![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Some of the differences between adults and children
|
A child’s head is larger in proportion to the rest of the body than that of an adult’s
Babies have an immature and unstable body temperature control mechanism Children have smaller airways with more soft tissue A child’s respiratory and heart rate is higher A child’s tracheal opening and oesophagus opening are closer together Children will dehydrate faster than an adult Children have a smaller blood volume and are at greater risk of death or shock from what would appear to be a relatively small blood loss |
|
|
Paediatric Chart
|
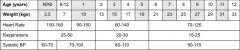
|
|
|
Air way difference in a paediatric
name them? |
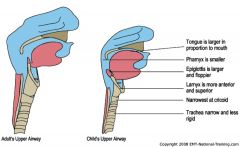
|
|
|
GCS
Eye opening Best verbal response Best motor response |
Eye Opening:
Spontaneous 4 Reacts to speech 3 Reacts to pain 2 No response 1 Best Verbal Response: Babbles, follows objects 5 Irritable, cries 4 Cries to pain 3 Moans and grunts 2 No response 1 Best Motor Response: Spontaneous 6 Localises to pain 5 Withdraws from pain 4 Flexion response 3 Extension response 2 No response 1 |
|
|
Poor Perfusion in Children
re Perfusion Status Assessment |
Radial Pulse:
unpalpable Pulse Rate: <60 or >110 Blood Pressure: <100mmHg Systolic Skin: pale, cold, clammy Level of Consciousness: altered |
|
|
Weight:- Describe Neonate Weight and other weights relevant to age?
|
Neonate 3.5kg
6 Month 7kg 1 Year10kg 2-12 Years (2xage)+9=____kg |
|
|
Define Croup?
(Laryngotracheobronchitis) |
Croup is acute inflammation of the upper and lower respiratory tracts most commonly caused by parainfluenza virus type 1 infection. It is characterized by a barking cough and inspiratory stridor. Diagnosis is usually obvious clinically but can be made by anteroposterior neck x-ray. Treatment is antipyretics, hydration, nebulized racemic epinephrine, and corticosteroids. Prognosis is excellent.
|
|
|
A child’s blood volume is approximately?
|
80 ml/kg
|

