![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dysmorphic Syndromes:
State the three types of abnormalities and define them. |
Malformation: caused during organogenesis
Deformation: abnormal shape/position due to mechanical forces Disruption: destructive process after fetal development |
|
|
Dysmorphic Syndromes:
What does CGH stand for? |
comparative genomic hybridisation (microarrays do this, they can also analyse SNPs)
|
|
|
Dysmorphic Syndromes:
What causes congenital malformations? |
genes and/or environment (chemical, infections, mechanical)
|
|
|
Dysmorphic Syndromes:
What deletion does a Prader-Willi kid have? |
15q11-13 paternal
|
|
|
Dysmorphic Syndromes:
What deletion does an Angelman syndrome kid have? |
15q11-13 maternal
|
|
|
Common ED Presentations:
What three systems are involved in cardiac arrest? |
Respiratory
Neurological Circulatory Failure in these -->hypoxia and acidosis -->cardiac arrest |
|
|
Common ED Presentations:
What are the normal ranges for kids (up to 12years) for RR, HR and BP |
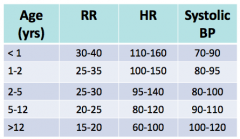
|
|
|
Common ED Presentations:
State the 7 classic red flags for a deteriorating kid. |
1. purpuric rash
2. bulging fontanelles 3. biphasic stridor 4. grunting 5. high pitched scream 6. bile stained vomit 7. persistent tachycardia |
|
|
Common ED Presentations:
What are the classic signs of respiratory distress in a child? |
1. intercostal indrawing
2. subcostal recession 3. grunting 4. nasal flaring 5. head bobbing (infants) 6. cyanosis 7. accessory muscle use 8. tripod posturing |
|
|
Common ED Presentations:
What things on history get you worried about fluid status for a child? |
<1/2 normal intake
<4 wet nappies in 24 hours |
|
|
Common ED Presentations:
What does decorticate posturing look like and what does it indicate? |
fingers, wrists and arms flexed.
Suggests a lesion above the brainstem. |
|
|
Common ED Presentations:
What does decerebrate posturing look like and what does it indicate? |
Arms straight and wrist and hangs flexed outwards (laterally)
Suggests a lesion below brainstem/brainstem about to herniate. |
|
|
Common ED Presentations:
What is the treatment for severe croup? |
1. oxygen
2. dexamethasone PO 0.15mg/kg 3. adrenaline neb 4mL 1:1000 4. admit patient |
|
|
Common ED Presentations:
What are the indicators of severe asthma? (6) |
1. persistent tahcycardia and tachypnoea
2. SpO2 <93% 3. use of accessory muscles 4. altered mental state: agitated, drowsy, unresposive 5. can't talk in sentences/count to 10 6. pulsus paradoxus BEWARE SILENT CHEST |
|
|
Common ED Presentations:
What is in a septic work up? |
1. FBC + film + cultures
2. CXR 3. UA 4. stool culture/faecal WCC 5. lumbar puncture |
|
|
Common ED Presentations:
How does an intussesseption classically present? |
crescendo-ing colicky pain that resolves spontaneously then repeats.
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
Define a macule |
flat and impalpable
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
Define a papule |
circumscribed and elevated lesions (bumps)
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
Define a vesicle |
circumscribed, elevated, fluid-filled lesions. Normally <0.5cm in diameter.
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
Define a pustule. |
elevated lesion with purulent contents.
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
Define peteichae |
flat, non blanchable spots caused by haemorrhage. Normally <0.5cm in diameter (bigger = purpura).
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
State the seven infections from the lecture that have vesicular rashes. |
Varicella
HSV Impetigo Hand foot and mouth Molluscum contagiosum Dermatitis herpetiformis Steven-Johnson syndrome |
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
Chickenpox; 1) What is the incubation period? 2) When is the infectious period? 3) Where is the rash? |
1) 10-21 days (28days if VZIG administered)
2) infectious form 48hrs prior to rash until lesions crust 3) predominantly truncal rash, can be on face and in hair line. |
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
What is a common complication of chickenpox in kids? |
Bacterial superinfection with group A strep or staph
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
What are complication of VZV in adults? |
Encephalitis
Cerebellitis Pneumonitis Hepatitis Arthritis |
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
What is shingles in the 7th nerve distribution called? |
Ramsey-Hunt syndrome
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
At what period of pregnancy must the mother be infected to put the foetus at risk of congenital varicella syndrome? |
First 5 months
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
At what perinatal period woud a VZV infection cause severe neonatal disease? |
48hours prior to birth and 5 days after delivery.
