![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is another name for panoramic Imaging?
|
Pantomography
|
|
|
What technique is used for panoramic imaging?
|
Extraoral technique - Image receptor and source are located extraorally
|
|
|
What type of receptors are used in panoramic imaging?
|
Digital Image receptors (sensors or
photostimulable PSP plates) or indirect exposure conventional film is used |
|
|
What are the characteristics of the image received in a panoramic radiograph?
|
Single tomographic image of the facial
structures including maxillary & mandibular dental arches & the supporting structures |
|
|
What are the three planes and associated lights that are used in patient positioning?
|
• Mid sagittal plane light
• Canine light (should be on mesial of maxillary canine) • Horizontal plane light |
|
|
What are the landmarks for the horizontal plane?
|
Frankfort plane: lower border of orbit &
superior point of tragus Or tragus to outer canthus of eye |
|
|
Reciprocal movement of Image receptor & x-ray source around a central point or plane called _____.
|
Image layer
This is where the object of interest is located |
|
|
Image receptor & x-ray source move
_____ but in _____ directions during exposure. |
Simultaneously, opposite
|
|
|
_____ of superimposed structures are _____ out to show the area of interest more clearly
|
Shadows, blurred
|
|
|
What are the advantages of panoramic imaging?
|
- Convenience; simple to perform
- Broad anatomical coverage - Low patient dose (dose equivalent to 4 BW) - Short Imaging time - Readily available in most dental offices - Useful as initial screening tool - For treatment planning, dental anomalies, trauma, etc. - Provides insight in determining the need for other projections - Minimal infection control procedures required - Well accepted by patients / patient education |
|
|
What is the imaging time for a panoramic radiograph?
|
<3-4 min including patient
preparation time and infection controls steps |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of panoramic imaging?
|
- Lack of fine anatomical detail
-->Lesser detail & definition than PA; shouldn't replace PA - Structure Overlap - Magnification (20 - 30 %) and distortion of structures - Initial expense is more - Patient positioning is important - Artifacts, ghost images - Incorrect interpretation |
|
|
Where is there overlap on a Panoramic Image?
|
Premolar interproximal surfaces
|
|
|
If patient positioning is NOT correct,
what problems will result? |
geometric distortion, magnification,
elongation, ghost image formation, superimposition of structures, overlap, leftright size variations |
|
|
The problems associated from improper patient positioning affect what types of machines?
|
Both conventional & digital machines
|
|
|
What is the size and path of the x-ray beam in a Panoramic machine?
|
Narrow vertical beam rotates in a horizontal plane around a rotation center.
Negative Beam Angle (-7 to -10°) |
|
|
Where is the rotational center?
|
- Invisible and positioned intraorally - Located off to the side, away from the object being imaged
- During the cycle, the machine automatically shifts one or more rotation centers |
|
|
_____ of movement of the receptor is regulated to be the same as that of _____ sweeping through the structures nearest the receptor.
|
Rate, CR
|
|
|
What are the usefully captured structures in a panoramic image?
|
Structures found near the image receptor
|
|
|
Which structures appear blurred, diffused or ghost-like?
|
Structures near the x-ray source
|
|
|
What defines a Rotograph imager?
|
Single rotation center
|
|
|
What defines a Panorex imager?
|
One or two rotation centers (split image)
|
|
|
What defines a Orthopantomograph model OPI imager?
|
Three rotation centers (continuous image)
|
|
|
What defines a Penelipse, Versaview imager?
|
Continuous image utilizing a continuously sliding rotation center
|
|
|
What defines a Orthopantomograph model OP2 & OP3 & Cranex imager?
|
Continuous image utilizing a combination of stationary & moving rotation centers
|
|
|
If a rotating narrow beam is used with
a stationary image receptor what occurs? |
Magnification in the horizontal direction would be greater than that in vertical dimension
|
|
|
What is used to equalize magnification in both the horizontal and vertical planes?
|
Moving Image Receptors
|
|
|
What is the Focal trough / image layer?
|
- Zone of sharpness
- 3D curved zone or image layer in which structures are reasonably well defined |
|
|
Vertical & horizontal magnification will only match if object lies within the _____ of the _____.
|
Central plane, focal trough
|
|
|
What happens to objects that are outside the focal trough?
|
Objects outside the focal trough are not sharp and appear fuzzy on the radiograph.
