![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the difference between AC and DC and what are examples? |
Direct current means the current flows the same way around the circuit all the time like a battery Alternating current keeps switching direction like the mains electricity in a home. |
|
|
What are photocells and how do they work? |
Photocells (solar cells) generate electricity directly from sunlight. They generate direct current and are usually made from silicon- a semiconductor. When the silicon absorbs the light it knocks a few electrons loose which then flow round a circuit creating electricity. |
|
|
What does the current and power output of a photocell depend on? |
1) The surface are (the bigger the cell, the more electricity produced) 2) The intensity of the light (brighter light, more electricity) 3) The distance from the light source (the closer the cell, the more intense the light hitting it will be) |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages to photocells? |
Advantages There are no moving parts- so they're sturdy, low maintenance and will last. You don't need cables or fuel and solar power won't run out. Disadvantages No sunlight = no power |
|
|
What is passive solar heating? |
Passive solar heating is when energy from the sun is used to heat something directly i.e. solar water heaters use this to heat water which can then be pumped to radiators to heat the building. |
|
|
What are advantages and disadvantages to wind turbines? |
Advantages 1) cheap to run 2) No polluting waste produced 3) Wind is renewable Disadvantages 1) You need many to replace a power station 2) Visual pollution 3) It's impossible to increase supply 4) Wind isn't fast enough. |
|
|
What is the national grid? |
The national grid is the network of pylons and cables which covers the whole county. It takes electricity from power stations to just where it's needed in homes and industry. |
|
|
What are the three stages of a power station? |
1) Use the fuel to produce heat which generates steam. 2) The steam drives the blades of a turbine. 3) This rotating movement is converted to electricity by the generator using electromagnetic induction. |
|
|
What are the five different power sources and what are their advantages and disadvantages? |
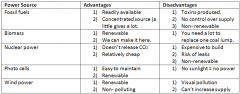
|
|
|
What is electromagnetic induction? |
The creation of a voltage in a wire which is experiencing a change in magnetic field. |
|
|
What is the dynamo effect? |
Using electromagnetic induction to transform kinetic energy into electrical energy is called the dynamo effect. |
|
|
How can you get a bigger voltage when a conductor moves through a magnetic field? |
Increase: 1) The strength of the magnet 2) The number of turns on the coil 3) The speed of the movement |
|
|
How do generators work? |
Generators rotate a coil in a magnetic field. Every half a turn, the current in the coil swaps direction. This means the generators produce an alternating (AC) current. |
|
|
What are transformers used for? |
To increase the voltage for distribution from a generator to homes you use a step-up transformer then to bring it down to safe usable levels you use a step- down transformer. |
|
|
What is the equation for efficiency? |
Efficiency= useful energy output/ total energy input (x 100%) |
|
|
What is power measured in? |
Watts (W) or kilowatts (kW) here 1 watt means 1 joule per second. |
|
|
What is the equation for power? |
power (W) = voltage (V) x current (A) |
|
|
What is a kilowatt- hour (kWh) |
A kilowatt hour is the amount of electrical energy converted by a 1kW appliance left on for 1 hour. |
|
|
What is off- peak electricity and what are the advantages and disadvantages? |
Electricity supplied during the night (off-peak) is sometimes cheaper. Advantages are that it is cost- effective for the electricity company and it's cheaper for consumers. Disadvantages are that there's a risk of fire if there's no one to see these appliances at night and you start fitting your routine around the cheap rate hours. |
|
|
What is the greenhouse effect? |
1) Energy from the Sun is absorbed by Earth. 2) The Earth then radiates this heat back out to cool us down. 3) This is absorbed by greenhouse gases such as CO2 and methane. 4) These gases then re- radiate in all directions including back to Earth. So the atmosphere acts as an insulating layer, stopping the earth losing all it's heat at night. |
|
|
How has the amount of greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane and water vapour) increased in recent years? |
Carbon dioxide People use more energy which we get from burning fossil fuels which releases CO2. More land is needed so deforestation is high. Methane Cattle farming has increased and cattle digestion produce methane. Decaying waste in landfill sites produce it Water vapour As global temperature increases so does this. Power stations also produce it. |
|
|
What are the human and natural causes of temperature/ weather change? |
Human 1) The rising CO2 level caused by humans 2) Soot and gases produced by factories can reflect heat from cities back don to Earth, which can cause an increase in temperature. Natural 1) Ash and gases from volcanoes can reflect radiation back to Space, cooling the Earth. 2) Changes in our orbit around the Sun can cause ice ages. |
|
|
How does nuclear radiation occur? |
When an unstable nucleus decays, it gives off one or more kinds of nuclear radiation over time. |
|
|
What are the three types of radiation and what do they cause? |
1. Alpha (α) 2. Beta (β) 3. Gamma (γ) All three cause ionisation- the atom loses or gains electrons to become ions. |
|
|
What could happen when radiation enters human cells? |
It can ionise molecules and damage DNA. This can cause mutations that could lead to cancer. Very high does can kill cells completely. |
|
|
Describe the three types of radiation. |
Alpha 1) Relatively big, heavy and slow moving with 2 protons and 2 neutrons. 2) They don't penetrate far and can be stopped by paper or skin. 3) They're strongly ionising- they bash into loads of atoms and knock them down. Beta 1) These are electrons- small and fast. 2) Penetrate moderately before colliding, so moderately ionising. They can be stopped by a thin sheet of metal. Gamma 1) High frequency EM wave. 2) No mass and no charge . They can penetrate a long way meaning they're weakly ionising. 3) Stopped by thick concrete or lead. |
|
|
Describe the uses of alpha radiation. |
