![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
143 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Most common hematologic problem seen in advanced HIV |
Leukopenia |
|
|
Formula for ANC |
(WBC - segmenters) / 1000 |
|
|
2 causes of neutropenia |
Inadequate/Ineffective granulopoeisis Accelerated removal/destruction |
|
|
4 drugs which can cause inadequate granulopoeisis |
Dose-related: chemotherapy Idiosyncratic: PTU, chloramphenicol, Phenylbutazine, Sulfa, Aminopyrine |
|
|
2 kinds of marrow in neutropenia |
Hypercellular - functioning marrow Hypocellular - dry tap on BMA |
|
|
Leukocytosis associated with myeloproliferative |
Basophilic |
|
|
Leukocytosis associated with viral infectiona |
Viral |
|
|
2 morphologic features of leukocytosis |
Toxic granules - azurophilic Dohle bodies - sky blue cytoplasmic puddles |
|
|
Primary lymphatic follicles enlarge and are transformed into germinal centers Follicular hyperplasia What condition? |
Lymphadenitis |
|
|
Non-tender swelling of lymph node Common in inguinal and axillary nodes What condition? |
Chronic lymphadenitis |
|
|
3 morphologc changes seen in chronic lymphadenitis |
Follicular hyperplasia Paracortical hyperplasia Sinis histiocytosis |
|
|
3 cells seen in follicular hyperplasia of chronic lymphadenitis |
Centroblasts - proliferating blast-like B cell Centrocytes - B cells with cleaved nuclear contours Tingible-body macrophages - phagocytic macrophages containing nuclear debris |
|
|
Trace pathway of WBC maturation |
Naive cell > Mantle cell > Germinal center cells/marginal zone |
|
|
3 types of neoplastic WBCs |
Lymphoid neoplasms - Bcell, Tcell, NKcell Myeloid neoplasms - early hematopoietic progenitors Histiocytes |
|
|
Most common cancer of children Neoplasts of immature B or T cells |
ALL |
|
|
3 differences between myelo and lymphoblasts |
Condensed chromatin Less conspicuous nucleoli Smaller cytoplasm |
|
|
3 morphologic features of ALL |
Hypercellular marrow with lymphoblasts MPO neg CALLA pos |
|
|
Leukemia most responsive to chemotherapy |
ALL |
|
|
Chromosome profile of ALL |
t(12,21) |
|
|
DOC for ALL |
Asparaginase WOF panceatitis |
|
|
Method for delivering chemotherapy drugs to CNS sanctuary sites |
Ommaya reservoir |
|
|
What condition? Leukemia that occurs at 15-39 years of age? |
AML |
|
|
3 morphologic features of AML |
Hypercellular marrow with myeloblasts Auer rods - needle-like, numerous in APML MPO/CD 34 positive |
|
|
Genetic profile of acute promyelocytic leukemia |
t(15,17) |
|
|
Coagulation disorder highly associated with APML |
DIC |
|
|
Treatment for APML |
All-trans retinoic acid |
|
|
Genetic profile of CML |
t(9,22) |
|
|
Peak incidence of CML |
4th decade of life 25-60 yrs |
|
|
Morphologic profile of CML |
Sea-blue histiocytes Myeloblasts < 10% Low leukocyte alk phos WBC > 100,000 |
|
|
3 stages of CML |
Chronic Accelerated Blast |
|
|
WHO criteria for accelerated phase in CML |
10-19% myeloblasts > 20% basophils Platelet < 100,000 no Tx Platelet > 1M Cytogenetic evolution |
|
|
WHO criteria for blast crisis |
> 20% myeloblasts/lymphoblasts Chloroma - solid focus outside a bone marrow |
|
|
DOC for CML |
Imatinib |
|
|
Most common leukemia of adults and elderly (median age of 60yrs) |
CLL |
|
|
Complication of CLL Transformation into a diffuse large B cell lymphoma |
Richter syndrome |
|
|