|
|
|
Width of focal trough /
image layer depends on what? |
- Direct proportion: Distance from center of rotation to central plane of image (effective projection radius)
- Inverse Proportion: Layer thickness to width of the long narrow slit beam. |
|
|
The _____ the radius, the _____ the image layer.
|
Longer, thicker
|
|
|
The _____ the beam, the _____ the image layer.
|
Narrower, wider
|
|
|
What is the shape of the focal trough or image layer?
|
- Narrow in anterior region,
- Thicker in posterior region - Shaped to center the jaws and adjacent structures within its boundaries |
|
|
What is optimized for all anatomical
conditions and adjustable to fit patient’s arch form? |
Adjustable focal trough
|
|
|
When object is displaced to the
_____ side of the focal trough, towards the source, the beam passes more _____ through the object compared with the Image receptor speed. What is the result? |
Lingual, slowly
- Structure elongated horizontally on Image receptor (Positioned to far back) |
|
|
When the object is displaced towards the _____ aspect of the focal trough, closer to the Image receptor, the beam passes at
a _____ rate through the structures,and the structure is compressed. What is the result? |
Buccal, faster, horizontally
- There appears to be more vertical magnification (Positioned to far forward) |
|
|
What are the important points to remember in regards to magnification for panoramic images?
|
- Certain degree of magnification in all images (25% - 30%)
- Varies from machine to machine - Take variation into account when making measurements - Varies with position of objects in the arch and in the focal trough |
|
|
What is concept 1 for Panoramic anatomy?
|
- Structures flattened & spread out
- Jaws, maxillofacial structures /spines: Split vertically in half down midsagittal plane with each half folded outwards - Nose remains in middle - Right & left sides of jaws are on each edge of the Image receptor |
|
|
When would be concept 1 be determined undesirable?
|
- Patient is positioned incorrectly in the machine certain structures would be flattened & spread out although they normally would not be
- Hyoid bone & inferior turbinates meati of nose |
|
|
What is concept 2 for panoramic images?
|
Formation of real images (single & double)
|
|
|
When do real images form?
|
When the object is located between the rotation center of the beam & the Image
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of double images?
|
- One image is mirror image of the other
- Both images are real images - Each image has same proportions & same location on opposite side - Double images only occur with midline objects falling in the diamond-shaped zone in midline |
|
|
Double Real Images are normally formed by what?
|
Hard & soft palate
Palatal tori Body of hyoid bone Epiglottis Cervical spine |
|
|
What is concept 3 for Panoramic imaging?
|
Ghost Images are Formed
|
|
|
When are ghost images formed?
|
- Forms when the object is located
between the x-ray source and center of rotation or the object is behind the rotation center. |
|
|
What are the characteristics of ghost images?
|
- Same general shape as its counterpart (No mirror image)
- Formed on the opposite side - Appears higher on Image receptor than the real image - Blurred and magnified (vertical component more blurry and enlarged than horizontal) |
|
|
What are the structures that generally form ghost images?
|
Cervical spine
Horns of hyoid bone Ramus of mandible Hard palate Neck chains, ear rings, necklaces, markers |
|
|
What is concept 4 in panoramic imaging?
|
Soft tissues are seen
|
|
|
Some soft tissues _____ the beam to sufficient degree to become visible on radiograph
|
Attenuate
|
|
|
What are the examples of the soft tissue that is seen on a panoramic image?
|
Posterior & superior edentulous regions,
fluids, cartilaginous tissues like nose ear and epiglottis, soft palate & uvula, dorsum of tongue, lips, nasolabial fold, soft tissues of turbinates and septum, posterior pharyngeal wall and palatine tonsils |
|
|
What is Concept 5 in panoramic imaging?
|
Air spaces are seen
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of concept 5 in panoramic imaging?
|
- Air does not attenuate x-ray beam
- Air spaces appear black |
|
|
Air spaces of panoramic images include...
|
- Nasopharyngeal
- Poropharyngeal - Palatoglossal - Hypopharynx, maxillary sinus, nasal fossa, |
|
|
What is Concept 6 in panoramic imaging?
|
Relative Radiolucencies & Radiopacities
seen |
|
|
What are the characteristics of concept 6 in panoramic imaging?
|
- Machine & patient components may produce single or / and double real images and / or ghost images
- Multiple areas of relative density changes are produced |
|
|
When it comes to multiple density changes you must remember what?
|
- Air obscures hard tissues
- Soft tissues obscure air - Hard tissues obscure soft tissues - Ghost Images obscure everything! |
|
|
What is concept 7 in panoramic imaging?
