![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name a condition that is paraneoplastic and causes proliferation of the melanocytes in the uvea
|
Bilateral Diffuse Melanocytic Proliferations (BDUMP)
|
|
|
Is this a common condition?
|
NO! Rare
|
|
|
Who does this more commonly occur in?
|
Mainly woman
Pk: 63 years |
|
|
Which systemic malignant neoplasms are associated with BDUMP?
|
Pancreatic
Lung Ovarian Uterine |
|
|
What symptoms may the patient complain of?
|
Visual loss
|
|
|
What are the clinical signs?
|
uveal thickening
serous retinal detachment rapid cataract formation. |
|
|
What are the general signs of BDUMP?
|
Uvea
Retina Cataract (rapid development) |
|
|
What are the uveal signs?
|
Uveal melanocytic tumours
Slightly elevated + Diffuse thickening of the uvea |
|
|
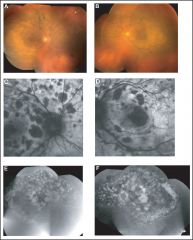
What are the retinal signs?
|
Lesions:
Multiple Round or oval Subtle red patches @ the level of the RPE Exudative neural RD |
|
|
What is the histopathology of BDUMP?
|
Diffuse uveal infiltration by benign hypopigmented spindle cells and occasional epithelioid cells.
There is focal infiltration of the choroid by heavily pigmented melanocytes with sparing of the choriocapillaris. Destruction of the RPE occurs in areas overlying the infiltrate |
|
|
What might be seen on Bscan and Goldmann Perimetry?
|
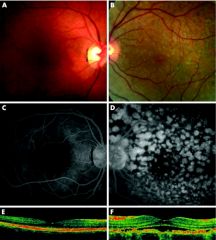
B-scan: diffuse choroidal thickening and discrete nodules with medium to high internal reflectivity.
Goldmann visual fields: scotomas corresponding to the pigmented tumors and a generalized decreased peripheral visual field. |
|
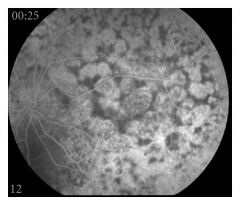
What is seen on FA?
|
Multifocal areasof early hyperfluorescence corresponding to the red patches
|
|
|
Possible treatment?
|
Plasmapheresis was initiated 3 times per week for the ophthalmic abnormalities.
Because we believed that a circulating growth factor might be responsible for the findings in BDUMP Improved vision to 20/20 until patient died (Arch of Opthal 2012) |
|
|
What is the life expectancy of someone diagnosed with this condition?
|
1 year from time of presentation
|
|
|
What unusual case was described the British Journal of Ophthalmology in 2007?
|
A case of unilateral diffuse melanocytic proliferations
|

