![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Osteoarthritis |
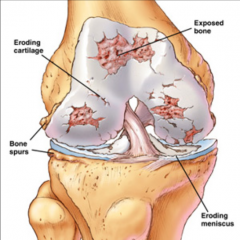
aka: DJD - Wear and tear - Most common type of arthritis. - Progressive disorder of the synovial joints (weight bearing) |
|
|
Septic Arthritis |
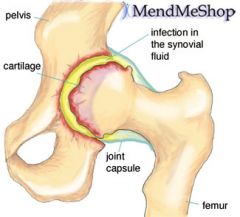
- Joint infection caused by bacteria or sometimes fungi. - Knee: most common - Children and Elders - Complete recovery |
|
|
Gout |
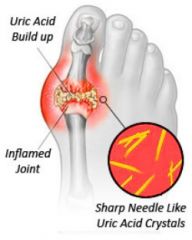
- Sever attack of pain, redness and tenderness in the joint - Men or women post menopause. - Urate crystals accumulate around the joint. |
|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) |
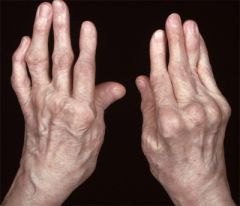
-Autoimmune Disease - More common in women (Bilateral) - Inflammation of the synovial membrane forming a pannus. |
|
|
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis |
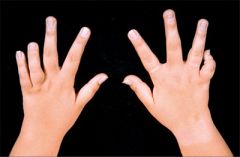
Pauciarticular: -4 joints. Knees. Eye inflammation and lymph node swelling. Polyarticular: +5 joints Systemic (stills): Joints and organs. |
|
|
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) |
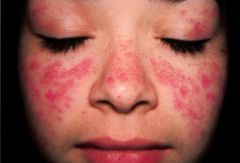
-ages 15-44 (females) -Low androgen levels -Renal failure is the most common cause of death. |
|
|
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) |
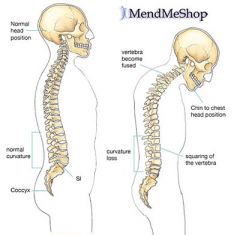
-Inflammatory disease where your spine fuses together. -Hunch forward posture. -Lower back and hip pain and stiffness. -Loss of lung capacity |
|
|
Reactive Arthritis (Formerly known as Reiter's Syndrome)
[Can't see. Can't Pee. Can't bend the Knee.] |
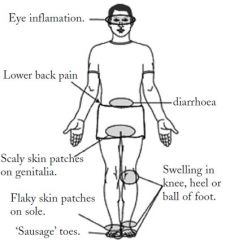
-Joint pain and swelling triggered by an infection elsewhere -Mostly Males -HLAB27 positive 90% -Chlamydia, most common cause |
|
|
Psoriatic Arthritis |
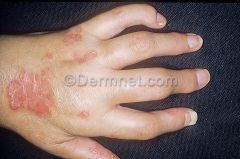
-HLAB27 positive with immune cases. -Mutilans: Most severe -Mild + slowly progressive. -Some psoriasis patients develop it. |
|
|
Enteropathic Arthritis |
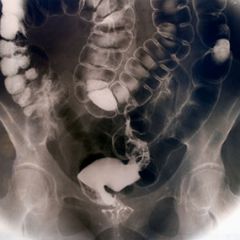
- Chronic - IBD (chrones + ulcerative colitis) -Inflammatory peripheral joints and abdomon. - Entire spine involved. -HLAB27 + Genetic link |
|
|
Cretinim (Neonatal Hypothyroidism) |
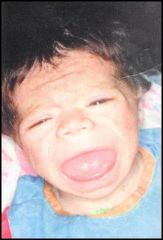
-Incomplete Development of the thyroid. -1 in 3000 births -Puffy face + thick protruding tongue -Slow mental and physical development |
|
|
Achondroplasia |
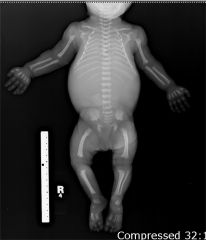
-Bone growth disorder: dwarfism -Abnormal hand appearance with space between the long and ring finger. -Bowed legs
|
|
|
Marfan Syndrom |
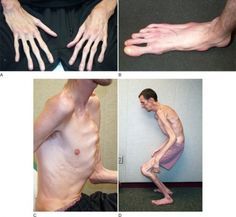
-Abnormality in the body's connective tissue (fibrillin) -Tall, slender with long extremities. -Chest deformities or scoliosis. |
