![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
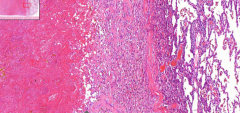
- Lung tissue
- Lots of RBC in alveoli = Congested area - Lot of pink eosinophilic substance - V-shaped granulation ETIOLOGY |
8. Hemorrhagic lung infarction - hemorrhagic necrosis
Etiology: - Pulmonary artery embolism |
|
- Lung tissue
- Black pigment (all lung slides) - Fibrotic nodules - Peripheral emphysema - Distended alveoli ETIOLOGY |
39. Anthracosis and silicosis of lung
- Black is carbon = Anthracosis - Fibrotic nodules are silica eaten by m.phages - create fibrosis. Center hyalinosis. Around granulation tissue - Silica not visible in LM - Distended alveoli; cor pulmonale ETIOLOGY: Anthracosis: Inhalation of carbon dust Silicosis: Inhalation of silica dust (1-4um size=perfect). M.phages does not have enzymes to destroy |
|
- Lung tissue
- Violet calcification in capillary walls of alveoli septa ETIOLOGY |
42. Metastatic calcification of lung
ETIOLOGY: Hypercalcemia with calcium deposits in: - Chronic renal failure - Massive osteolysis due to carcinoma - Primary hyperparathyroidism due to adenoma |
|
- Lung tissue
- Large embolus stuck - organized - Small thrombus are fresh - Many stages of recanalization - Postembolytic bridges - Increased fibrosis of vessel wall ETIOLOGY |
58. Successive pulmonary embolism
ETIOLOGY Pulmonary emboli released from: - DVT - Mural thrombi from right side of heart - Thrombi of jugular veins |
|
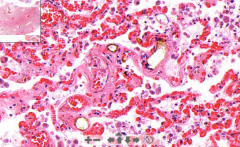
- Lung tissue
- Dilated caps with nothing inside - Dark color rim around fat - RBC congestion in septa ETIOLOGY |
63. Fat embolism of lung
- Empthy spaces is fat removed in fixation - Black rim is fat reacted with formalin. Artifact but proof of fat embolism ETIOLOGY - Fracture of bone, fat from bone marrow - Crash injury - Extensive burns |
|
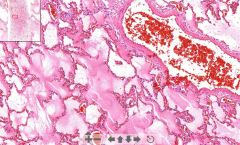
- Lung tissue
- Pinkish edematous stuff inside alveoli - RBC congestion in septa ETIOLOGY |
64. Pulmonary edema
ETIOLOGY - Increase hydrostatic pressure (LV failure, mitral valve disease) - Increase capillary permeability (infections) - Increaes in altitude (Rapid change change intravascular pressure |
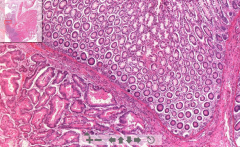
|
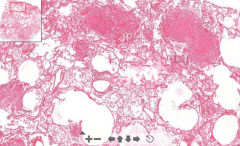
- Lung tissue
- Small pink nodules (necrotic) -- These are accumulation of histiocytes with necrotic center - Langhans cells ETIOLOGY |
98. Miliary tuberculosis of lung
ETIOLOGY - Hematogenous spread of MTB --> Cause granulomatous inflammation = Accumulation of histiocytes with necrotic center - Histiocyte is a tissue macrophage or dendritic cell |
|
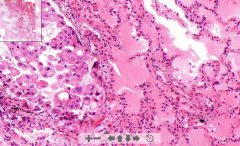
- Lung tissue
- Alveoli filled by edema - Dilated lymph vessels with neoplastic "signet cells" -- Nuclei in periphery and filling lumen. ETIOLOGY |
153. Carcinomatous lymphangiopathy of lungs
- Edema is due blockage of lymph channels by the signet cells ETIOLOGY: - Metastatic carcinoma ells originate from breast of stomach CARCINOMA = Invasive malignant tumor derived from epithelial tissue that tends to metastasize |
|
