![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
102 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the lysosomal storage diseases?
|
Tay-Sachs and Gaucher Diseases
|
|
|
what are the glycogen storage diseases?
|
Von Gierke’s and Pompe’s Diseases
|
|
|
how can you classify genetic disorders?
|
Mendelian Single Gene Disorders
- Autosomal Dominant - Autosomal Recessive - X-linked Non-Mendelian Single Gene Disorders Multi factorial Disorders Chromosomal Disorders |
|
|
what are exs of autosomal dominant disorders?
|
Neurologic: Huntington’s Disease
Renal: Polycystic Kidney Disease GI: Familial Polyposis Coli Heme: Hereditary Spherocytosis Skeletal: Marfan Syndrome Metabolic: Familial Hypercholesterolemia |
|
|
what are exs of X linked disorders?
|
Musculoskeletal: Muscular Dystrophy
Heme: Hemophilia Metabolic: Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome Neurologic: Fragile X Syndrome |
|
|
what genetic disorders result from of messed up/missing enzymes that metabolize a.a.?
|
Phenylketonuria
Maple Syrup Urine Disease Homocystinuria |
|
|
what genetic disorders result from of messed up/missing enzymes?
|
Galactosemia
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia MCAD (Fatty Acid Oxidation) Lysosomal Storage Diseases Glycogen Storage Diseases |
|
|
what genetic disorders result from messed up/missing enzyme inhibitors?
|
Alpha-1-Antitrypsin Disorder
|
|
|
what genetic disorders result from messed up/missing transport molecules?
|
Sickle Cell Anemia
Cystic Fibrosis Hemochromatosis |
|
|
how do you screen the population for gene disorders?
|
newborns
|
|
|
when do you test family or at-risk testing?
|
Prenatal
Carrier Detection |
|
|
how do you test to find out if genetic disorder?
|
Clinical Findings
Measure Abnormal Accumulations Measure Enzyme Activity or Phenotype Morphologic Changes in Tissues Gene Defect or Mutation |
|
|
what are newborns tested for?
|
Pathology - Newborn Screening Laboratory: (population based testing -all newborns)
Phenylketonuria Homocystinuria Maple Syrup Urine Disease Galactosemia Hypothyroidism Sickle Cell Anemia Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Biotinidase Deficiency Other Disorders (detectable by MS/MS techniques) Fatty Acid Metabolism defects Organic Acid Metabolism defects Other Amino Acid Metabolism defects Pediatrics Programs/Services: (selected testing) Others: Genetics, Pathology, Neurology, etc: (selected testing) |
|
|
how do you collect sample from baby for testing?
|
put drops of blood on filter paper
|
|
|
what's the incidence of phenylketonuria?
|
Incidence: 1:12,000
Classical - 1:20,000 Hyper-phenylalaninemia - 1:20,000 |
|
|
how is phenylketonuria transmitted?
|
auto recess
|
|
|
what's the problem in phenylketonuria?
|
Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (decrease activity)
Accumulations of Phenylalanine and metabolites *toxic to neural tissue |
|
|
what are the symptoms of phenylketonuria?
|
Mental Retardation
Motor Dysfunction Seizures |
|
|
how do you diagnosis phenylketonuria?
|
Phenylalanine (blood)
Tyrosine (blood) |
|
|
what's the phenylalanine metabolic pathway?
|
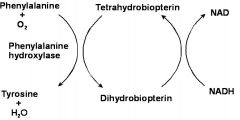
|
|
|
tx phenylketonuria?
|
limit phenylalanine in diet
|
|
|
what newborn test is used for pku?
|
guthrie testing: bac inhibition assay
BIA plate (guthrie test) - elevated phenylalanine: old method current: ms/ms |
|
|
what's the incidence of maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)?
|
1: 250,000
|
|
|
what's the inheritance of MSUD?
|
auto recess
|
|
|
what's the defect in MSUD?
|
Branch Chain keto-acid decarboxylase
|
|
|
what's the pathology/symp in MSUD?
|
Acidosis
retardation respiratory failure |
|
|
how do you diagnose MSUD?
|
Leucine/Isoleucine (screen), Valine levels
|
|
|
what's the incidence of homocystinuria (HCU)?
|
1:60,000-150,000
|
|
|
what's the inheritance of HCU?
|
auto recess
|
|
|
what's the defect in HCU?
|
Cystathionine synthase
|
|
|
what's the pathology/symp of HCU?
|
Cataracts
skeletal vascular defects |
|
|
how do you diagnosis HCU?
|
Methonine (screen), Homocysteine levels
|
|
|
MSUD tx?
|
restrict: isoleucine
leucine valine *branched chain aa |
|
|
what's the incidence of galactosemia?
|
1:35,000
|
|
|
how's galactosemia transmitted?
|
auto recess
|
|
|
what's the defect in galatosemia?