Give VZIG! |
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
What abnormalities do you see in congential varicela syndrome? |
skin scars ~80%
limb abnoramalities (hypoplasia) ~70% eye defects (cataracts, chorioretinitis, optic atrophy) ~60% prematurity ~50% brain abnormalities (cortical atrophy low IQ) ~ 46% |
|
|
Infectious diseases:
How efficacious is the VZV vaccine? |
prevents any disease in 80-85%.
Better at preventing severe disease (>95%) |
|
|
Infectious Disesases:
What causes a herptic whitlow? |
HSV 1 or HSV 2.
Can be confused with a bacterial infection but DO NOT DEBRIDE! As this may cause a bacterial superinfection. |
|
|
Infectious diseases:
What is the mortality rate of neonatal HSV infection? |
25%
(give IV acyclovir!) |
|
|
Infectious diseases:
What causes hand, foot and mouth disease? How does it present? |
Enteroviruses (most common Coxsackie 16 and EV71).
Constitutional symptoms, plus: papular-vesicular rash on hands, feet, mouth and buttocks. EV71 associated with neurological demyelination syndromes/ encephalitis |
|
|
Infectious diseases:
What bugs cause impetigo? |
Staph and Strep
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
What infections present with a maculopapular rash? |
• Measles • Rubella • Scarlet fever • Kawasaki disease • Erythema infectiosum or fifth disease • Roseola infantum (HHV-6/7) • Viral rashes in general
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
How does measles present? |
Catarrhal illness
fever conjunctivitis Koplik spots rash (maculopapular, blotchy, red or pink in colour, raised in places, and starts behind the ears and on the face, spreading downwards) |
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
How can you diagnose measles? |
PCR
IgM 3 days after rash appears |
|
|
Infectious diseases:
What causes Scarlett fever? How does it present? |
Group A Streptococci
Rash - dark red, punctiform, circumoral pallor, Desquamation Inflammation of tongue |
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
What cardiac problem is associated with Kawasaki disease? |
coronary artery aneurysm
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
What are some synonyms for slap cheek disease? How does it present? |
Fifth's disease
Parvovirus B19 Erythema Infectiosum Rash: red cheeks then 1-2 weeks later lacy rash on arms and legs. Heat can make it worse. Arthralgia |
|
|
Infectious Disease:
What causes Roseola Infantum? How does it present? |
Human herpes virus 6
High fever then widespread maculopapular rash mainly on the trunk. |
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
What does the rash of a meningococcal infection look like? |
ealry maculopapular rash on trunk (which may blanch) then characteristic petechial rash anywhere on body, non blanching.