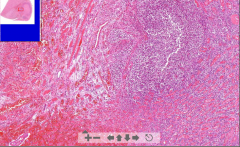
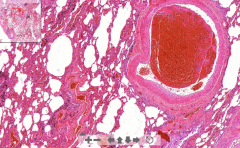
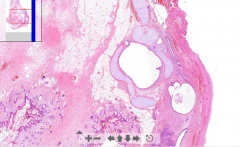
- Kidney tissue
- Wedge-shaped necrosis - Lots of lymphatic infiltration = zone of demarcation - Kidney tubules lost nucleus - very eosinophilic - only see outline of structures - Zone of hyperemia ETIOLOGY |
1. Kidney infarction
ETIOLOGY - Emboli from heart valve, atheromatous plaque or previous MI |
|
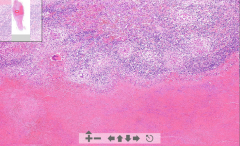
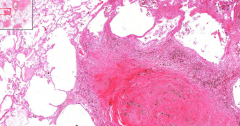
- Normal adrenal gland tissue (z. glomerulosa, fasciculata, reticularis)
- Large area of homogenous eosinophilic substance - Large lymphatic infiltration - Langhans cells (horse shoe) ETIOLOGY |
10. Caseous necrosis of adrenal gland (tuberculosis)
- Homogenous substance is the caseous necrosis ETIOLOGY - Complication of mycobacterium tuberculosis |
|
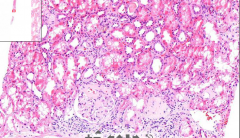
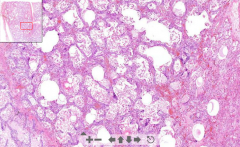
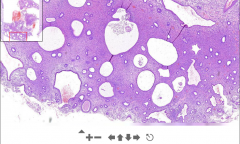
- Kidney tissue (thin streak)
- Some pinkish material deposited in glomeruli - Thicker walls of glomeruli vessels ETIOLOGY |
29. Amyloidosis of kidney
- Pinkish material = Amyloid deposition AMYLOID = Group of pathological proteins. ETIOLOGY - Primary amyloidosis = Comlication of too high production of monoclonal light chain antibodies (plasmacytoma). They get deposited - Secondary amyloidosis = Chronic inflammatory diseases. Acute phase proteins produced --> cleaved by m.phages --> Produce amyloid protein A --> Deposited |
|
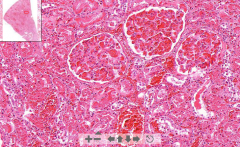
- Kidney tissue & large glomeruli
- Pink homogenous thrombi in glomeruli ETIOLOGY |
62. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
ETIOLOGY - Widespread microthrombi causing necrosis - Consumption of platelets & clotting factors causing bleeding (consumptive coagulopathy) Caused by: - Injury (crush sy) - Obstretic complication (birth) - Infections by gram- - Neoplasms |
|
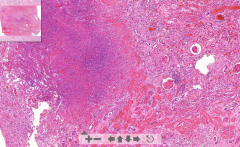
- Kidney tissue
- Abscesses in cortex - Scattered neutrophils - Bacterial basophilic thrombi in glomerulus (bacterial colony) - black ETIOLOGY |
85. Hematogenous abscess of kidney
ETIOLOGY - Ascending UTI - Hematogenous bacterial spread from heart (infective endocarditis) |
|
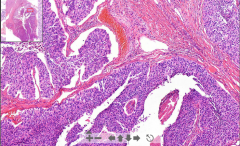
- Kidney tissue seen
- > 7 layers of urothelium - Fibrovascular core with neoplastic epithelium with hyperchromasia (very purple color) - Glomeruli are hyalinized (pink fibrotic circles) - Kidney tubule dilatation ETIOLOGY |
144. Papillary carcinoma of renal pelvis
- A transitional cell carcinoma. All the purple stuff!! Bladder, renal pelvis and ureters. ETIOLOGY - Chemical carcinogens - Smoking - Drugs "End stage of kidney" --> "Kidney thyroidization" |
|
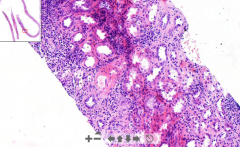
- Remnants of kidney tissue
3 areas: 1. Thrombosis & cortical necrosis 2. Lymphatic infiltrations 3. Narrow arteries, ischemia ETIOLOGY |
181. Acute rejection of transplanted kidney