|
Galactose-1-Phosphate Uridyltransferase (Gal-1- PUT)
Phenotypes: N (normal), G (Galactosemia), D (Duarte) GG (0 % activity); DG (25%); GN (50%); DN (75%) *we're really worried about GG |
|
|
what's the pathology/symp of galactosemia?
|
Jaundice,
Sepsis (E. coli), acidosis |
|
|
what's the diagnosis of galactosemia?
|
Galactose, Galactose-1-Phosphate levels (RBC/serum)
Gal-1-PUT Activity and Phenotype (RBC’s) |
|
|
what's the galactose metabolic pathway?
|
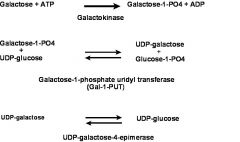
|
|
|
where does galactose accumulate in galactosemia?
|
liver
*shows w/ PAS stain |
|
|
what's the incidence of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)?
|
1:12,000
|
|
|
how is CAH transmitted?
|
auto recess
|
|
|
what's the defect in CAH?
|
21-Hydrolase - 95% (also 17 and 3-Hydroxylases)
|
|
|
galactosemia tx?
|
restrict: lactose and galactose
|
|
|
what's the pathology/symp in CAH?
|
Adrenal Hyperplasia with Virilization (androgen excess), ambiguous genitalia
Salt-wasting >> hypotension, death |
|
|
how do you diagnose CAH?
|
17-OH Progesterone Level
Other hormones, gene typing |
|
|
what's the adrenal steroid synthetic/metabolic pathways? how affected in CAH?
|
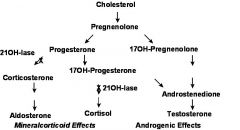
|
|
|
what's the incidence of MCAD? what kind of disorder is MCAD?
|
1: 15,000
fatty acid oxidation disorder |
|
|
what's the defect in MCAD?
|
Deficiency of Medium Chain Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
|
|
|
what's the clinical finding in MCAD?
|
Acidosis, liver dysfunction, coma, death
Sequelae: developmental delay, retardation |
|
|
what are the lab findings for MCAD?
|
Abnormal increase in C8 and C10 fatty acids detected by MS/MS
|
|
|
are there other chain length Acyl-CoA DH deficiencies?
|
yes
|
|
|
MCAD tx?
|
feed often and when get sick - monitor closely
give carnitine to stop buildup of fatty acids |
|
|
what are the types of lysosomal storage diseases?
|
Sphingolipidoses
sulfatidoses mucopolysaccharidoses mucolipidoses + others |
|
|
what diseases fall under sphingolipidoses?
|
GM2 Gangliosidosis: Tay-Sachs (Hexosaminidase A)
|
|
|
what type of disease is Hurler's disease (alpha-L-Iduronidase)?
|
mucopolysaccharidoses
|
|
|
what diseases fall under sulfatidoses?
|
Gaucher Disease (Glucocerebrosidase)
Nieman-Pick Disease (Sphingomyelinase) Metachromatic leukodystrophy (Arylsulfatase A) Krabbe Disease (Galactosylceramidase) Fabry Disease (alpha-Galactosidase A) |
|
|
what's problem w/ lysosome enzyme defect?
|
normally, things that go into lysosome are broken into smaller units that leave
if messed up lysosome: can't break down stuff stuff can't leave damages cell func --> cell death |
|
|
which lysosomal storage diseases affect neurologic systems?
|
Gangliosides (Tay-Sachs)
Sphingomyelin (Niemann-Pick) Galactosylceramides (Krabbe’s) Glucocerebrosides (Gaucher - juvenile) |
|
|
which lysosomal storage diseases affect hepatic/splenic systems?
|
Glucocerebrosides (Gaucher- adult)
|
|
|
what's the defect in Tay-Sachs? what's result?
|
Hexosaminodase A enzyme defect, brain rich in gangliosides
|
|
|
what pop is there a high incidence of Tay Sachs in?
|
Ashkenazic Jewish pops
|
|
|
what's the prognosis of Tay Sachs?
|
Progressive neurologic damage with death at 2-3 years of age
|
|
|
how do you diagnose Tay Sachs?
|
Measure enzyme activity in serum, white cells
|
|
|
what's the defect in Glucocerebrosides (Gaucher's adult) disease?
|
Glucocerebrosidase enzyme defect
|
|
|
how do you diagnose Gaucher's adult disease?
|
WBC’s and RBC’s with glucocerebrosides
|
|
|
what pop is there an inc incidence of Gaucher's adult?
|
High incidence in Eastern European Jewish population
|
|
|
how does adult Gaucher's disease present?
|
Massive hepatosplenomegaly, adult presentation, normal life span
|
|
|
what's the defect in Tay Sachs? what accumulates?
