![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Primary Hosts:
All mammals and birds You can find me all over the body but especially the axilla, inguinal region, face, and ears characteristic: spur coxa I that overlaps with coxa II. |

Genus: Ixodes
Species: ricinus (castor) Bean tick or sheep tick 3 host tick- mouse, sheep, cow year1: larva year2: nymph year3: adult |
The engorged female is light grey, bean shaped, and has 4 pairs of legs. The Ixodes genus are inornate ticks without festooons or eyes. The palps are long and the ventral surface of the male is almost entirely covered with a series of plates. An anal groove is present anterior to the anus. The tarsi are tapered. The posterior culeinal angle of the first coxa bears a spur which overlaps the second coxa.
|
|
|
Knowledge of general structure of Ticks
|
- Anal opening subterminal
- Genital opening- coxa -4th pair legs - haller's organ on 1st tarsus (humidity/olfactory receptor) - |
|
|
|
Discuss the epidemiology of
Ixodes ricinus in Ireland. SPRING feeders * overwinter are they engorged? * what temp does activity begin? |
march-June
eggs hatch in autumn and larvae and nymphs moult autumn. *winter= unengorged * temp. >10c |
Ireland, south west England, Wales west scotland- BOTH occur (spring and fall feeders)
elsewhere in UK, only spring feeders |
|
|
Discuss the epidemiology of
Ixodes ricinus in Ireland. AUTUMN feeders -*overwinter are they engorged? * what temp does activity cease? |
August - November
eggs do not hatch until the following summer. Larvae and nymphs are in diapause over whole period. * winter: engorged and do not moult until summer * activity ceases < 10 c |
|
|
|
Boophilus microplus is an example of a ____ (#) host tick.
|
1 host tick
BOO YA! (2 molts) |
drop off an doviposit
Hatch land on cow (2 molts) more or less continuous |
|
|
Rhipicephalus evertsi is an example of a ____ (#) host tick.
|
2 host tick
1st year: 2nd year: |
|
|
|
Ixodes ricinus has how many hosts?
|
3 hosts!
|
|
|
|
what posture do ticks adapt when host seeking?
|
Questing
|
|
|
|
Are Aergasidae hard or soft ticks?
|
SOFT
|
|
|
|
Are Ixodidae hard or soft ticks?
|
HARD
|
|
|
|
True or False?
Soft ticks (Argasidae) have no scutum, no visible mouthparts dorsally and no swell as ofter as hard ticks |
TRUE
|
|
|
|
True or False:
Argasidae (soft ticks) have stigmata between coae III & IV |
TRUE
|
|
|
|
True or False:
Hard ticks have: Scutum- hard chitinous covring prominent mouthparts festoons (notches) ornate (enamel like coloured patches) |
TRUE
|
|
|
|
True/false:
hard ticks have their stigmata anterior to coxae IV |
false: Posterior
ps. stigmata (respiratory opening) |
|
|
|
what is the difference in eyes between soft ticks and hard ticks?
|
soft: supra-coxal fold (only 1 species)
hard: on each side of scutal margin |
eyes:
only ornithodoros savignyi (soft) not in haemophysalis and Ixodes (hard) |
|
|
Tick mouthparts:
|
Gnathosoma- capitulum
pair of pedipalps- sensory chelicerae- pierce skin hypostome- toothed (medial and ventral) |
Feeding:
pedipalps grasp skin chelicerae cut through skin hypostome inserted in wound anchor with teeth. Dorsal groove (saliva and blood) |
|
|
Discuss Ixodes ricinus
Habitat and humidity requirement? |
survival of I. ricinus is dermined by:
habitat: water requirements humidity: >90% or at least excess 80% |
|
|
|
where can you find Ixodes spp of rough grazing (presence of a mat with high moisture)?
|
Britian
|
|
|
|
where can you find Ixodes spp of woodlands?
|
mainland Europe
|
|
|
|
where can you find Ixodes spp of high water table- survivor on arable ground and around hedgerows
|
Ireland
|
|
|
|
True or false:
1. Ixodes ricinus has festoons and eyes 2. anal groove present anterior to the anus |
1. FALSE (no festoons or eyes)
2. True (my anal groove is anterior to the anus) |
|
|
|
Name the three important species of Ixodes in Europe
|
ricinus- castor bean
canisuga- British dog hexagonus- hedgehog |
|
|
|
Three host tick life cycle:
Host 1: mouse, small rodents, birds year 1 |
- larva feed on host 1 and fully fed larva drop to the ground and moult to nymph and attach to host 2
|
A female tick feeds for 14 days after insemination, drops to the ground and lays several thosand eggs in sheltered location.
Eggs hatch in summer and the larvae feed the following year for about 6 days, drop off and moult to nymphs and again feed for a few days the next year. They then drop off, moult to adults and find a host in year 3. Thus while the total feeding time is only 26-28 days, it takes 3 years to complete entire life cycle. |
|
|
Three host tick life cycle:
Host 2: year 2 |
- nymph moults to adult and female attaches and feeds on host 3
|
A female tick feeds for 14 days after insemination, drops to the ground and lays several thosand eggs in sheltered location.
Eggs hatch in summer and the larvae feed the following year for about 6 days, drop off and moult to nymphs and again feed for a few days the next year. They then drop off, moult to adults and find a host in year 3. Thus while the total feeding time is only 26-28 days, it takes 3 years to complete entire life cycle. |
|
|
Three host tick life cycle:
Host 3: year 3 |
- fully fed female drops from host to ground and lays eggs
|
A female tick feeds for 14 days after insemination, drops to the ground and lays several thosand eggs in sheltered location.
Eggs hatch in summer and the larvae feed the following year for about 6 days, drop off and moult to nymphs and again feed for a few days the next year. They then drop off, moult to adults and find a host in year 3. Thus while the total feeding time is only 26-28 days, it takes 3 years to complete entire life cycle. |
|
|
Three host tick life cycle: how many days does the female feed after insemination?
|
14 days
|
|
|
|
Total feeding time in three host tick life cycle?
|
26-28 days
|
|
|
|
methods of control for Ixodes ricinus in Ireland.
|
- acaricide (hand spraying) when tick observed in cattle.
- Sheep dipped in spring -pasture improvement (improve drainage) - pasture spelling - enhanced resistance to host -immunoprophylaxis |
|
|
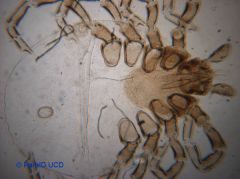
Primary Hosts
Dog, sheep, horse and mole secondary Host fox |
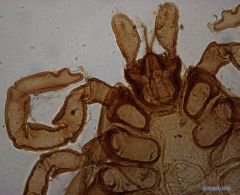
Genus: Ixodes
Species: canisuga British dog tick or Fox tick |
differentiated from I. ricinus by the presence of humped tarsi and the absence of a spur on the posterior internal angle of the first coxa.
|
|
|
Ixodes canisuga
- details to know * ID * clinical relevance * host- parasite interaction |
- absense of spur on posterior angle of first coxa.
- occasionally problem in kennels - also occur on cats - causes pruritus, hair loss and anaemia |
|
|

