![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
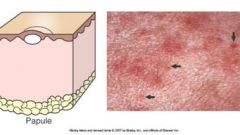
Papule is a small solid (palpable) raised spot on the skin up to 1 cm in diameter. (Plaque larger)
Examples causes? |
Examples: edema, infiltration of inflammatory cells (allergic dermatitis, superficial bacterial folliculitis, calcinosis circumscripta) <- Cushing's!! cause calcinosis
>lead to scales or crust after dries up |
|
|
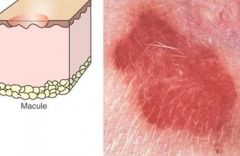
Macule is a flat non-palpable spot (less than 1cm in diameter) characterized by a change in color from the surrounding skin.
>disease etiology??? |
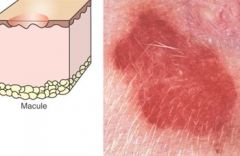
Macule
hypopigmentation (vitiligo), hyperpigmentation, petechiae, ecchymoses. |
|
|
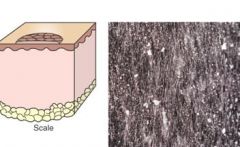
Scale is an accumulation of loose fragments (flakes) of stratum corneum (cornified cells) on skin.
disease 1° or 2° etiology? |

Scale is an accumulation of loose fragments (flakes) of stratum corneum (cornified cells) on skin. Dry or Oily
Primary: primary idiopathic seborrhea, endocrine dermatoses (cornification disorders)…Cushing’s!!!! Secondary: chronic inflam, icthyosis, sebaceous adenitis |
|
|
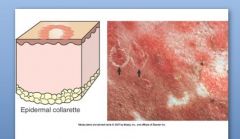
Epidermal collarette: FLAT to minimally elevated ring of scales (keratinocytes), flakes of epidermis that slough off, Possible causes?
|
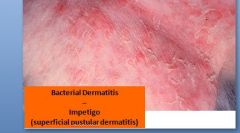
Epidermal collarette
Caused by: superficial bacterial inf., fungal inf., dermatophytes, ring worm, insect bites b/c have lytic enz. |
|
|
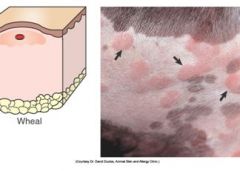
Wheal is an irregular elevated edematous white to pink skin area which usually changes in size and shape (within hours). If distensible areas (eyelids or lips) are affected, it is called angioedema.
Examples disease etiology?: |

Examples disease etiology?: (immune mediated) urticaria, insect bite, and positive reaction to allergy skin test.
Wheal is irregular elevated edematous white to pink skin area; ~changes (Transient!!!). If distensible areas (eyelids or lips) are affected = angioedema. |
|
|
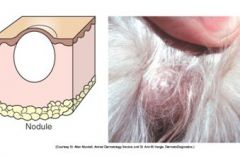
Nodule is circumscribed, solid elevation greater than 1 cm that usually extends into the deeper layers of the skin and it is larger than a papule.
Examples disease etiology?: |
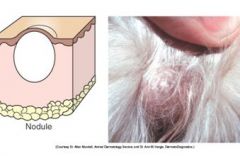
Examples disease etiology?: neoplasia, hyperplasia, inflammation, and deposition (e.g. calcium)
|
|
|

