding from trachea shown when u cough up blood c. hydrocele- extra fluid within the membrane around the testis d. hydrosalpinx- too much fluid in the fallopian tube |
|
|
Define the following terms
a. infarct b. milk leg c. propagation d. pyothorax |
a. infarct- localized area of necrosis due to ischemia
b. milk leg- another name for venous thrombosis in later pregnancy or after delivery c. propagation- movement d. pyothorax- pus in pleural cavity |
|
|
Define the following terms...
a. thrombus b. vegetation c. ascites d. ecchymosis |
a. thrombus- blood that has solidified within a vascular lumen or cardiac chamber
b. vegetation- - are thrombi that occur on cardiac valves. (bacterial endocarditis) c. ascites- excess free fluid in the peritoneal cavity d. ecchymosis- above 10 mm hemorrhage, or bruises from trauma, (‘aka contusion) |
|
|
Define the following terms...
a. elephantiasis b. exudate c. hematoma d. hemorrhage |
a. elephantiasis- clinical presentation of lymphedema that involves the extremities caused by filaria worms. Also caused by shoelessness where the soil is volcanic. Glass like particles invade and clog the lymphatics
b. exudate- differs from transudates in that they are not clear (pus) and protein rich, they are due to leaky vessels c. hematoma- enough blood in tissues to create a palpable mass d. hemorrhage- blood cells that have escaped from a vessel. |
|
|
Define the following terms...
a. hydrocephalus b. hydrothorax c. loculation d. mural thrombus |
a. hydrocephalus- increased volume of cerebrospinal fluid from any cause; dilated cerebral ventricles
b. hydrothorax- clear fluid in pleural space c. loculation- presence of numerous small spaces or cavities d. mural thrombus- forms on the walls of the cardiac chambers |
|
|
Define the following terms...
a. pupura b. edema c. transudate d. clot |
a. pupura- bigger hemorrhages in tissues, often multiple surface bleeds common in people with fragile vessels
b. edema- excess interstitial fluid for various reasons. Can be labeled many different name c. transudate- fluid accumulations that are usually clear, full of salt water d. clot- blood that has solidified anywhere else other than vascular lumens or cardiac chambers. |
|
|
Define the following terms...
a. embolus b. hemarthrosis c. hemopericardium d. hemothorax |
a. embolus- free sailing part of thrombus that causes clotting in vessels
b. hemarthrosis- - bleeding into a joint c. hemopericardium- blood in the pericardial cavity d. hemothorax- if excess fluid found in pleural cavity is blood |
|
|
Define the following terms...
a. hydropericardium b. hyperemia c. melena d. petechiae |
a. hydropericardium- “pericardial effusion” excess fluid in the pericardial cavity
b. hyperemia- increased blood flow to an organ that results in increased blood content. Occurs when arteriole have dilated more than its venules have. (Blushing, throbbing erections, reddening of skin to disperse heat, and rubor of acute inflammation.) c. melena- black, tarry, partially digested blood out rectum, from upper- GI bleed. d. petechiae- little hemorrhages in tissues generally defined to be under 3 mm across |
|
|
Define the following terms...
a. pyemia b. recanalization |
a. pyemia- word used for infected venous thrombus that has embolized. Ex. Septic venous thrombus near an inflamed appendix that has embolized to the portal vein
b. recanalization- thrombi usually turned into granulation tissue and contraction opens many channels |
|
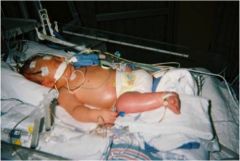
Patient presents with generalized or sever edema... what is this?
|
anasarca
|
|
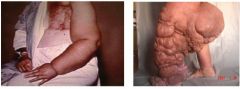
What condition do the two patients show?
|
elephantiasis
|
|
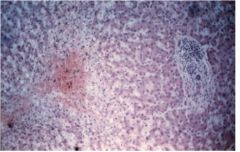
What do the liver cells show?
|
blood pooling around hepatic central vein, adjacent cells died of lack of good blood flow due to congestion
|
|
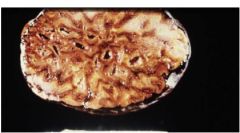
What does picture show? What is the cause?
|
nutmeg liver due to congestion
|
|
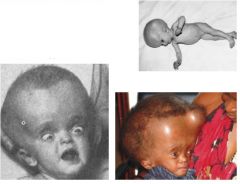
What condition is shown?
|
hydrocephalus- too much fluid to head
|
|
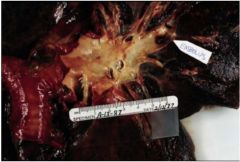
What is picture showing?
|
lethal pulmonary thromboembolism
|
|
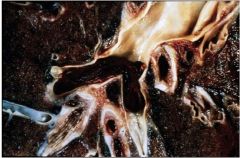
What does picture show?
|
pulmonary thromboembolism
|
|
What does picture show?
|
pulmonary thromboembolism
|
|
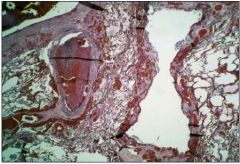
what does picture show?
|
little pulmonary thromboembolism
|
|
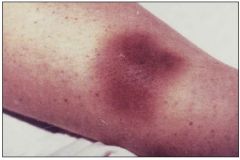
What does the picture show?