Mature B cell tumor in the elderly |
Hairy cell tumor * stained using tartrate resistant acid phosphatase |
|
|
3 features of leukemoid reactions |
> 50,000 WBC Elevated NAP/LAP Elevated CRP |
|
|
Diagnostic histologic finding of Hodgkin's lymphoma |
Reed-Sternberg cells "owl's eye" |
|
|
Which lymphoma shows involvement of Waldeyer's ring? |
Non-hodgkin's lymphoma |
|
|
5 types of Hodgkin's lymphoma |
Nodular sclerosis Mixed cellularity Lymphocyte rich - depleted - predominant |
|
|
Hodgkin's with the worst prognosis? |
Lymphocyte depleted |
|
|
Hodgkin's associated with EBV |
Lymphocyte depleted |
|
|
Most common type of Hodgkin's lymphoma |
Nodular sclerosis |
|
|
Name of staging used for Hodgkins |
Ann Arbor |
|
|
Most common hematopoietic malignancy |
NHL |
|
|
Most common form of indolent NHL |
Follicular t(14,18) |
|
|
2 histologic findings of follicular lymphoma |
Centroblast Centrocytes |
|
|
Most common form of NHL |
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
|
|
Lymphoma associated with translocations of c-MYC on chromosome 8 |
Burkitt's lymphoma t(8,14) |
|
|
Histologic pattern seen on Burkitt's lymphoma |
Starry sky pattern Burkitt cells - interspersed macrophages |
|
|
Genetic profile of mantle cell lymphoma |
T(11,14) Lacks cyclin D1 |
|
|
3 morphologic features of mantle cell lymphadenopathy |
Homogenous popn of small lymphocytes No centroblasts No proliferation centers |
|
|
Oncogene causing adult T-cell lymphoma |
HTLV 1 |
|
|
Histologic finding of adult T-cell lymphoma *cells with multilobulated nuclei |
Clover-leaf or flowe cells |
|
|
3 manifestations of mycosis fungoides *cutaneous T-cell lymphoma |
Mycosis fungoides - chronic proliferative d'emblee - aggressive nodular eruptive Sezary syndrome - diffuse erythema and scaling |
|
|
2 histologic findings of mycosis fungoides |
Sezary-Lutzner cells Pautrier microabscesses |
|
|
What substance produced by neoplastic plasma cells lead to B-cell proliferations |
IL-6 |
|
|
Most common and deadly plasma cell neoplasm |
Multiple myeloma |
|
|
Synthesized excess light or heavy chains with complete Igs from neoplastic plasma cells are secreted in the urine aa |
Bence-Jones proteins |
|
|
Lytic bone lesions seen in multiple myeloma |
Plasmacytoma |
|
|
Fiery red cytoplasm seen in MM |
Flame cells |
|
|
Multiple grapelike cytoplasmic droplets seen on MM |
Mott cells |
|
|
Pink globular cytoplasmic inclusions in MM |
Russell bodies |
|
|
M protein causes RBCs in PBS to stick in linear arrays in MM |
Rouleaux |
|
|
3 histologic findings of myelodysplastic syndrome |
Ringed sideroblasts Pseudo-Pelger-Huet Pawn ball megakaryocytes |
|
|
Associated mutation with chronic myelodysplastic disorders |
JAK 2 mutations |
|
|
Condition? Panmyelosis Polycythemia |
Polycythemia vera |
|
|
3 morphologic findings of polycythemia vera |
Hypercellular marrow Spent phase Massive hepatosplenomegaly |
|
|
Treatment for polycythemia vera |
Phlebotomy |
|
|
Diagnosis of exclusion Marked thrombocytosis Giant platelets |
Essential thrombocytosis *activating point mutations in JAK2 |
|
|
Throbbing/burning of hands and feet due to occlusion of small arterioles |
Erythromelalgia |
|
|
Hallmark is the development of obliterative marrow fibrosis |
Primary myelofibrosis |
|
|
Tennis racket like granules seen in Langerhans cell histiocytosis |
Birbeck granules Langerin |