- We find normal kidney tissue - We find 3 stages: 1. Hyperacute rejection : Thrombosis and cortical fibrinous necrosis (seen as pale pink necrotic areas) 2. Acute: The lymphatic infiltration 3. Chronic: Narrowing of the vessel walls and ischemia of the graft ETIOLOGY - Transplanted kidney |
|
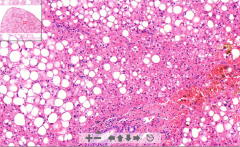
- Liver sinusoids
- Surrounded by A LOT of fat sinusoids, fat removed by fixation ETIOLOGY |
24. Liver steatosis
ETIOLOGY - Hypoxia - Overeating - Ingestion of toxic substances (alcohol) |
|
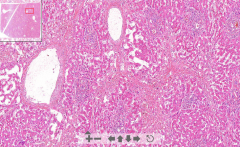
- Liver tissue
- Central vein dilatation - Steatosis around central vein - Low hepatocytes - Fibrosis and fibroblast proliferation between liver lobules in congested areas due to hypoxia ETIOLOGY |
53. Chronic liver congestion
ETIOLOGY - RV failure - Thrombotic occlusion of hepatic veins |
|
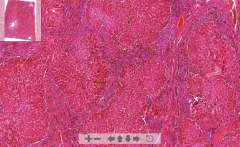
- Liver lobar structure lost
- Nodular structures - Rusty pigment of hepatocytes - Fibrous tissue with hemosiderin between nodules & bile ducts (normally no hemosiderin in liver) Macro: Rusty liver ETIOLOGY |
93. Pigmented liver cirrhosis
ETIOLOGY - Hemochromatosis: Heriditary disease with abnormal absorption of iron from gut - stored in liver, pancreas heart. = "Bronze diabetes" |
|
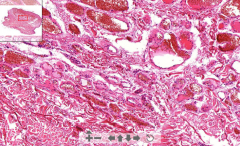
- LOTS of RBC in lots of septa
- Dilated blood vessels w/endothelium - Liver or skin tissue - Some really weird shaped cells in center (bottom left) ETIOLOGY |
131. Cavernous hemangioma = benign vascular tumor
ETIOLOGY - Benign tumor arising from blood vessels. Affect skin or internal organs |
|
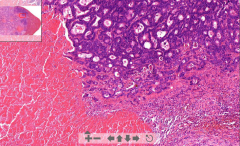
- Remnants of liver sinusoids
- Very purple liver parenchyma with irregular tubules - Tubules contain pinkish substance of necrosis ETIOLOGY |
154. Metastasis of adenocarcinoma to liver
Irregular tubules are nodes of spreaded tumor cells with pinkish necrotized tissue in the middle ETIOLOGY - Metastasis of cancer cells spreading via portal vein from large bowel, pancreas etc. |
|
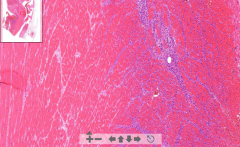
- Cardiac muscle tissue
- Eosinophilic necrotic area with no nuclei - Zone of demarcation = blue lymphocytes - See thrombus in endocardium (mural) - See occluded coronary artery ETIOLOGY |
3. Myocardial infarct
ETIOLOGY - Occlusion of coronary artery by thrombus Thrombus consist of: - RBC - Platelets - Fibrin |
|
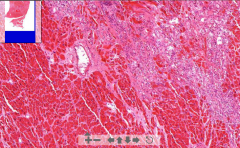
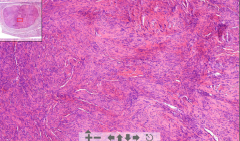
- Irregular low cellular pink fibrotic tissue
- +/- hyalinization ETIOLOGY |
4. Scar after myocardial infarction
ETIOLOGY - Post infarction. - Granulation tissue of fibroblasts and capillaries grow in => Fibrotic scar NB! Aneurism may occur. Lower CO of LV Also trichrome stain: Scar = green |
|
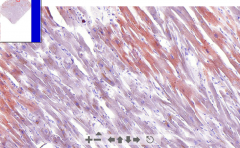
- Cardiac muscle tissue
- Organge droplets within cardiomyocytes (in sarcoplasm) ETIOLOGY |
23. Myocardial steatosis
- Microvesicular steatosis, sudan III (red) stains vesicles - "Tiger heart" macroscopically ETIOLOGY - Hypoxia - Sepsis ==> Toxic damage leads to fatty change. |
|
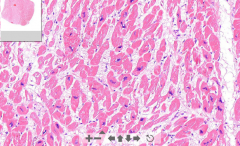
- Large irregular pleomorphic dark myocardial nucleus
