![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Duke's criteria for diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis (3)
|
1- Positive culture
2- Echo findings 3- New murmurs |
|
|
What is Carcinoid Syndrome?
|
SCALP
Skin, Cardiac, Abdomen, Liver, Pulmonary |
|
|
What is carcinoid heart disease?
|
Carcinoid tumors originate from neural crest cells that are capable of APUD (Amine Precursor Uptake and Decarboxylation)
|
|
|
What substances do carcinoid tumors produce?
|
1- Serotonin
2- Histamine 3- 5HIAA- serotonin metaboite |
|
|
Most common infectious cause of myocarditis
|
Viral
|
|
|
Non-infectious causes of myocarditis
|
1- Hypersensitivity
2- Reaction to drugs |
|
|
When you see lymphocytes and monocytes in interstitial, perivascular areas, think
|
VIRAL
|
|
|
When you see neutrophils, think
|
Bacterial
|
|
|
When you see eosinophils, think
|
Drug Hypersensitivity
|
|
|
When you see giant cells, think
|
Giant Cell myocarditis
|
|
|
Dilated cardiomyopathy leads to
|
Systolic failure- flabby HYPOcontracting heart
|
|
|
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy leads to
|
Diastolic failure
|
|
|
Microscope- disarray and disorganization
|
HCM
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of sudden death in athletes?
|
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy is what type of dysfunction? Systolic or diastolic
|
Diastolic because muscle can't relax
|
|
|
What is endomyocardial fibrosis?
|
Fibrosis of the endocardium and myocardium, may be from thrombus origin, cause unknown
|
|
|
What is Loeffler's Endomyocarditis?
|
High Eosinophils cause damage
|
|
|
Endocardial Fibroelastosis
|
fibrosis and elastosis
|
|
|
3 examples of restrictive cardiomyopathy
|
1- Endomyocardial fibrosis
2- Loeffler's endomyocarditis 3- Endocardial fibroelastosis |
|
|
What is cardiac myxoma?
|
Most common benign primary tumor of the heart, from primitive mesenchymal cells
|
|
|
Where is cardiac myxoma most commonly found?
|
Left atrium
|
|
|
Lepidic cells found in
|
Cardiac myxoma
|
|
|
Peculiar structures resembling glands or blood vessels are characteristic of
|
Cardiac Myxoma
|
|
|
Myxomas can cause
|
Valve obstruction and embolism
|
|
|
How do you diagnose myxomas?
|
Echocardiogram
|
|
|
Causes of concentric LVH (3)
|
1- Essential Hypertension (most common)
2- Aortic stenosis 3- HCM |
|
|
Causes of concentric RVH (2)
|
1- Pulmonary HTN
2- Pumonary artery stenosis |
|
|
In ventricular hypertrophy, increased AFTERLOAD causes what
increases PRELOAD causes what |
Afterload- Concentric hypertrophy
Preload- Eccentric hypertrophy |
|
|
Causes of eccentric hypertrophy of left ventricle (2)
|
1- Mitral or aortic valve regurgitation
2- Left to right shunting |
|
|
Causes of eccentric hypertrophy of right ventricle (1)
|
Tricuspid valve or pulmonary valve regurgitation
|
|
|
Most common cause of IE
|
Strep viridans
|
|
|
Most common valve with IE
|
Mitral
|
|
|
Aortic and tricuspid involved with IE with IVDA (Intravenous drug abuse)
|
Notes
|
|
|
Endocarditis with regurgitation, RF and fibrotic heart disease with stenosis
|
Notes
|
|
|
IE pathology
|
Vegetations destroy valve leaflet and chordae tendinae
|
|
|
IE signs
|
1- Immunocomplex vasculitis- glomerulonephritis, Roth's spot
2- Microembolization- splinter hemorrhages, janeway lesions, osler's nodes, petechiae, infarctions |
|
|
SLE causes LSE
|
Notes
|
|
|
Libman-Sacks endocarditis
|
Sterile vegetation, caused by SLE, Mitral valve involvement- regurg more common
-On both sides of valve |
|
|
Acute IE caused by what bacteria
|
Staph aureus
|
|
|
Subacute IE caused by
|
Strep virdians
|
|
|
Strep bovis and IE
|
Colon cancer
|
|
|
Staph epidermidis and IE
|
Prosthetic valves
|
|
|
FROM JANE
|
Fever
Roth's spots Osler's nodes Murmur Janeway lesions Anemia Nail-bed hehorrhage (splinter) Emboli |
|
|
Most common cause of myocarditis and pericarditis
|
Coxsackie virus
|
|
|
Doxorubicin and daunorubicin can cause
|
Myocarditis
|
|
|
Increased CK-MB and Troponins I and T indicate
|
Myocarditis
|
|
|
Pericardial friction rub most likely indicates
|
Pericarditis
|
|
|
Most common cause of Dilated cardiomyopathy
|
Myocarditis
|
|
|
3 Types of Cardiomyopathy
|
1- Dilated
2- Hypertrophic 3- Restrictive |
|
|
Murmur intensity increases with DECREASED preload (Standing up, Valsalva)
|
HCM
|
|
|
Tx for HCM
|
Beta Blockers
|
|
|
How does HCM cause Sudden Death?