|
Panoramic images are unique
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of of concept 7 in panoramic imaging?
|
- Helpful to assess & interpret
- Broad anatomical coverage - Depict angular interrelationships of structures - Excellent projection of variety of structures on single Image receptor |
|
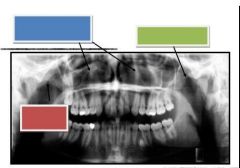
|
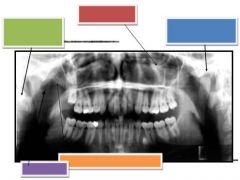
Blue: Nasal turbinates & meati
Green: Zygomatic arch Red: Zygomatic arch |
|
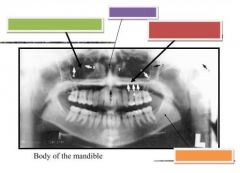
|
Green: Maxillary sinuses
Purple: Nasal Septum Red: Hard palate & floor of nasal fossa Orange: Mandibular canal |
|
|
Mandibular Canal
|
|
|
Mandibular Foramen
|
|
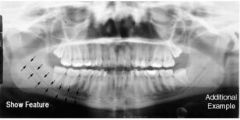
|
Mental Foramen
|
|
|
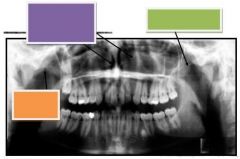
Purple: Nasal concha, turbinates & meati
Green: Zygomatic arch Orange: Zygomatic arch |
|
|
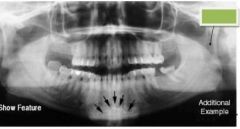
Mental Ridge or protuberance
Green: Lingula |
|
|
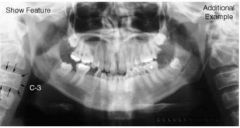
Cervical spine
|
|
|
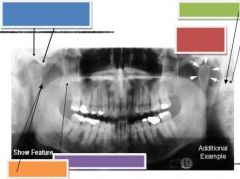
Blue: Articular eminence & Glenoid fossa
Green: Mastoid process Red: Condyle Orange: Sigmoid notch Purple: Coronoid process of mandible |
|
|
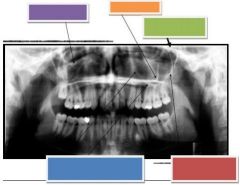
Purple: Infraorbital rim
Orange: Malar process Green: Pterygomaxillary Fissure Blue: Medial wall of max. sinus Inferior border of max. sinus Red: Posterolateral Wall of max. sinus |
|
|
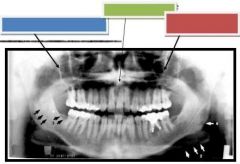
Blue: Posterior wall of max. sinus
Green: Anterior nasal spine Red: Zygomatic process of maxilla |
|
|
Stylo-hyoid ossicles
|
|
|
Styloid Process
|
|
|
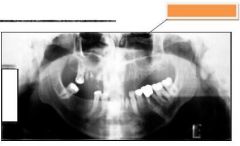
Orange: Infraorbital canal
|
|
|
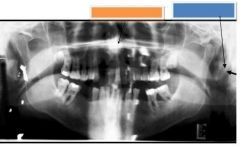
Orange: Anterior nasal spine
Blue: Styloid Process |
|
|
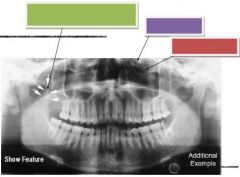
Green: Coronoid process
Purple: Ethmoid sinus Red: Infraorbital canal |
|
|
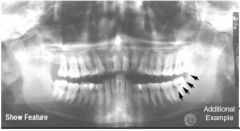
External oblique ridge
|
|
|
Green: Cervical spine
Red: Infraorbital Rim Blue: Articular eminence & Glenoid fossa Purple: Sigmoid notch Orange: Coronoid process of mandible |
|
|
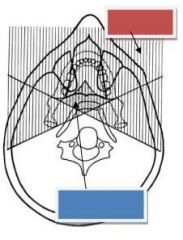
