![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the clinical manifestations of opportunistic infections from Pseudomonas Aeruginosa?
|
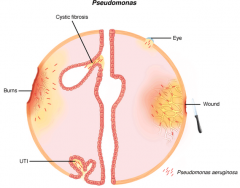
Burn - leading cause M&M
Immune compromised hosts Eye - conjunctivitis & keratitis -> blindness CF pts - bronchitis & pneumonia (biofilm) UTI Ear - Swimmer's ear (otitis externa) Nosocomial - 10% all hosp. acquired Skin |
|
|
What toxins does Pseudomonas Aeruginosa deliver and how?
|
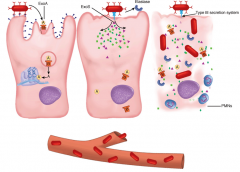
ExoA - AB toxin that blocks protein synthesis (same as DT)
ExoS - delivered by type 3 secretion system to cytoplasm. Intracellular dysfunction (cytoskeleton) Elastase - secreted extracellularly 3 toxins - destroy cell and lead to bacteremia |
|
|
What toxin does Pseudomonas Aeruginosa form that attacks the lung & blood vessels in the lung?
|
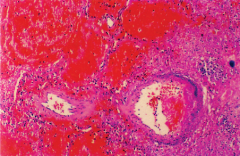
Elastase breaks down elastin which is in high concentration in lung and blood vessels.
Hemorrhagic destruction of vessels is shown above. |
|
|
How is Pseudomonas Aeruginosa different in CF patients? How does it persist?
|
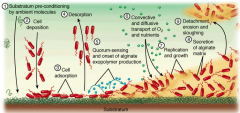
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in CF patients has mutations that cause over secretion of alginate exopolymer that forms a biofilm. High Osm & thick CF secretions promote biofilm formation.
Desquamation in CF pts facilitates binding and hinders clearing of the organism |
|
|
What is unique about the color of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa cultures?
|
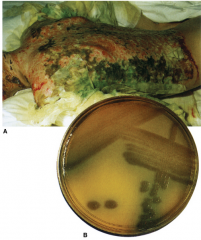
It forms pyocyanin which gives it a blue hue mixed to the underlying yellow. This is regularly seen on cultures & occasionally on pts.
This is used in addition to Oxidase (+) to identify from other species. |
|
|
What is the effect of the biofilm?
|
It prevents antimicrobial drug penetration.
Retards access by immune cells. Retards phagocytosis & PMN fx. |
|
|
What is alginate and describe its properties?
|
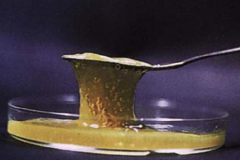
It is viscous and mucoid and mutations overproduce in CF pts.
|
|
|
Describe the pathology of Legionella pneumonia
|
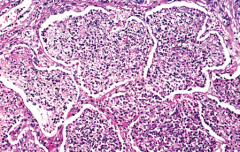
Alveoli fill with exudate. Septa begin to degenerate. LP has a tropism for lung and causes necrotizing multifocal pneumonia and intracellular bacteria (in macrophage)
|
|
|
Describe how Exotoxin A works on host cells?
|
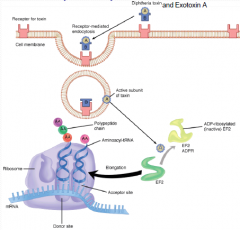
An AB toxin that inhibits EF-2 via ADPR to inhibit protein synthesis (just like DT)
|
|
|
Does ____ produce glycocalyx/capsule?
Staph aureas Coagulase neg staph GAS List. Monocytogenes E Coli Haemophilus Infl. |

|
|
|
Where does Legionella Pneumophila reside?
|
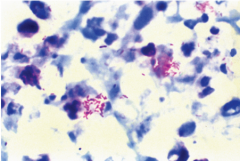
Legionella Pneumophila is a facullative intracellular pathogen that replicates in monocyte-macrophages. Especially alveolar macrophages
It is found in 10% of healthy people |
|
|
What is the bacteriology of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa?
|
Large slim gram negative bacilli
Aerobic & motile & oxidase positive Grows in many medias & at many temperatures Frequent contaminate in labs, thus quality direct sample is required. Produces pyocyanin Highly resistant due to porins that restrict entry to periplasma space. |
|
|
What are the extracellular products that P. Aeruginosa produces? (5)
|
Alginate capsule - resists phagocytosis
Exotoxin A (95% of strains) - AB toxin that endocytosis & inhibits EF2. Stops protein synthesis. (same MOA as DT) Exoenzyme S - AB toxin that ADPR intracellular proteins (cytoskeleton) Elastase - Degrades elastin, Human IgG, IgA, complement & some collagens. Phospholipase C - hemolysin, degrades phopholipids & causes beta hemolysis (like Staph Aureas) |
|
|
How does Alginate capsule/mucoid exopolysaccharide aid p. aeruginosa in pathology?
|
Aids in adhesion to bare epithelium (CF)
Retards immune response & PMN Decreases antibiotic penetration (majority due to outer membrane porin protein) |
|
|
How does exoenzyme S aid p. aeruginosa in pathology?
|
A cytopathic toxin which is injected by type 3 mech. The toxin ADPR several intracellular proteins including cytoskeleton filament, vimentin, but NOT EF2.
|
|
|
How does Elastase aid pseudomonas aeruginosa in pathology?
|
Elastase - Degrades elastin, Human IgG, IgA, C3b, C35a & some collagens
Elastin is a major component of lung * blood vessels |
|
|
How does Phospholipase C aid pseudomonas aeruginosa in pathology?
|
Phospholipase C - degrades phopholipids to lyse cells to acquire nutrients. Causes beta hemolysis (like Staph Aureas).