Alpha is used in smoke detectors. Smoke detectors have a weak source of alpha radiation next to two electrodes. The radiation ionises the air and a current flows between the electrodes. But if there's fire, the smoke absorbs the radiation- the current stops and the alarm sounds. |
|
|
Describe the uses of beta radiation. |
Beta can be used as medical tracers. If the radiation is injected into the body it can be followed using an external radiation detector. A computer converts the reading to a TV display showing where the strongest reading is coming from. These 'tracers' can show if the body is working properly. Beta is also used in thickness control. You direct radiation through the stuff being made (e.g. paper or cardboard), and put a detector on the other side, connected to a control unit. When the amount of detected radiation goes down, the paper is too thick so the control unit pinches the rollers and vice versa. |
|
|
Describe the uses of gamma radiation. |
Gamma rays will kill all living cells so can be used to treat cancers. It must be directed carefully so no normal cells are damaged. They are also used to sterilise medical instruments- by killing ll the microbes. Several industries also use it to do non-destructive testing. |
|
|
How does a nuclear power station differ from a regular power station? |
Nuclear fission produces the heat to make the steam instead. Atoms in the nuclear fuel (uranium) are split into two, releasing lots of heat energy. Water is used as a coolant to take away the heat produced and use it to produce steam to drive a turbine and generator. |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear power? |
Advantages 1) No CO2 is produced. 2) It releases a lot more energy so less is needed. 3) Uranium is relatively cheap. 4) There's still plenty uranium left. Disadvantages 1) Power stations are expensive to build and maintain. 2) The power stations take longer to start up. 3) Processing the uranium before use causes pollution. 4) Risk of leaks and radioactive waste. 5) Uranium is non-renewable. |
|
|
What is the order of planets including the asteroid belt? |
1. Mercury 2. Venus 3. Earth 4. Mars 5. Asteroid Belt 6. Jupiter 7. Saturn 8. Uranus 9. Neptune |
|
|
What are the slightly elongated circles called that the planets orbit on? |
Ellipses. |
|
|
What is the solar system held together by? |
Gravitational attraction. |
|
|
What is a force that causes a circular motion caused by? |
A centripetal force. |
|
|
How can we tell that asteroids have collided with Earth? |
1) Big craters. 2) Layers of unusual elements in rocks. 3) Sudden changes in fossil numbers between adjacent layers of rock, as species suffer extinction. |
|
|
What are comets? |
Balls of rock, dust and ice which orbit the Sun in very elongated ellipses. |
|
|
What are NEOs? |
Near Earth Objects are asteroids or comets which might be on a collision course with Earth. |
|
|
How do we believe the moon was formed and what is the evidence for this theory? |
After the Earth was formed, a Mars- sized planet crashed into it and the debris formed the moon. The evidence to support is: 1) The moon has a lower density than Earth and doesn't have a big iron core. 2) Moon rocks contain few substances which evaporate at low temperatures- suggesting that the Moon formed from hot material. |
|
|
What do scientists use to measure distances in Space? |
Light years- one light year is the distance that light travels through a vacuum in one year. |
|
|
How are black holes formed? |
When a really big star has used up all its fuel, it explodes. What's left is really dense- so much so that nothing can escape it's strong gravitational attraction; a black hole. |
|
|
Why would it be difficult keeping astronauts alive for a couple years trip to Mars? |
1) The spacecraft would have to carry loads of food, water and oxygen. 2) You'd need to regulate the temperature and remove toxins from the air. 3) The spacecraft would have to shield the astronauts from radiation in space. 4) Long periods in low gravity causes muscle wastage and loss of bone tissue. 5) It would be psychologically stressful. |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages to unmanned probes? |
Advantages 1) They don't have to carry food, water etc. 2) They can withstand lethal conditions. 3) With no people, more instruments can fit. 4) They're cheaper. 5) No possibility of anyone getting hurt. Disadvantages 1) They can't think for themselves. 2) They can't do maintenance or repairs. |
|
|
What is the red- shift? |
As the universe expands, galaxies move further and further away from us an the frequencies are all lower than they should be- they've shifted towards the red end of the spectrum This is called the red-shift. |
|
|
What is the Big Bang Theory? |
1) All the matter in the Universe occupied a very small space. Then it exploded- the space started expanding and it is all still going on. 2) It lets us guess the age of the Universe- around 14 billion years old. |
|
|
What is the life cycle of a star? |
1) Stars form from clouds of dust and gas. 2) The fore of gravity makes them spiral together to form a protostar. The heat rises. 3) When the heat rises enough, hydrogen nuclei undergo thermonuclear fusion to become helium nuclei and give out massive amounts of heat and light. A star is born. It's then in a stable period called a main sequence star and this lasts several billion years. 4) Eventually the hydrogen runs out and the star swells to form a red giant. 5) If the star was small- medium it then becomes unstable and ejects its outer layer of dust and gas as a planetary nebula. This leaves behind a hot, dense solid core- a white dwarf which just cools down and fades away. 6) Big stars, however, form red super giants- they glow more brightly and expand and contract until they explode and become a supernova. 7) The supernova then throws several outer layers of dust and gas into Space, leaving a dense core called a neutron star. If the star is big enough it will become a black hole. |
|
|
What was the original theory for the universe, what was Galileo and Copernicus' new theory and what is the current theory? |
The Greeks believed in the Ptolemaic model: the Sun, moon, planets and stars all orbited the Earth which was the centre of the universe. Galileo and Copernicus proved that they actually orbited the Sun. It was later prove that it wasn't perfect circles either but ellipses. |