|
|
Small yellow-brown, brown or rust colored foci seen in congestive splenomegaly |
Gandy-Gamma nodules |
|
|
Average volume of a red cell |
MCV |
|
|
Average Hg per red cell (mass) |
MCH |
|
|
Average concentration of Hg in a given volume of packed red cells |
MCHC |
|
|
3 mechanisms of hemolytic anemias |
Premature destruction of red cells Elevated EPO Accumulation of Hg degradation products |
|
|
Erythroid precursors seen in the bone marrow in hemolytic anemia |
Normoblasts |
|
|
PBS of hemolytic anemias |
Normo Normo |
|
|
Deficient RBC cell membrane proteins in hereditary proteins |
Ankyrin Band 3 Spectrin Band 4.2 |
|
|
Small hyperchromic RBCs lacking central pallor |
Spherocytes |
|
|
Etiologic agent in aplastic crisis of hereditary spherocytosis |
Parvovirus B19 |
|
|
Etiologic agent in hemolytic crisis of hereditary spherocytosis |
EBV mononucleosis |
|
|
Small dark nuclesr remnants present in the RBS of asplenic patients |
Howell-Jolly bodies |
|
|
Condition where RBCs are unable to protect themselves against oxidative stress |
G6PD |
|
|
2 histologic findings of G6PD |
Heinz bodies - membrane bound precipitates Bite cells - RBC with damaged membranes |
|
|
Hallmark of recovery phase in G6PD deficiency |
Reticulocytosis |
|
|
Mutation seen in sickle cell anemia |
6th codon of beta-globin Replacement of glutamate and valine |
|
|
Trapping of sickled red cells leading to splenic infarction, fibros and shrinkage |
Autosplenectomy |
|
|
Dehydrated RBCs with bull's eye appearance |
Target cells/codocytes |
|
|
3 typles of crisis in sickle cell anemia |
Vasooclusive - hypoxix injury and infarction Sequestration - massive entrapment of sickle cells Aplastic - Parvoviris B19 |
|
|
What mechanisms cause the right sided shift of the O2-Hg disassociation curve? |
CO2 Acidosis Elevated temp 2,3 diphosphoglycerate Exercise |
|
|
DOC for sickle cell anemia |
Hydroxyurea - increases Hbf |
|
|
Condition in which inherited mutatiobs decrease synthesis of adult hemoglobin |
Thalassemia |
|
|
Thalassemia Reduced or absent synthesis of alpha-globin chains |
Alpha-thalassemia |
|
|
4 types of alpha thalassemia *depends on how many globin genes are deleted |
Silent carrier - single Alpha thalassemia - 2, HbA2 levels are normal and low Hemoglobin H - tetramers of B-globin are formed (HbH), 3, disproportionate tissue hypoxia, Hydrops fetalis - Hb barts |
|
|
Thalassemia Mutations that diminish synthesis of b-globin chain |
Beta thalassemia |
|
|
B-thalassemia type RBCs completely lack HbA Major red cell Hg is HbF |
Beta thalassemia major |
|
|
B thalassemia Increase in HbA2 with normal Hbf |
Beta thalassemia minor |
|
|
PBS of thalassemia |
Microcytic Hypochromic |
|
|
Marked variation in RBC size |
Anisocytosis |
|
|
Marked variation in RBC shape |
Poikilocytosis |
|
|
SSx of thalassemia |
Crew cut appearance of skull Chipmunk facies Hemosiderosis Hemochromatosis |
|
|
Treatment strategy for thalassemia if not responsive to phlebotomy |
Chelation with deferoxamine |
|
|
Intravascular hemolysis due to increased complement-mediated RBC lysis |
PNH |
|
|
Deficient proteins in PNH |
DAF CD55 CD59 - increased risk to undergo lysis, targets membrane-attack complex |
|
|
Acute anemia triggered by cold Mycoplasma pneumonia, infectious mononucleosis |
Cold agglutinin |
|
|
Anemia where RBCs are damaged when passing through obstructed or narrow vessel lumen |