|
petechiae or ecchymoses (contusion)
|
|
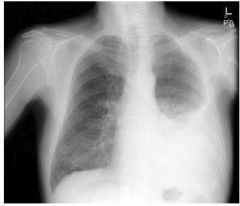
What does the x-ray show?
|
pleural effusion
|
|
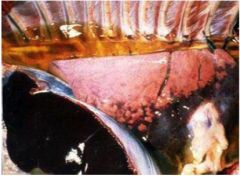
What specific thing does the gross thing show?
|
a hydrothorax pleural effusion
|
|
What is the picture showing?
|
pleural effusion- empyema "pus" in pleural cavity
|
|

What is shown and what type?
|
brain stem infarct
white |
|
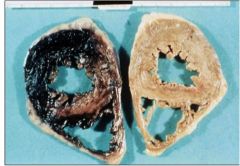
What is going on here? and what type?
|
myocardial infarct- white
|
|
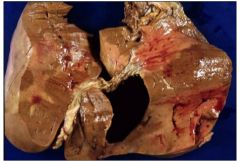
What is shown and what type?
|
liver infarct- red
|
|
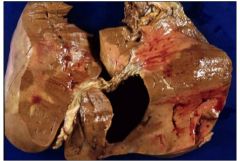
What is shown and what type?
|
kidney infarct- white
|
|
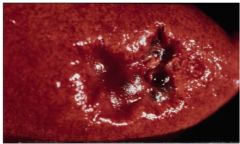
What is shown and type?
|
old kidney infarct- white
|
|
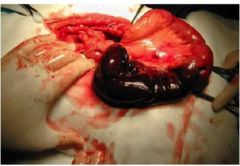
what is shown in this picture? What type is it?
|
bowel infarct- red
|
|
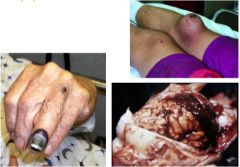
What do these pictures show?
|
hematomas
|
|

How does the ear get like that and what is it called?
|
transformation of a hematoma called cauliflower ear
|
|
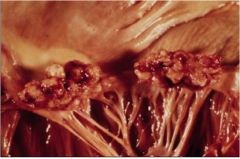
What does this picture show?
|
cardiac vegetation
|
|
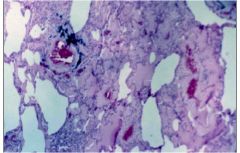
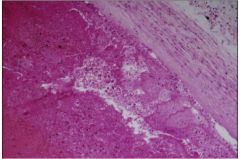
What does this slide show?
|
pulmonary edema that is protein rich (exudate)
|
|
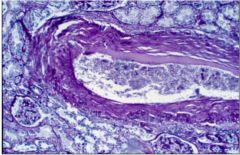
What does this slide show?
|
post mortem thrombi... liquid on top and red cells on bottom
|
|
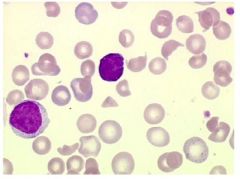
What does this slide show and what about it leads you to believe a certain diagnoses?
|
fragmented red cells and too few platelets, consider DIC
|
|
What does this slide show and what diagnosis is there?
|
DIC and microthrombi
|
|
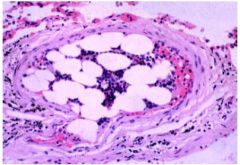
What does this slide show... what causes it?
|
Marrow embolus
caused by CPR that broke ribs |
|
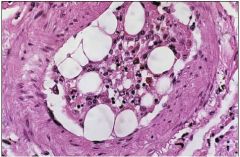
What does this slide show and what causes it?
|
marrow embolism caused by CPR that cracked ribs
|
|
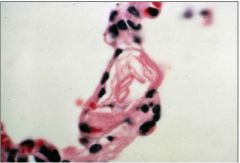
What is this slide showing?
|
amniotic fluid embolus
|
|
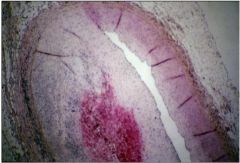
What does slide show and where?
|
hemorrhage in coronary artery
|
|
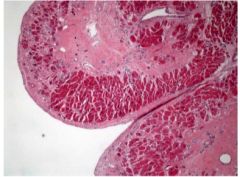
What does the slide show?
|
Scarring of subendocardium where infarcts healed
|
|
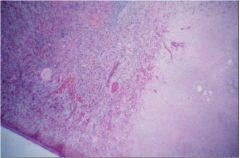
What does this slide show?
|
spleen infarct
|
|
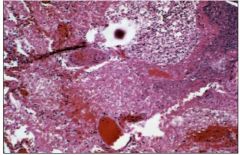
What does this slide show?
|
lung infarct- bloody and dead
|
|
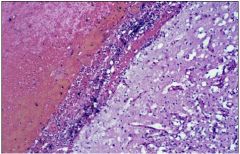
What does this slide show?
|
brain infarct- more hemorrhagic
|
|
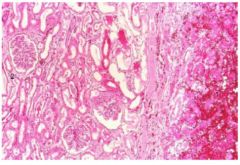
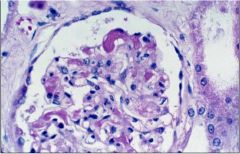
What kind of infarct is this?
|
kidney
|