- Nuclei are MUCH larger than usual ( and surrounding endothelial and fibrolast cells) ETIOLOGY |
65. Cardiac hypertrophy
ETIOLOGY LV hypertrophy (normal thickn = 12mm) - Increase in systemic BP - Aortic stenosis RV hypertrophy (normal thickn. = 4 mm) - Pulmonary hypertension - lung diseases / fibrosis, emphysema, mitral valve dis. NB! Know it grossly not by heart size but weight. Normal weight = 350-400g Hypertrophic = 400-650 g |
|
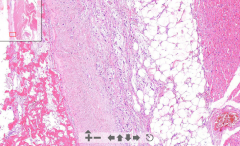
- Heart muscle tissue
- Epicardial side we see "flames" - This is fibrin tissue (pericardium removed) - Capillary ingrowth and fibroblasts ETIOLOGY |
71. Fibrinous pericarditis
ETIOLOGY Complication of: - Uremia - MI - Heart surgery (most common) Increases the permeability of capillaries for fibrinogen which is deposited on surface of heart! "BREAD AND BUTTER APPEARANCE" |
|
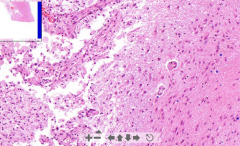
- Left = Necrotic area w/ guitter cells (m.phages eating myelin)
- Right = Normal brain tissue - At border there is gemistocytes (scar cells) ETIOLOGY |
7. Cerebral infarction / Brain malacia
ETIOLOGY - Occlusion of cerebral artery due to thrombus or thrombemboli Create a post-malaic pseudocyst (no lining!) |
|
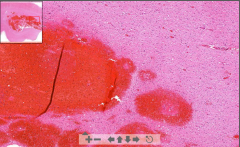
- Fresh RBC in brain = Bleeding (since no cyst!)
- Inside we see some eosinophilic zone = Necrosis - Dilated veins close to bleeding - Edema of surrounding tissue with vacuolization ETIOLOGY |
55. Intracerebral hemorrhage
ETIOLOGY - Arterial hypertension - Vascular malfunction - Neoplasm - Bleeding disorders - Stroke(?) |
|
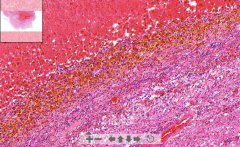
- A pseudocyst inside brain
- Wall is of rusty pigment - Clean outer surface - Edema of surrounding tissue |
56. Post hemorrhagic pseudocyst
Pseudocyst created after resorption of hematoma, lined with: - Hemosiderin deposition is reddish brown pigment - Siderophages - Hematoidin crystals - Guitter cells - Gemistocytes |
|
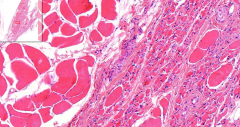
- Mixed normal and atrophic skeletal muscle
- Loss of sarcoplasm; increase of nuclei ETIOLOGY |
197. Neurogenic atrophy of skeletal muscle
- Missing cells are replaced by adipose tissue ETIOLOGY - Lack of nerve stimulation (motor neuron, peripheral axon) |
|
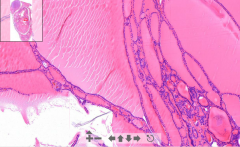
- Varied size of follicles
- Regression (darker areas) = Dystrophic calcification (it wastes away) ETIOLOGY |
146. Nodular goitre of thyroid gland
ETIOLOGY - Iodine deficiency - Hashimotos thyroiditis - Defects in thyroid hormone synthesis. THS increased but T3,T4 decreased . Vicious cycle |
|
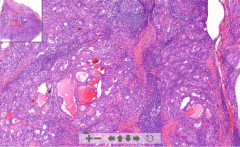
- Almost no follicles left - looks like a lymph node with some thyroid follicles
- A lot of lymphatic cells with germinal centers ETIOLOGY |
179. Hashimoto´s thyroiditis
ETIOLOGY - Autoimmune disease, autoantibodies against: -- Thyroglobulin -- TSH receptors |
|
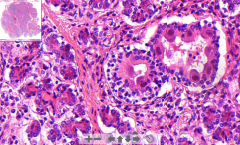
- Infected cells by viral particles in ducts
- Increased "basophility" - Sereous acini are intact - Lymphatic infiltration ETIOLOGY |
26B. Cytomegalovirus of parotid gland