Vesicle (blister) is an intra- or subepidermal saccule filled with clear fluid.
Bulla is vesicle over 1 cm in size. Examples disease etiology?: (3 or 4) |
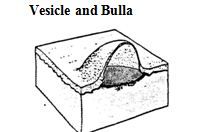
Examples disease etiology?: auto-immune, irritant, burn, and VIRAL etiology e.g. ves. stomatitis in horse, FMD
~can become pustules then erosion |
|
|
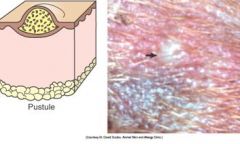
Pustule is an intra- or subepidermal saccule (vesicle) filled with pus (inflammatory cells). pustule can be sterile or infectious.
Examples disease etiology?: |
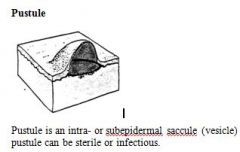
Examples disease etiology?: pemphigus, impetigo (superficial pyoderma)
|
|
|
|
Cyst is an epithelium-lined cavity containing fluid or sometimes semisolid material (keratin).
Examples disease etiology?: |
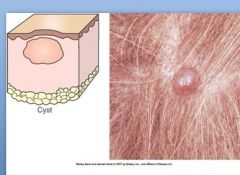
Cyst is an epithelium-lined cavity containing fluid or sometimes semisolid material (keratin).
Examples disease etiology?: various adnexal cysts!!!!!!!!! Actinic Keratosis – Solar Dermatitis, |
|
|
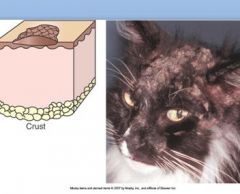
Crust is formed when dried exudate, serum, pus, blood, cells, scales, or medications adhere to surface of skin.
>disease 1° or 2° etiology? |
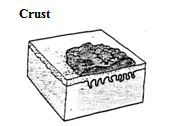
Primary: primary idiopathic seborrhea, zinc-responsive dermatosis
2°: pyoderma, chronic pruritic dermatoses |
|
|
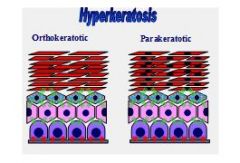
Hyperkeratosis (Orthokeratotic and Parakeratotic):
Hyperkeratosis is an increase in thickness of horny layer of epidermis. >disease 1° or 2° etiology? |
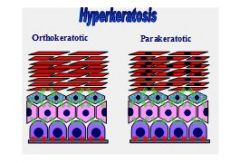
Hyperkeratosis (Orthokeratotic and Parakeratotic):
Primary: vitamin A-responsive dermatoses, primary idiopathic seborrhea, zinc-responsive dermatosis 2°: chronic inflammation |
|
|
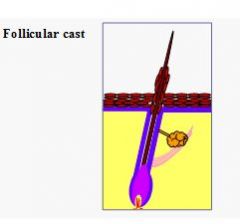
Follicular cast
Follicular cast is an accumulation and adherence of keratin and follicular material to hair shafts above follicular ostia. >disease 1° or 2° etiology? |
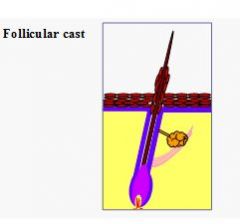
Follicular cast examples:
1°: vitamin A-responsive dermatoses, 1° idiopathic seborrhea, sebaceous adenitis 2°: demodicosis, dermatophytosis |
|
|
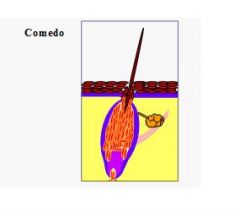
Comedo is dilated hair follicle filled with cornified cell and sebaceous material.
disease 1° or 2° etiology? |
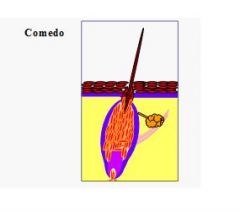
1°: Cushing’s dz., feline acne
2°: seborrhea, demodicosis, dermatophytosis, Actinic dermatosis, chin acne, Schnauzer comedo syndrome, Hyperadrenocorticism <--- b/c cause hyperkeratosis! and plugs up hair follicle!! |
|
|
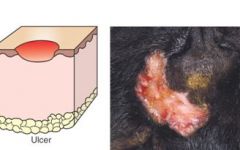
Ulcer
The epidermis is lost with exposure of underlying dermis. disease 1° or 2° etiology? |
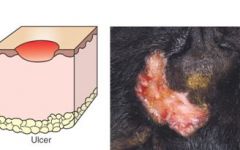
Ulcer epidermis & BM is lost with exposure of underlying dermis.
Disease 1° or 2° etiology? >burns, deep pyoderma in birds, and vasculitis (ischemia), feline herpes – ulcerative dermatitis in cats |
|
|

Epidermal collarette is spec. type of scale arranged in circular rim of loose keratin flakes or peeling keratin. IS OFTEN 2° TO ???
|
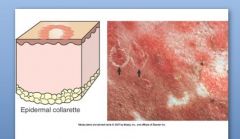
Epidermal collarette
Examples: 2° to ruptured vesicles or pustules, sfc. bacterial inf, fungal infections, Impetigo (superficial pustular dermatitis), Pityriasis rosea in pigs, insect bites |
|
|
|
Erosion is a partial loss of epidermis with intact basement membrane.
Examples: ? |
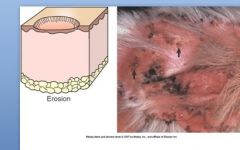
Examples: epidermal diseases (Pox viruses), Immune mediated dermatitis can cause erosions. e.g. deep (pemp.vulgaris) can lead to ulcer
Erosion can be secondary to vesciles/pustules |
|
|
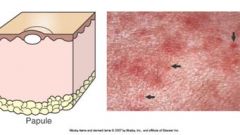
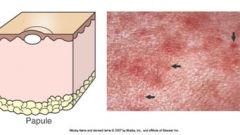
Papule is a small solid (palpable) raised spot on the skin up to 1 cm in diameter.
Plaque is a larger, flat-topped elevation. Examples disease etiology?: |
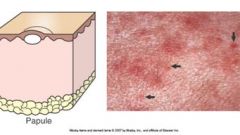
Examples disease etiology?: edema, infiltration of inflammatory cells (allergic dermatitis, superficial bacterial folliculitis, calcinosis circumscripta)
|
|
|
|
Intertriginous Inflammation ?
|
(skin against skin) - Intertriginous is a medical term used to define an area where two skin areas may touch or rub together.
..CHRONIC DERMATITIS, |
|