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia |
|
|
Associated diseases with microangiopathic hemolytic anemia |
DIC TTP-HUS SLE Malignant hypertension |
|
|
2 histologic findings in RBC trauma |
Schistocytes - fragmented RBC, helmet cell Burr cell/echinocytes - RBC with spikes |
|
|
3 histologic findings of megaloblastic anemia |
Macro-ovalocytes Hypersegmented neutrophils Hypercellular bone marrow |
|
|
Parasitic infection causing megaloblastic anemia |
Diphyllobothrium latum DOC Praziquantel |
|
|
Anemia caused by autoimmune gastritis leading to failure of intrinsic factor production |
Pernicious anemia |
|
|
3 morphologic findings of pernicious anemia |
Atrophy of fundic glands Intestinalization Atrophic glossitis |
|
|
Test for pernicious anemia |
Schilling test *oral vitB12 and IM vitB12, intrinsic factor *vitamin B12 deficiency, pernicious anemia, malabsorption |
|
|
Most common nutritional disorder in the world |
IDA |
|
|
Parasitic infection which results in micro-hypo anemia |
Hookworms (Necator, Ancylostoma) Albendazole |
|
|
Staining for IDA |
Prussian blue stain |
|
|
Associated with IDA Components of Plummer-Vinson syndrome |
Esophageal webs Micro-hypo Atrophic glossitis |
|
|
MCC of anemia among hospitalized patients |
Anemia of chronic disease *IL-6 leads to increase in hepcidin |
|
|
Syndrome of chronic primary hematopoietic failure and attendant pancytopenoa |
Aplastic anemia |
|
|
Drug that causes idiosyncratic aplastic anemia? Occupational chemical exposure? |
Chloramphenicol Benzene |
|
|
Selective hypoplasia of marrow erythroid elements Normal granulopoiesis and thrombopoiesis |
Pure red cell aplasia |
|
|
Etiology of ITP |
Anti-platelet antibodies Directed against glycoproteins IIb-IIIa |
|
|
Most feared complication of ITP |
Intracranial bleeding |
|
|
Treatment for ITP |
Splenectomy IVIg, anti-CD20 antibody (Rituximab) |
|
|
Pentad of TTP |
Fever Thrombocytopenia Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia Transient neurologic deficits Renal failure |
|
|
Triad of hemolytic uremic syndrome |
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia Thrombocytopenia Renal failure |
|
|
Causative agent of HUS |
EHEC O157:H7 |
|
|
Platelet dysfunction Decreased gp IB for defective platelet adhesion Decreased platelet count |
Bernard-Soulier |
|
|
Platelet dysfunction Decreased gp IIb-IIIa leads to defective platelet aggregation Normal platelet |
Glanzmann's thrombasthenia |
|
|
Most common inherited bleeding disorder |
Von Willebrand disease |
|
|
Treatment for Von Willebrand |
Desmopressin Concentrate contaning factor VIII and vWF |
|
|
Most common hereditary disease with life-threatening bleeding |
Hemophilia A *factor VIII deficiency + deep bleeding only |
|
|
Christmas disease Factor 9 deficiency |
Hemophilia B |
|
|
Acute, subacute, chronic thrombohemorrhagic disorder |
DIC |
|
|
Fibrin thrombi lead to massive adrenal hemorrhage Condition? |
Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome |
|
|
Postpartum pituitary necrosis |
Sheehan syndrome |
|
|
Widespread microthrombi in placenta |
Toxemia of pregnancy |
|
|
Diagnostics for DIC |
Fibrinogen Platelet count PT/PTT Fibrin degradation D-dimer |
|
|
Platelet dysfunction comparison table |

|
|
|
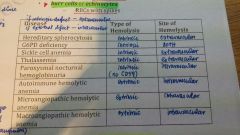
Site of hemolysis |
|