|
Ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation
|
|
|
3 common causes of Restrictive cardiomyopathy
|
1- Amyloidosis
2- Myocardial fibrosis after open-heart surgery 3- Radiation |
|
|
Cardiac myxomas are most common where?
|
Left atrium
|
|
|
Metastasis is more common than primary heart tumors
|
Notes
|
|
|
Myxomas more common in what age
|
Adults
|
|
|
Rhabdomyoma common in what age
|
Children and infants
|
|
|
Most common causing organism of IE
|
Strep viridans
Staph- IV drug abusers |
|
|
Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis
|
Sterile masses of fibrin, platelets, and blood elements
-No inflammation -May embolize -Associated with hypercoagulable states -Seen in burns , cancer, sepsis, pulm. thrombosis, indwelling catheters of heart, leukemias, mucin-producing tumors of ovary, pancreas, GI tract |
|
|
Carcinoid affects what side and features
|
Right side
-Valve and endocardial plaque like lesions- smooth muscle fibers, sparse collagen, and acid mucopolysaccharide rich matrix and subsequent fibrosis |
|
|
Chaga's disease
|
T cruzi protozoa causes trypanosomiasis
Can cause dilated cardiomyopathy |
|
|
Viral myocarditis
|
Coxsackie A and B and other enteroviruses most common
-Infants, pregnant women, and immune compromised people -Suffer from flu-like disease without cardiac problems OR sudden death -Most heal without sequelae |
|
|
Fielder's or Giant Cell Myocarditis
|
UNKNOWN CAUSE!
Multinucleated giant cells, poor prognosis Tx- cardiac transplantation |
|
|
Tissue changes in myocarditis
|
Focal, patchy necrosis or damage
|
|
|
X-linked DCM linked with what mutation
|
Dystrophin
|
|
|
Cause of death of DCM
|
Cardiac failure
Arrhythmia/sudden death |
|
|
Cause of IE with prosthetic valves or indwelling central lines
|
Staph epidermidis
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of HCM
|
Mutations in SARCOMERE!
|
|
|
Disarray and disorganization
Myocypte Hypertrophy Interstitial and replacement fibrosis |
HCM
|
|
|
HCM complications (4)
|
1) Cardiac failure
2) Thromboembolism 3) IE 4) Arrhythmia/Sudden death |
|
|
Enlarged dilated heart and DYSTOLIC DYSFUNCTION is
|
Restrictive
|
|
|
Some causes/assoctiations of dystolic dysfunction
|
Amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, storage diseases, radiation fibrosis
|
|
|
Seen in infants and young children
Focal or diffuse cartilage-like thickening of the mural endocardium of cardiac chambers owing to fibrosis and elastosis -Associated with congenital cardiac anomaly, such as aortic valve obstruction Can lead to cardiac failure and death |
Endocardial fibroelastosis
|
|
|
Tropical African countries
Children and young adults Fibrosis of the endocardium and subendocardium restricts ventricular volume and compliance, diastolic filling is reduced and cardiac failure |
Endomyocardial fibrosis
|
|
|
Lepidic cells seen in
|
Myxomas
|
|
|
Complications of myxomas
|
Valve obstruction/embolism
|
|
|
PECULIAR structures resembling poorly formed glands or vessels are characteristic of
|
Myxomas
|
|
|
Myxomas are Benign
|
Notes
|
|
|
Most common primary tumor of the heart in children and associated with tuberous sclerosis
|
Rhabdomyoma
|
|
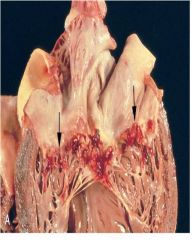
What is this?
|
Infective endocarditis
|
|
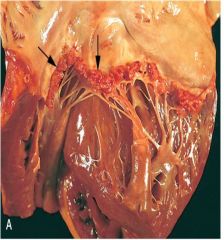
|
Nonbacterial Thrombotic Endocarditis
|
|
|
NBTE caused by sepsis is called
|
Marantic Endocarditis
|
|
|
Mucinous tumors of ovary, pancreas, and GI tract can cause
|
NBTE
|
|
|
Yellow white fibrotic patch, mucopolysaccarhide material, think
|
Carcinoid Lesion
|
|
|
Remember the left side of the heart is protected in carcinoid due to
|
1) Metabolized by liver
2) Inactivated by the monoamine oxidase system in the pulmonary |
|
|
Remember HCM also known as
Assymetric septal hypertrophy Idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis Hyptertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy |
Notes
|