ETIOLOGY - Herpetic virus transferred usually mother-baby - Affects immunocompromized patients Cyto = Cell Megalo = Enlargement |
|
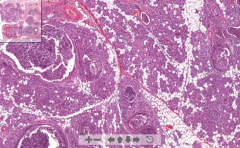
- See cavities of abscess with WBC & pus
- Exudate destroy all duct walls - Leukocytes in ducts - See some sereous acini ETIOLOGY |
83. Acute suppurative sialadenitis (parotid gland abscess)
ETIOLOGY - Infection from staph & streptococci |
|
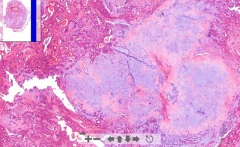
- Ducts with cuboidal cells surrounded by myoep. cells
- Large white areas looking like cartilage - Great variety of structures (pleiomorphic) |
149. Pleiomorphic adenoma of parotid gland
Tumor of parotid gland. - White areas are compact masses of myoepithelial cells, with myxoid stroma (mucus containing) stellate cells - looking like hyaline cartilage |
|
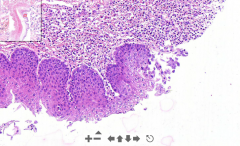
- Esophagus slide
- Muscularis mucosae, muscularis externa, mucosa & submucosa - Stratified epithelium of esophagus - BUT this stops - at edges we see large eosinophilic inclusions of "halo"-cells - See ulcers without any stratified epithelium ETIOLOGY |
26a. Herpetic esophagitis
ETIOLOGY - The halo cells are viral inclusions of herpes simplex 1 virus - They travels in nerve and stay in nerve ganglion. -- Stay latent and replicate in stress, menstruation and infections. Travels ==> Coald soars |
|
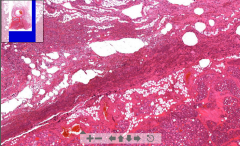
- See carotid artery
- See thyroid gland in bottom - See a lot of neutrophils in interstitial tissue and between adipose tissue ETIOLOGY |
74. Cellulitis of neck / Phlegmona
ETIOLOGY - Haemolytic streptococci - release enzymes that cause spreading of inflammation to within the tissue (streptokinase, hyaluronidase) - Starts from mouth floor in e.g. tooth decay --> Spread to neck |
|
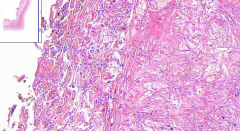
- Its a esophagus
- Loss of epithelium - Replaced with a pseudomembrane - We see there is candida below in 2 forms: 1. Pseudohyphae - Long filaments 2. Blastospores - Ovoid ETIOLOGY |
113. Candida esophagitis
Candida in gram stain if blue = Active infection ETIOLOGY: - Caused by yeast candida albicans, in immunocompromized patients. - Opportunistic infection PSEUDOMEMBRANE - Fibrin - Necrotic ep. - Neutrophils - Bacteria (the pseudohyphae & blastospores) |
|
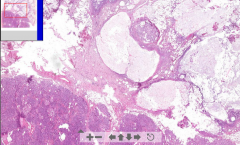
- Normal pancreatic tissue (islets of langerhans, acini) is half of the slide
The rest is messed up: - White = Adipose tissue = liquefactive necrosis - Pink = Necrosis - Dark pink = Zome of demarcation, border of lymphocytes ETIOLOGY |
6. Acute pancreatic liquefactive necrosis
ETIOLOGY: - Internal activation of pancreatic enzymes due to e.g. biliary / vaters ampulla obstruction --> Reflux - Alcohol abuse - toxic to acinar cells - Ischemia - Abdominal trauma |
|
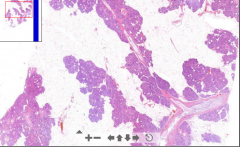
- Pancreatic tissue islands with LOADS of adipose tissue
- Pancreatic parenchyma lost - Only exocrine part is affected. Islets of Langerhans are normal ETIOLOGY |
11. Lipomatous atrophy of pancreas
ETIOLOGY - Chronic ischemia due to atherosclerosis of supplying vessels - Adipose tissue cause pancreatic enlargement |