|
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
How do you diagnose Meningococcal infection? |
Clinical features
Gram stain culture from blood, CSF or petechial lesions PSR blood and CSF Serology FBC - WCC high or low, DIC thrombocytopaenia |
|
|
Infectious Diseases:
What is the treatment for meningococcal disease? |
IV ampicillin AND
IV 3rd gen cephalosporin (cefotaxime/ceftriaxone) (Rifampacin to close contacts for prophylaxis) |
|
|
Infectious diseases:
What do you do for any neonate that is febrile? |
Septic workup AND start on empirical antibiotics
FBC, cultures, UA, LP, CXR |
|
|
Infectious diseases:
What are the common causative organisms of meningitis in the neonate? |
Group B strep
E. coli Then... other GNR, Listeria, Strep Pneumoniae, enterococci, N. meningtidis, S. aureus |
|
|
Infectious diseases:
Which GNR can cause severe brain abscesses? |
Enterobacter sakazakii
Citrobacter species |
|
|
Infectious diseases:
What are the symptoms of congenital CMV? |
Microcephaly/IUGR
Jaundice Petichial rash Chorioretinitis Hepatosplenomegaly Long term: 5% cerebral calcification -> reduced IQ, deafness. [Most common congenital infection in Aus 1/200] |
|
|
Infectious diseases:
What is the congenital rubella triad? |
Cataracts
Cardiac CNS (deaf, microcephalic) |
|
|
Adolescent Health:
The HEADSS assessment is a psychosocial biopsy. What does it stand for? |
Home
Education, eating, exercise Activities and peers Drugs Sexuality Suicide and depression Sleep, safety, spirituality |
|
|
Adolescent Health:
What are the top three reasons for adolescents to be in hospital? |
1. Pregnancy
2. Injury or poisoning 3. digestive system problems |
|
|
Adolescent Health:
What are some changes in sleep architecture during adolescence? |
Sleep onset delay
Less slow wave sleep [means less restorative sleep] |
|
|
Adolescent Health:
What are the diagnostic criteria for insomnia? |
All of the following occurring in the last 4 weeks causing significant impairment or distress:
1. difficulty initiating and maintaining sleep 2. Early morning waking and non-restorative sleep |
|
|
Adolescent Health:
What are the top three burden of disease illnesses in 10-14 yr olds? |
1. Asthma 22%
2. ADHD 15% 3. Autism spectrum disorder 9% |
|
|
Adolescent Health:
What is the major burden of disease in 15-19 yr olds? |
1. Anxiety and depression 26% F, 16% M
2. Asthma 14% [75% of mental health problems begin in adolescence] |
|
|
Asthma:
What percentage of asthmatics experience atopy? |
80%
|
|
|
Asthma:
Define mild, moderate and severe asthma. |
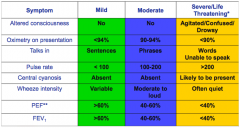
|
|
|
Asthma:
What medications are used to treat acute asthma? |
1. Oxygen
2. Salbutamol [6 puffs/2.5mg neb <20kg, 12 puffs/5mg neb >20kg] - repeat as needed q20m 3. Oral prednisolone (redipred) [stat 2mg/kg max 60mg, then 1mg/kg for 3 days] (mod to severe) 4. Ipatropium bromide (atrovent) [4 puffs <20kg, 8 puffs >20kg] - q6h (severe) 5. IV salbutamol (severe) 6. IV MgSO4 (severe) 7. Aminophylline (severe) 8. CPAP (severe) 9. intubate (severe) |
|
|
Asthma:
What are the criteria for discharge after as asthma attack? |
depends on patient, but generally salbutamol < q3h
|
|
|
Cardiology:
What are the features of fetal circulation? |
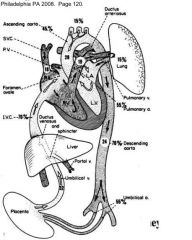
Ductus venosum + SVC -> foramen ovale -> LA, LV -> aorta
Ductus venosum + SVC -> RA, RV -> pul. art -> PDA (85%), lungs (15%) |
|
|
Cardiology:
When does the patent ductus arteriosus close? |
Functionally, 10-15 hrs after birth, permanently at 2-3 weeks.
|
|
|
Cardiology:
Which ventricle is dominant as a neonate? |
Right ventricle. This slowly diminishes throughout childhood.
|
|
|
Cardiology:
What is the incidence of congenitial heart disease? What are the most common defects? |
6-9/1000 of live births (most common congenital defect) 75 are curable or mild.
VSD 30-35% PDA 10-11% ASD 8-10% |
|
|
Cardiology:
What are the four major aetiological categories for congenital heart disease? |
Chromosomal abnormalities (21, 18, 13, XO)
Genetic syndromes Toxins (alcohol, DM, warfarin) Maternal SLE, rubella Most don't have a clear explanation |
|
|
Cardiology:
What features does congenital heart disease present with? |
Cyanosis
Increased WOB Sweating Feeding problems Growth problems |
|
|
Cardiology:
What are the 6 grades of murmurs? |
1. scarcely audible, thrill absent
2. soft, thrill absent 3. loud, thrill absent 4. loud, faint thrill 5. very loud, thrill 6. audible without a steth |
|
|
Cardiology:
What are the features of an innocent murmur? |
Normal peripheral exam and history.
Systolic, ejection, grade 1-3, change with body position. [eg. Still's, pulmonary flow murmur, carotid bruit, venous hum] |
|
|
Cardiology:
When will you see acyanotic congenital heart disease? |
Left to right shunts.