|
Hexosaminidase A: accumulation of gangliosides
|
|
|
what builds up in Gaucher's adult disease?
|
glucocerebrosides
|
|
|
what are some types of glycogen storage diseases?
|
Hepatic: von Gierke Disease
Myopathic: McArdle Syndrome Generalized: Pompe Disease |
|
|
what enzyme is messed up in von Gierke disease?
|
Glucose-6-phosphatase
|
|
|
what symptoms are seen in von Gierke disease?
|
Hepatomegaly, hypoglycemia, hyperlipidemia
|
|
|
what enzyme is messed up in McArdle Syndrome?
|
muscle phosphorylase
|
|
|
what symptoms are seen in McArdle Syndrome?
|
Muscular weakness, cramps, normal life span
|
|
|
what enzyme is messed up in Pompe disease?
|
alpha-1,4-Glucosidase
|
|
|
what symptoms are seen in Pompe disease?
|
Diffuse organ involvement, early death
|
|
|
where in pathway are glycogen storage diseases messed up?
|
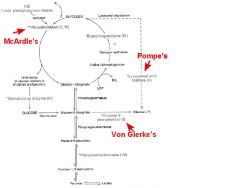
|
|
|
how do you diagnose / what tests do you do for lysosomal/glycogen storage diseases?
|
Enzyme Activity: (synthetic substrates)
Serum, urine Leukocytes Cultured fibroblasts or amniotic fluid cells Gene probes: gene typing Tissue Biopsies: liver, bone marrow, muscle |
|
|
what's the incidence of alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency?
|
Incidence: 1% population with abnormal phenotype (1:7,000 with ZZ)
|
|
|
how is alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency transmitted?
|
auto recess
|
|
|
what's the defect in alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency?
|
Deficiency or defective enzyme
Anti-Protease: chymotrypsin, trypsin, plasmin, WBC elastase and collagenase, etc |
|
|
what's the pathology of alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency?
|
Hepatic cirrhosis, pulmonary emphysema
|
|
|
how do you diagnose alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency?
|
A-1-AT Levels and Phenotype (Immunoassay and IEF)
Pi: MM (100%); MZ (58%); ZZ (15 %); SS (60%); MS (80%) |
|
|
what stain do you use to identify alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency?
|
PAS stain
|
|
|
what's the incidence of sickle cell anemia?
|
1:4,000 (Indiana), 8% carrier rate in black population.
|
|
|
how is sickle cell anemia inherited?
|
auto recess
|
|
|
what's the defect in sickle cell anemia?
|
Amino acid substitution
Abnormal hemoglobin structure |
|
|
what's the pathology of sickle cell anemia?
|
Anemia, SS crisis, thrombosis, organ infarcts, infections
|
|
|
how do you diagnose sickle cell anemia?
|
Hgb Phenotyping (electrophoresis)
Gene Defect *see HbF prominent in sickle cell anemia and SC disease |
|
|
what's the incidence of cystic fibrosis?
|
1: 2000
|
|
|
how is cystic fibrosis transmitted?
|
auto rec
|
|
|
what's the defect in cystic fibrosis?
|
Sodium/Chloride Ion Transport System
Multiple allele defects - delta F508 (95% in Indiana) Chloride transport across membranes |
|
|
what's the pathology in cystic fibrosis?
|
Pulmonary Brochiectasis, Pneumonias, Failure
Hepatic Cirrhosis Malabsorption Infertility meconium ileus: dense, thick stool that needs surgery |
|
|
how do you diagnose cystic fibrosis?
|
Trypsinogen level (screen) - increased
Sweat Chloride Test (increased) Gene Defects - 700+ allele variants |
|
|
what's the problem w/ pumps in cystic fibrosis?
|
normal: body pumps Cl- back in and Na+ follows.. skin not so salty
cf: Cl- can't be in.. Cl- stays outside w/ Na+ ... skin salty normal: Cl- pumped out into airway and some Na+ and H2O goes into cell cf: Cl- not pumped out into airway.. pulls Na+ and H2O into cell --> more mucus -> bronchiecstases |
|
|
what is incidence of hemochromatosis?
|
1:400 (whites, western europe)
|
|
|
what's the transmission of hemochromatosis?
|
auto recess
|
|
|
what's the etiology of hemochromatosis?
|
Primary - hereditary disorder, excessive iron absorption
Secondary - excessive iron overload states, example: beta-thalassemia with multiple transfusions |
|
|
what are the anatomical findings in hemochromatosis?
|
Micronodular cirrhosis - iron deposits
Diabetes - iron deposits in Islets, fibrosis Skin pigmentation - increased melanin |
|
|
how do you diagnose hemochromatosis?
|
Iron levels, blood and liver
Gene defect (s) |
|
|
cystic fibrosis tx?
|
pulmonary toilet: pound on back and beat secretions free
|