|
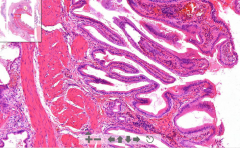
- Gall bladder with mixed smooth muscle & CT
- Glands are stained very dark - Fibrosis of the galbladder wall - Some inflammatory infiltrate ETIOLOGY |
79. Chronic cholecystitis
ETIOLOGY - From acute cholecystitis - From gallstones: Irritate mucosa chronically - fibrous production - lead to dysplastic changes - risk of carcinoma |
|
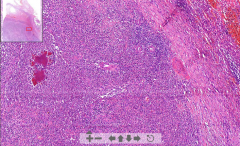
- Area full of neutrophils
- Abscesses with bacterial colonies = strong pink - Eosinophilic ring around colonies ETIOLOGY |
108. Actinomycosis of oral cavity
ETIOLOGY - Caused by Actinomyces israelii. Usually harmless but may enter tissue in trauma, surgery, tooth decay - Around: Soft tissue. Not sure from where |
|
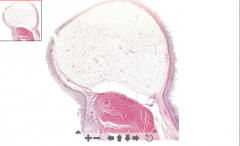
- Huge nodule(s) of adipose tissue in submucosa
ETIOLOGY |
133. Lipoma of intestine
ETIOLOGY: - Benign tumor, may develop anywhere Lipoma = White fat Hibernoma = Brown fat |
|
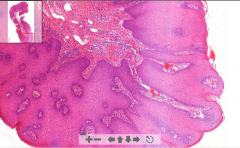
- Fibrovascular core
- Neoplastic epithelium (!!) Squamous cell papilloma - Chronic inflammation in stroma - Koilocytes seen in stroma (round with halo-rim) ETIOLOGY |
143. Condyloma acuminatum - anal region = benign papilloma
ETIOLOGY - HPV type 6 / 11 (human papilloma virus) Grossly it grows like a cauliflower |
|
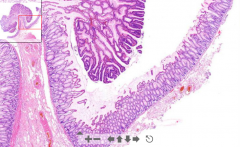
- Stalk lined with normal epithelium
- See very dark dysplastic epithelium, dark nucleis, pseudostratification - Low goblet cells, elongated tubular glands ETIOLOGY |
145. Tubular adenoma of colon / colonic adenomatous polyp
ETIOLOGY - Lesion growing from mucosa into lumen of large intestine 1. Non-neoplastic polyp 2. Neoplastic polyp (true adenoma) Blood in stools. |
|
- Normal colon partly
- Very irregular glandular cells and tubules other places - Mitotic activity and invade smooth muscle layers ETIOLOGY |
157. Colorectal cander - adenocarcinoma
ETIOLOGY - Common tumor in modern world due to a lot of red meat and low fibers - Also familial adenomatous polyposis NB! - Adenoma: Non-invading - Carcinoma: Invading |
|
- Dilated cystic endometrial glands
- At smooth surface there is columnar epithelium - Light cells in cytoplasm (glycogen storage) "SWISS CHEESE" ETIOLOGY |
49. Cystic glandular endometrial hyperplasia
ETIOLOGY Increased levels of estrogen - Premenopause - Ovulation - Tumors - Estrogen replacement therapy |
|
- Few cm big nodule
- Consist of long spindle shaped smooth muscle cells - Eosinophilic and wavy / fascicular pattern - May see regressive changes like hyalinization, myxomatous change, dystrophic calcification ETIOLOGY |
129. Leiomyoma of uterus
ETIOLOGY - Benign smooth muscle tumor - Hormone dependent: - Enlarge during pregnancy Characterized as: 1. Intramural - in myometrium 2. Submucosal 3. Subserosal |
|
All premordial germ cell layers present:
Ectoderm: Skin, nervous tissue, sebaceous glands Mesoderm: Bone, cartilage, smooth muscles, adipose t. Endoderm: Cysts lined with respiratory or digestive ep ETIOLOGY |
170. Ovarian teratoma
ETIOLOGY: - Tumour from primordal germ cells |