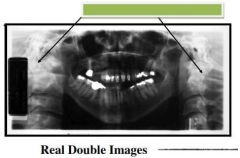
Red: Region where Real Images Form (vertical hatch marks)
Blue: Real Double images (objects are intercepted by the beam twice) |
|
|
Genial tubercles & Lingual Foramen
|
|
|
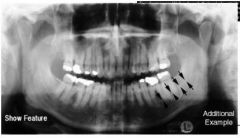
Internal oblique ridge
|
|
|
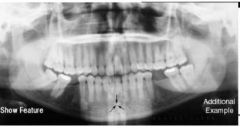
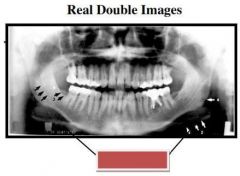
Red: Hyoid bone
|
|
|
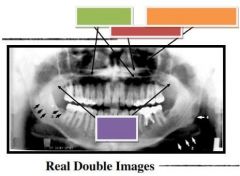
Green: Hard palate
Red: Ghost formation Orange: Floor of nasal cavity Purple: Soft palate |
|
|
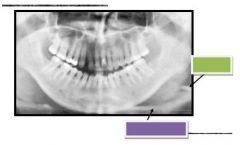
Green: Epiglottis
Purple: Hyoid bone |
|
|
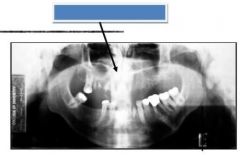
Green: Cervical spine - real image
|
|
|
Blue: Ghost image of cervical spine
|
|
|
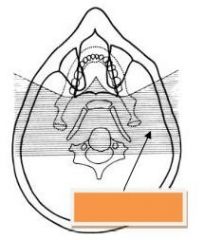
Orange: Region where Ghost Images
Form |
|
|
Epiglottis
|
|
|
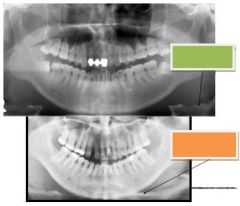
Green: Real image of hyoid bone
Orange: Ghost image of hyoid bone |
|
|
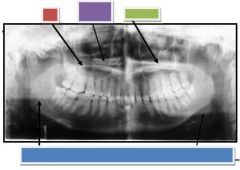
Red: Hard Palate
Purple: Ghost Hard Palate Green: Floor of Nasal Fossa Blue: Ghost image of inferior border of the mandible |
|
|
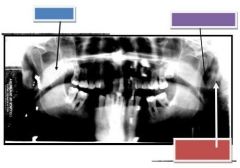
Blue: Soft palate
Purple: Soft tissue of ear Red: Styloid process |
|
|
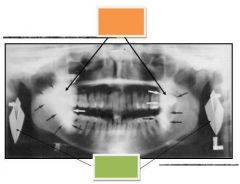
Orange: Ghost image
Green: Real Image |
|
|
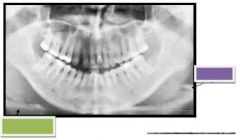
Green: Hyoid bone
Purple: Epiglottis |
|
|
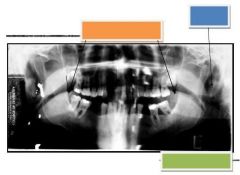
Orange: Dorsum of tongue
Blue: Ear lobe or auricle Green: Styloid process |
|
|
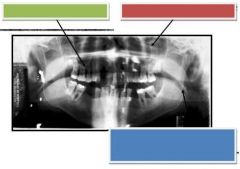
Green: Palatoglossal air space
Red: Nasopharyngeal sir space Blue: Oropharyngeal air space or Glossophsryngeal air space |
|
|
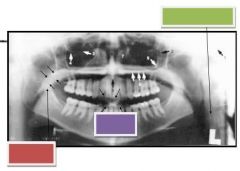
Green: Soft tissue of neck
Red: Soft palate Purple: Lip outline |
|
|
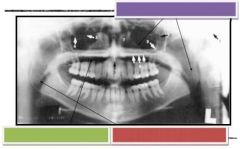
Purple: Nasopharyngeal sir space
Green: Palatoglossal air space Red: Oropharyngeal air space |
|
|
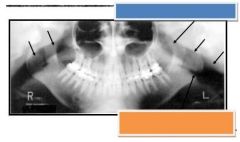
Blue: Nasopharyngeal sir space
Orange: Oropharyngeal air space |
|
|
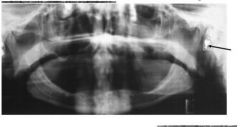
Hearing Aid
|
|
|
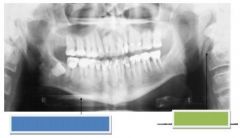
Blue: Ghost image of Hyoid bone
Green: Styloid process |