Primary Hosts
Dogs, ferrets and weasels humped tarsi and spur on first coxa does not overlap the second |

Genus: Ixodes
Species: hexagonas Hedgehog tick (also dogs and cats) |
|
|

Primary Hosts:
Domestic and wild mammals - ornate 3-5 mm ornate 3 host tick. - palps and mouthparts short w/ rectangular basis capituli. - festoon and eyes present - anal groove posterior to anus - coxa increases in size from I- IV |

Genus: Dermacentor
Sheep tick or marsh tick |
Dermacentor reticulatus- NOT IN IRELAND (wooded area)
Dermacentor Marginatus- w. Europe (forest) ireland? |
|

Primary Hosts: Poultry
Secondary Hosts: Humans Where found: Under the wings |

Genus: Argas
species: persicus Soft tick or fowl tick |
It is cosmopolitan in disribution and has only been recorded from Britain on a few occasions.
Ireland.. only a few occasions Argos are oval in shape, narrower anteriorly then posteriorly. The scutum is absent and the mouthparts are not visible from the dorsal aspect. There is no sexual dimorphism and they are round in shape. |
|
|
Important Genera in Family Argasidae
|
Argas persicus (fowl)
Otobius spp (spinose ear tick) dogs Ornithodoras spp (sand tampans) |
|
|
|
Who am I:
small 3 mm 3 host tick (larvae and nymoh: small mammals and birds) (adults: larger mammals, cattle and sheep) habitat: humid, EURASIA |
Haemaphysalis punctata
|
|
|
|
What tick transmits BABESIA?
and tick paralysis (3 host tick) |
Haemaphysalis punctata
|
S. England and Wales
b. major (cattle) b. motasi (sheep) other Europe area b. bigemina (cattle) b. motasi (sheep) anaplasma (cattle) |
|
|
Who is the Blue tick?
How many hosts? |
Rhipicephalus (Boophilus)
One host- BOO YA |
|
|
|
Blue tick is a vector for which 2 Babesia species and one other species?
|
babesia bigemina
babesia bovis Anaplasma marginale |
|
|
|
Who am I?
very large 3- host tick tropic/subtropic Africa (1 species temperate N. america) highly ornate- long banded legs both eyes and festoons present long mouthparts (deep bites) |
Amblomma
|
Ehrlichia ruminantium and Q fever?
wounds damage hides myasis |
|
|
Who am I?
2 host tick minor importance in temerate climates yellow and red bands on the legs eyes and festoons present long mouth parts |
Hyalomma
|
Babesia ovis,
Crimean congo haemorrhagic fever Q fever * wounds - 2 bacterial - damage hides -myiasis |
|
|
Amblyomma and Hyalomma are vectors of various diseases.
name 3 |
1. Ehrlichia ruminantium-Amblymomma
2. Q fever- Hyalomma 3. Crimean Congo Haemorrhagic fever- Hyalomma |
|
|
|
which tick= VECTORS
Babesia divergens (cattle) - redwater Louping ill virus ( sheep) Anaplasma phagocytophilum (sheep and cattle) - tick borne fever staphyloccous aureus (young lambs) - Tick pyaemia Borrelia burgdorferi (man, dogs) - Lyme disease |
Ixodes ricinus
|
|
|
|
which tick= VECTORS
Borrelia burgdorferi? |
Ixodes hexagonas
Ixodes canisuga Ixodes ricinus |
|
|
|
which tick= VECTORS
babesia (dogs, horses, cattle sheep) Theileria (sheep and horses) Anaplasmosis (sheep) Q- fever |
Dermacentor reticulatus
|
NB: transtadial only in Theileria
|
|
|
which tick= VECTORS
Borrelia anserina- fowl spirochetosis aegyptianella pullorum (rickettsial infection) |
Argas percicus
|
|
|
|
Name the control method advised for 3 host ticks (Rhipicephalus (Boophilus)
|
Avermectins & Milbemycin
|
|
|
|
What chemical is used to treat ticks?
|
Acaricides
|
|