|
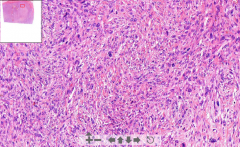
- Smooth muscle tumor
- Spindle shaped irregular fishmeat structure - Hyperchromasia nuclei - enlarged - All pink is tumor ETIOLOGY |
185. Leiomyosacroma of uterus (smooth muscle sarcoma)
ETIOLOGY - Malignant tumor of smooth muscle affecting 1. Muscular walls of hollow organs 2. Smooth muscles of other structures (vessels, dermis) |
|
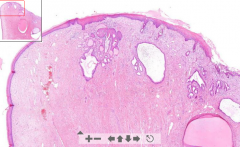
- Cysts seen in transition zone of uterine cervix (Nabothian cysts)
- They should not be there! Should be in endocervix - ETIOLOGY |
70. Squamous metaplasia of uterine cervix
ETIOLOGY - Endocervix (columnar ep.) may be pulled down during delivery, which is exposed to acidic environment of vagina and changing into stratified squamous ep. (metaplastic change) Exocervix is all that protrude into vagina. Glands usually above this! |
|
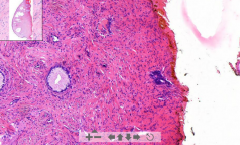
- Stratified squamous ectocervix
- Not normal endocervix: No glycogen, not normal stratification, something weird with the glands, large hyperchromatic nuclei, mitotic activities ETIOLOGY |
182. Dysplasia of uterine cervix
ETIOLOGY - HPV types 16 & 18 - Smoking - Early 1st intercourse - Increased number of sexual partners NB! Also colonize the glands - but this is not invasive - this is since glands are connected to surface! |
|

- Red cells = Superficial cells - red due to estrogen
- Green cells = Intermediate cells - green due to progesterone |
184. Normal cervical cytology
- Smear stained according to papanicolau - Done to identify early stages of cervical dysplasia |
|
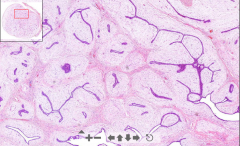
- Round slide with "hieroglyfs" inside
1. Slitlike = Intracanalicular spaces composed of fibrous stroma 2. Tubular epithelial spaces surrounded by stroma = Glandular ETIOLOGY |
150. Fibroadenoma of breast
ETIOLOGY - Common benign tumor of breast |
|
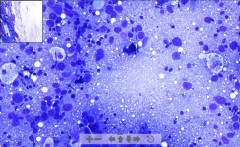
- FNAC (fine needle aspiration cytology) of a cancerous lesion
Blue dots: - Pleomorphic cells - High nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio - Hyperchromatic nuclei |
183. FNAC of breast carcinoma
|
|
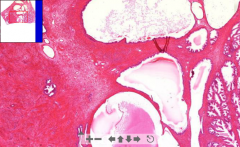
- Some normal fibromuscular stroma of prostate gland seen
Otherwise: - Huge cystic glands with prostatic concretions inside - Large increase of stroma. - Hyperplasia - nodules seen in hyperplastic tissue ETIOLOGY |
120. Nodular hyperplasia of prostate
ETIOLOGY - Happen usually in periphery of prostate - Caused by hormone imbalance (incr. estrogen, decr. testosterone) - Estrogen increase expression of DHT receptors (dihydrotestosterone) which stimulate prostate tissue growth |
|
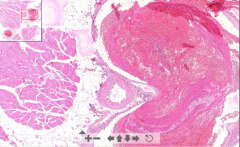
- Muscle of leg
- Veins completely filled by thrombus - No signs of recanalization = FRESH |
57. DVT / phleothrombosis
Consist of: - Platelets - Fibrin - RBC´s - WBC´s - Without WBC = Red thrombus |
|
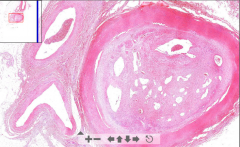
- Artery occluded by fibrous tissue
- 2ndary channels in thrombus = Recanalization (Start of recanalization --> Granulation tissue trying to "heal" the thrombus - will reestablish blood flow) - Granulation tissue and siderophages |