ASD, VSD, PDA, AVSD and obstructive lesions: AS, PS, coarctation |
|
|
Cardiology:
What are some causes of cyanotic congenital heart disease? |
Tetralogy of Fallot
Transposition of the great arteries Truncus arteriosus (aorta and pulmonary trunk don't divide) Tricuspid atresia |
|
|
ENT:
Which type of otitis will you get increased pain when the pinna is gently pulled? |
Otitis externa
|
|
|
ENT:
What are some of the causative organisms in otitis media? |
S. pneumoniae, H.flu, M. catarrhalis, S. areus
Viral (Usually precipitated by an URTI then bacteria grow in the fluid in teh blocked Eustachian tube) |
|
|
ENT:
What are the subtypes of Otitis Media? |
Acute
OM with effusion/secretory OM Chronic suppurative OM Adhesive OM |
|
|
ENT:
What are the indications for tonsillectomy/adenoidectomy? |
Recurrent tonsillitis.
6x/yr, 4-5x/yr for 2 years, 3x/yr 3 years OSA |
|
|
Derm:
What are the two causes of impetigo? |
Staph aureus and GAS (more rare)
|
|
|
Derm:
What causes ringworm? |
Groupd of fungii called dermatophytes.
|
|
|
Derm:
What causes molluscum contagiosum? |
a DNA poxvirus called the molluscum contagiosum virus.
Individual papules take 6-12 months to resolve. Can deroof or use topical irritants, imiquimod. |
|
|
Derm:
What are the four types of HPV wart formations? |
1. verrucae
2. plane warts 3. plantar warts 4. condyloma accuminata |
|
|
Resp:
What percentage of ARIs are viral? State causative organisms. |
90%
Rhinovirus Respiratory syncytial virus Parainfluenzae types 1, 2, 3 Influenza types a, b Adenovirus Metapneumovirus |
|
|
Resp:
10% of ARIs in children are caused by bacteria. What are the common causative organisms? |
• Beta-haemolytic streptococcus
• Streptococcus pneumoniae • Haemophilus influenzae • Staphylococcus aureus • Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Legionella |
|
|
Resp:
Classify Streptococcus |
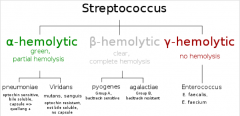
|
|
|
Lifestyle precursors to adult disease:
What make sup the metabolic syndrome? |
Central adiposity, BMI>30
Insulin resistance Dyslipidaemia Hypertension |
|
|
Haem:
What is the pathophysiology of G6PD deficiency? |
G6PD is the enzyme required to prevent RBCs from oxidative damage. Most deficient people have enzyme variants that keep them going and only experience cell lysis when there is an oxidative challenge - eg fava beans, certain drugs, infection
|
|
|
Haem:
What are the three variables that determine tissue oxygen delivery? |
Cardiac output
Haemoglobin Hb saturation |
|
|
Gastro:
What is the most common cause of viral gastroenteritis? |
rotavirus (watery stools, vomiting, fever)
|
|
|
Gastro:
What are the 5 broad aetiological categories for steatorrhoea? |
Pancreatic insufficiency
Inadequate bile salt action Inadequate absorptive service Enterocyte defect Defective lymphatic drainage |
|
|
Gastro:
What is the gene deletion in CF |
xsome 7, delta 508
|
|
|
Gastro:
What are the 2 screening/diagnostic tests for coeliac disease? |
IgA to tTG (tissue transglutaminase)
Endomysial antibody (EMA) Duodenal biospy - crypt hyperplasia, villous atrophy |
|
|
Gastro:
How do you calculate the osmotic gap in stool fluid? |
= stool osmolality - 2([Na]+[K])
>100 = osmotic diarrhoea (will cease when feeds ceased) <100 (50 in lecture) = secretory diarrhoea |
|
|
Gastro:
In a stool assessment, what does the presence of fat globules or fatty acid crystals indicate? |
fat globules: lipase def OR liver disease
fatty acid crystals: mucosal disease |
|
|
Gastro:
Which syndromes have an increased prevalence of coeliac disease? |
Downs
Turners Williams |