|
|
Hyperkyphosis (Hunchback) |
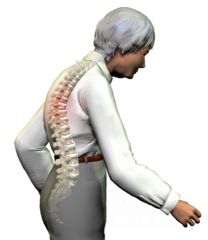
-Thoracic spine curve +40% -May cause ankylosing spondylitis or osteoporosis. -Physical therapy: Stretch Pecks, strengthen rhomboids |
|
|
Hyperlordosis |
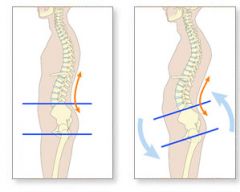
-Lumbar Spine -Postural compensation in obesity or pregnancy. -Lower back pain and inflammation of lower facets. |
|
|
Scoliosis |
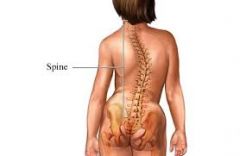
-Idiopathic in 80% -Classified as structural or postural (bend forward test) -High shoulder, rib or projection of scapula. |
|
|
Cleft Palate |
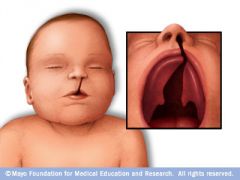
failure of the palatine process of the maxillary bone to unite during embryonic development. Treated with orthodontics and surgery. |
|
|
Spondylolysis |
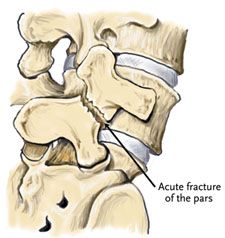
-L5 affected in 90% of cases. -Occurs in 2-6% of the population. -Diagnosed at 15 -Leads to stress fractures or spondylolisthesis. |
|
|
Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) |
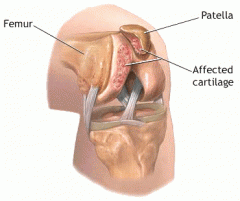
-Breakdown of the cartilage that lines the underside of the kneecap. -Movie theatre sign -Normal x-rays -Physical therapy |
|
|
Dislocation and Subluxation |
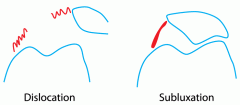
-Displacement of 2 bones at the joint. -Usually MVA or Sport -Misshapen Joint -Swelling -Discolouration -Loss of function and pain. |
|
|
Sprain |
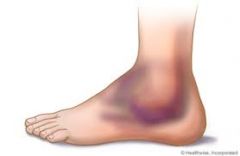
- Joint trauma that stretches or tears the ligaments. - 3 Grades - PRISH - Treatment: RICE |
|
|
Osteopenia |
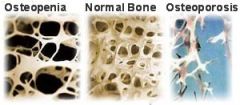
- Mild thinning of bone mass. - Sigh of Osteoporosis - Bone density test T-Score 0 Normal, 1-2.5 Osteopenia, Less is Osteoporosis. |
|
|
Osteogenesis Imperfecta [Brittle Bone Disease] |
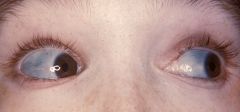
- Disorder of connective tissue caused by mutilation in the gene for collagen. - Type I and II |
|
|
Osteogenesis Imperfecta [Brittle Bone Disease] Type I |
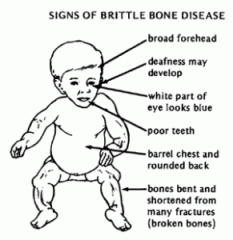
- Most common - Blue scalar, hearing problems, teeth - Autosomal dominant |
|
|
Osteogenesis Imperfecta [Brittle Bone Disease] Type II |
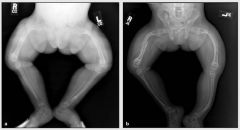
- Lethal - Die due to crushing of bones at birth. - Sclera are blue. - Autosomal recessive |
|
|
Acute Osteomyelitis |
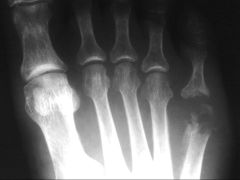
- Bacterial (open wound) - local or spread via blood stream. - Staphylococcus aureus characteristics allow it into bone. |
|
|
Chronic Osteomyelitis |
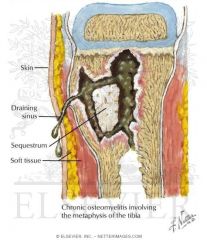
- From and acute infection that lasts longer than 6-8 weeks. - Persists or reoccurs. - Minimal symptoms - E.coli, pseudomas and staph epidermis common.