60. Recanalized thrombus
1. Thrombus irritate endothelium 2. Endothelium produce fibroblasts - create granulation tissue 3. A lot of small vessels and channels produced - fuse together - large lumen 4. Recanalization - reestablish blood flow but not completely 5. FIbrous scar |
|
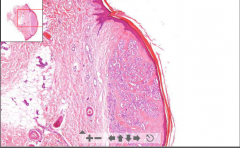
- Lesion of a "strawberry nevus" under epidermis
- Closely packed capillaries with endothelium & RBC in lumen ETIOLOGY |
130. Capillary hemangioma
ETIOLOY - Benign tumor arising from blood vessels - very common |
|
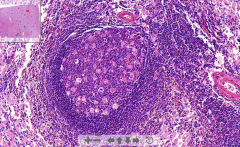
- Normal spleen tissue seen: White and red pulp
- Gaucher cells seen (macrophages) - eccentric nuclei due to accumulation of glucocerebroside - RBC´s & lymphocytes = Spleen ETIOLOGY |
26. Gaucher´s disease
ETIOLOGY: - Familiar disorder of lipid metabolism - Storage of pathogenic lipids like glucocerebroside in macrophages (gaucher cells) |
|
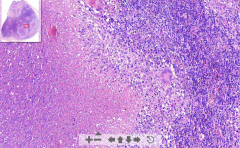
- Large areas of caseous necrosis
- Large blue areas as well (WBC of lymph node) - Langhans cells around necrotic areas! (fused histiocytes / m.phages) ETIOLOGY |
97. Tuberculous lymphadenitis
ETIOLOGY - Mycobacterium tuberculosis - to periphery of lungs - Transmitted via lymphatics to lymph nodes |
|
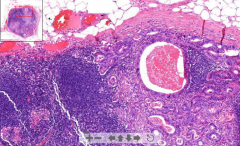
- Lymph node (fat around, capsule)
- Neoplastic tubules with irregular shaped glands with dark nuclei - Necrotic substances in middle of tubules ETIOLOGY |
152. Metastatic adenocarcinoma to lymph node
ETIOLOGY - Metastasis of carcinoma Breast --> Auxilary lymph nodes Intestine --> Mesenteric lymph nodes |
|
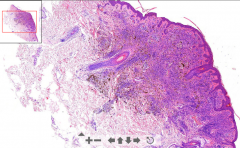
- Dermal nevus (føflekk)
- Melanin seen above nevus - Melanocytes in deeper layers produce melanin - Cluster of melanocytes = brownish ETIOLOGY |
35. Pigmented nevus (mole)
ETIOLOGY: - Benign accumulation of melanocytes |
|
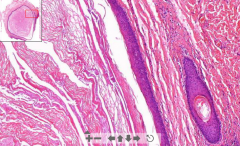
- Cystic cavity lined by stratified squamous epithelium
- Keratin in lamellar arrangement ETIOLOGY |
47. Epidermoid cyst of skin
ETIOLOGY: - Cystic dilatation of hair follicle infundibulim - due to occlusion by a keratinous plug |
|
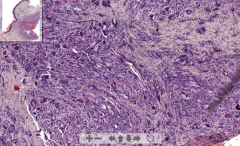
- Big granuloma
- Macrophages trying to eat foreign material - FIbrous tissue around - Macrophages fused = Giant cells ETIOLOGY |
111. Foreign body granuloma
ETIOLOGY: - Presence of something foreign in tissue (glass, dust, thread) - Nonspecific inflammation |
|
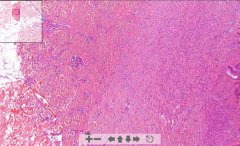
- Storiform architecture in dermis
- Spindle-shaped fibroblasts - Collagen fibers deposition - Pigmentation with acantosis - Thick epidermis ETIOLOGY |
125. Dermatofibroma
ETIOLOGY - Benign fibrous lesion of skin - Often pigmented |
|
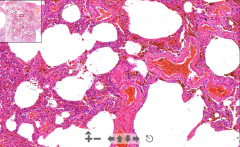
- Lung tissue
- Lots of red siderophages in septa (eat hemosiderin form RBC) - Thus rusty decoloration - Thickened wall of alveolar septa ETIOLOGY |
54. Chronic pulmonary congestion
ETIOLOGY - RV failure - Thrombotic occlusion of hepatic veins |