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of infection of CF patients w/ p aeruginosa?
|
Causes bronchitis & pneumonia. It is the leading cause death in CF pts
Mutation in Cl- secretion leading to fluid depletion on airway surface. Leads to decreased mucociliary clearance. Majority start non mucoid but become mutated mucoid to overproduce to allow formation of biofilm |
|
|
How does p aeruginosa clinically present?
|
opportunistic infections in a variety of locations.
It is rapid, destructive infection that invades vessels. Commonly causes foliculitis in hot tubs |
|
|
Describe Pseudomonas Aeruginosa skin lesions?
|
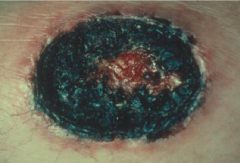
Bacteremia may lead to papules that progress to black necrotic ulcres due to the direct invasion of vessels.
Result from environmental contamination, leads to necrotic lesions that may lead to bacteremia. |
|
|
What is the bacteriology of legionella?
|
Thin, pleomorphic gram (-) bacilli
Stains poorly Requires special BYCE medium to aerobically grow slowly (2-5d) Multiple serotypes, majority are serotype 1 |
|
|
Who gets legionella pneumophila how is it spread and are they immune?
|
5% Attack rate in healthy pts but higher in immunocompromised pts. Person2person infection has NOT been observed. Mortality is 15% but higher in those w/o CMI. Post infection immunity is uncertain.
Associated w/ large building cooling towers water sources which aerosolize |
|
|
What are the important virulence factors in legionella pneumophila?
|
MIP - macrophage invasion potentiator is found on its outer membrane
Produces peptide toxin that blocks oxidative burst to persist in macrophages |
|
|
How do each of the virulence factors contribute to disease (MOA)?
|
MIP - aids the LP into the macrophage to evade immune system.
Peptide toxin that blocks oxidative burst to persist in the macrophage. |
|
|
How would legionairres disease present?
|
Begins w/ myalgia & HA. then raising fever, a dry cough. Sometimes chils, pleuritic chest pain, vomiting, diarrhea & confusion can be present.
This is a severe toxic multifocal pneumonia that is restricted to large airways. |
|
|
How would Pontiac Fever present? What are the symptoms likely from?
|
This is self limited and mild febrile illness. It is described as "flu like"
No pneumonia Low mortality rate Symptoms may be from immune response |
|
|
How would you confirm a possible case of legionairres disease?
|
Gold standard is direct, quality sample culture on special BYCE medium.
DFA & Urine detect Ab to the Ag found only on Serotype 1 (majority) and is 25-50% sensitive. Rapid but not accurate. |
|
|
What is the source of legionaires disease?
|
Associated w/ large building cooling towers water sources which aerosolize
Can be found in amoebas, parasites (resemble macrophages) |
|
|
Does p. aeruginosa have any antibiotic MOA to persist?
|
Resistant to many species due to porins which restrict entry into the periplasmic space.
Have to use newer aminoglycosides or 3rd generation cephalosporin. |
|
|
Does legionella pneumophila have any antibiotic MOA to persist?
|
It has beta lactamase making beta lactams innefective.
Treated for 10-21d w/ erythromycin. azithromycin, or clarithomycin. |
|
|
What is the signifigance of biofilm? Who produces it and in what situations?
|
Biofilm decreases susceptibility to enviroment. Forms in water pipes. And commonly in CF pts.
|
|
|
What is the difference between the capsule and biofilm production observed in p. aeruginosa?
|
Both are the same substance, an alginate polymer. The genes encoding this mucoid exopolysaccharide slime layer may mutate (common in CF pts) leading to overproduction.
|
|
|
What is swimmer's ear?
|
It is otitis externa commonly caused by pseudomonnas aeruginosa.
|
|
|
What toxins produced by p aeruginosa have ADPR fx? What do they target in our cells? Who shares this same target?
|
Exoenzyme S - targets cytoskeletin intracellular protein
Exotoxin A - targets EF2 (same target as DT) |
|
|
Why are mucoid strains of p. aeruginosa isolated from CF patients but not by other type of infections?
|
Selective advantage, as they form biofilm and chronic infection state...?
|
|
|
What are the microbes that cause lung infection in CF patients?
|
PBS (MMM)
p. aeruginosa Burkholderia cepacia Stenotrophomonas maltophila Methicillin resistnat Staph aureas Mycobacterium avium (resistant) Mycobacterium abcessus |
|
|
What body system and cell type are most affected by Legionella infection?
|
Tropism is for lungs.
Targets and survives in macrophages. |
|
|
What test gives the most rapid diagnosis for a suspected Legionella infection? Which test is most sensitive?
|
DFA or urine Ag screen are both rapid but inaccurate for diagnosis. Gold standard is culture on BYCE which takes 2-5d.
Serology take 3-4wks to show up. |