|
|
|
Tuberculous Osteomyelitis |
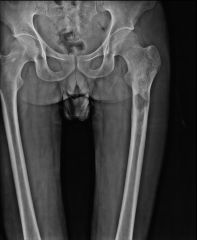
- Caused by spread of primary infection. - In the thoracic or lumbar spine - called Pott Disease. -Psoas abscess often associated with bone infection. |
|
|
Paget's Disease [Osteitis Deformans] |
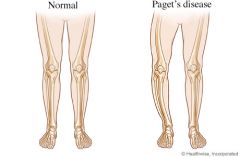
-Progressive bone disease -Excessive bone remodelling -Pelvis, spine, skull or leg bones. -Men more likely |
|
|
Osteoporosis |
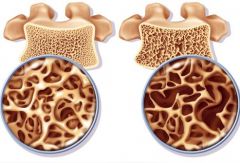
-Low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue. -Increased bone fragility and risk of fracture. -Spine, hips and wrist -peek bone mass: 16 women and 20 males. Loss: Post-30 |
|
|
Osteomalacia |
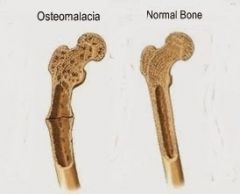
-Softening of adult bone due to Vit. D deficiency. -Fracture happens with very little injury. -Muscle weakness. |
|
|
Rickets |
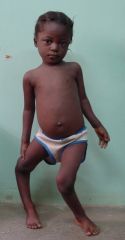
- Childhood disease - Lack of Vit. D - Bone pain and tenderness. -Pelvic/Spinal/Dental deformities + bowleged |
|
|
Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease |
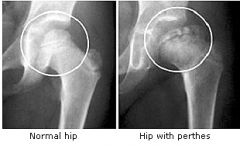
- Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the capital femoral epiphysis (growth plate) of the femoral head. - Insidious onset. Child does not complain. - 1-1200 children - Hip/Groin pain, referred to thigh. |
|
|
Kienbock's disease |
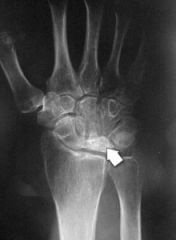
- Avascular necrosis of the carpal lunate. - age 20-40 - Pain and disability - Treated surgically |
|
|
Scheuermann's Disease |
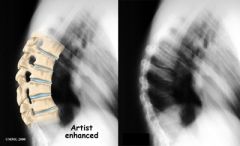
- Osteochondrosis of thoracic vertebrae with associated vertebral wedging (compressed nerve.) - Ages 13-17 - Males more than females
|
|
|
Osgood-Schlatter's disease |
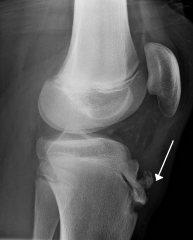
- Common cause of knee pain. - Micro-fractures in area where the patellar tendon inserts into the tibial tubercle. - Bony bump on the tibial tuberosity. |
|
|
Sever's Disease |
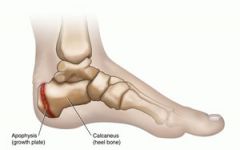
- AKA:Calcaneal Apophysitis - Inflammation in the growth plate of children. - Heel - Due to repetitive stress |
|
|
Osteochondritis Dissecans
|
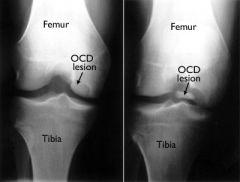
- Bone/cartilage inflammation. - Loss of blood supply to an area of bone beneath the surface of a joint. *Knee* common |
|
|
Benign Bone Tumours |
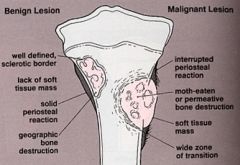
- Well-demarkated edges. - Sharpey's fibers attach periosteum to bone. Very painful. - Ex: Osteoma... |
|
|
Osteochondroma [Exostosis] |
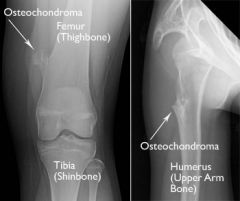
- Most common benign skeletal tumour (20%) - Can be sessile (flat) or pedunculate (mushroom shaped.) and attached to a bone by a bony stalk. |
|
|
Osteoid Osteoma [Osteoma] |
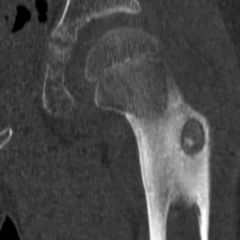
- Small, painful lesion of bone composed go osseous tissue and surrounded by a halo of reactive bone formation. - Compact or spongy bone. - Found on the surface of long bone, flat bone or skull. |
|
|
Malignant Bone Tumours |
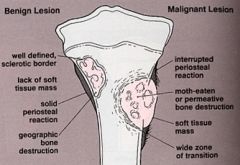
- Rare before age 10 - Grow rapidly - Extend beyond bone - Ill-defined edges
|
|
|
Osteosarcoma |
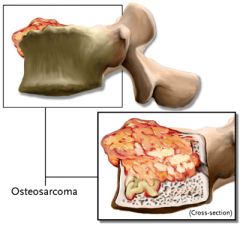
- Most common primary malignant bone tumour (20%) - Due to Paget's or radiation exposure. - Spreds to the lymph nodes or local soft tissues. - Deep local pain - Night time awakening |
|
|
Chondrosarcoma |
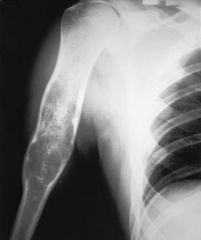
- 2nd most common primary malignant bone tumour. - Cartilaginous in origin. - Knee, pelvis, shoulder, femer - After age 40 - Usually painless. |
|
|
Ewing Sarcoma |
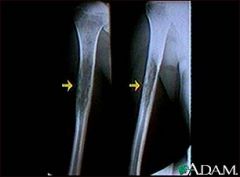
- A group of small, round cell, undifferentiated tumours thought to be of neural crest origin. - Early teen years - Metastasizes to the lungs. |

