![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cementum is not laid down until what disintegrates?
|
epithelial root sheath
|
|
|
Precursors of cementoblasts are what type of cells? From what area do they originate?
|
fibroblasts, dental sac
|
|
|
___________ is similar to bone.
|
cementoid (cementum)
|
|
|
Cementum begins being deposited when the tooth is where in position?
|
occlusion
|
|
|
At the time of cementum deposition, how much of the root has already been formed?
|
2/3
|
|
|
T or F: Cementum, like dentin, is laid down and then mineralized.
|
True
|
|
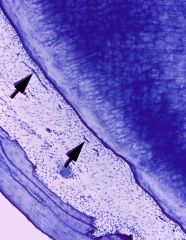
What are the black arrows pointing to? From what do they originate?
|
epithelial rests; epithelial root sheath
|
|
|
Acellular cementum is also known as _____________?
|
primary cementum
|
|
|
T or F: acellular cementum thickness has huge variations throughout life?
|
False, varies little
|
|
|
Acellular cementum is found on the (cervical/apical) 1/2 of the root?
|
cervical
|
|
|
Cellular cementum is found on the (cervical/apical) 1/2 of the root?
|
apical
|
|
|
What type of cell does cellular cementum have?
|
cementocytes
|
|
|
T or F: cellular cementum overlaps acellular cementum only at the middle 1/3 of the root?
|
True
|
|
|
Canaliculi in cementum are oriented towards the ____?
|
PDL
|
|
|
What provides nutrients for the cementoblasts?
|
PDL
|
|
|
T or F: Cementum is deposited throughout life and undergoes extensive remodeling?
|
False, it is deposited throughout life, but undergoes little remodeling
|
|
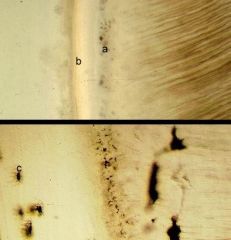
What are a-c? Also is the PDL to the left of the bottom picture or to the right? How can you tell?
|
a- granular layer of Tome's
b- acellular cementum c- cementocyte PDL is to the left because the processes of the cementocytes project in that direction to recieve nutrients. |
|
|
____________ occur when the cementoblast layer pauses.
|
arrest lines
|
|
|
Arrest lines are ________ calcified.
|
highly
|
|
|
Arrest lines appear (rough/smooth)?
|
smooth
|
|
|
Reversal lines are (more/less) common in cementum than bone?
|
less
|
|
|
Reversal lines are due to ___________ of the cementum.
|
remodeling
|
|
|
Reversal lines are (resistant/conducive) to resorption?
|
resistant
|
|
|
T or F: Like arrest lines, reversal lines are smooth in appearance?
|
False, they are scalloped
|
|

What are these lines?
|
arrest lines
|
|
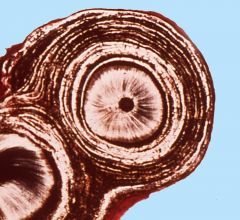
What are these concentric circles?
|
arrest lines
|
|
|
T or F: chemicals can be absorbed into cementum?
|
True, tetracycline is an example.
|
|
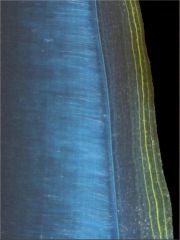
What chemical was absorbed into the cementum in this picture?
|
tetracycline
|
|
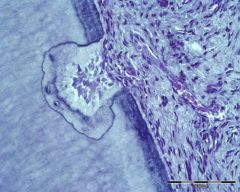
This picture looks like a tooth in bud stage, but it's not. What is this?
|
reversal line in cementum
|
|
|
Sharpey's fibers are (extrinsic/intrinsic)?
|
extrinsic, they are produced outside the tissue
|
|
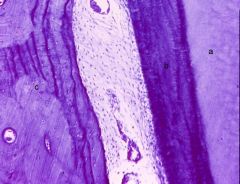
What are a-c?
|
a- dentin
b- cementum c- bone |
|
|
Cementicles are found in the (cementum/dentin/PDL)?
|
PDL and cementum
|
|
|
State the locations of free, attached and embedded cementicles.
|
Free are in the PDL. Attached are in the PDL but attached to the cementum. Embedded are within the cementum.
|
|
|
T or F: cementicles form on debris such as epithelial rests?
|
True
|
|
|
Cementicles resemble (true/false) pulp stones in that they have a ringed appearance?
|
false
|
|
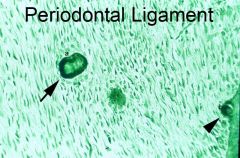
What are a and b?
|
a- free cementicle
b- attached cementicle |
|
|
Where are enamel pearls located?
|
On the outside of the root
|
|
|
What type of cytodifferentiation goes wrong in order to produce an enamel pearl?
|
a fibroblast becomes an ameloblast instead of a cementoblast
|
|
|
Name the OMG percentages for cementum and enamel.
|
overlap - 60%
meet - 30% gap - 10% |
|
|
T or F: if one spot on a tooth has overlap of cementum and enamel, the whole tooth will.
|
False, overlap changes from spot to spot on a tooth.
|
|
|
OMG percentages refer to (surfaces on a tooth/people)?
|
surfaces
|
|
|
T or F: overlap, meet and gap can all occur on the same tooth?
|
True
|
|
|
There are two types of bone around the tooth, what are they?
|
alveolar, basal
|
|
|
Basal bone occurs (above/below) the root?
|
below
|
|
|
T or F: Basal bone is continuous with the jaw bone?
|
True
|
|
|
If a tooth is extracted, __________ bone will be absorbed until only ________ bone remains.
|
alveolar, basal
|
|
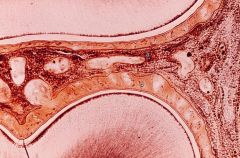
What are a and b?
|
a- cribriform plate
b- bundle bone (thin dark line) |
|
|
Cortical bone is the portion of the alveolar bone which is (next to/away from) the tooth?
|
away from
|
|
|
Cortical bone is comprised of ____________, ___________ bone.
|
compact, lamellar
|
|
|
______________ is the bone socket around the tooth?
|
cribriform plate
|
|
|
T or F: Cribriform plate is a loosely organized bone which allows no communication or passing of nutrients from bone to PDL?
|
False, it is compact bone and has numerous openings which allow blood vessels and nerves to pass to PDL
|
|
|
Where is spongy bone located?
|
inbetween cortical and cribriform plates
|
|
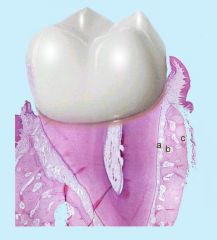
What are a-c?
|
a- cribriform plate
b- spongy bone c- cortical plate |
|
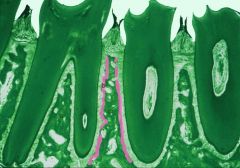
What are a-c?
|
a- interradicular bone
b- bundle bone c- cribriform plate |
|
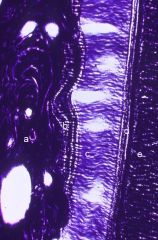
What are a-e?
|
a- cribriform plate
b- bundle bone c- PDL d- cementum e- dentin |
|
|
What is mesial drift?
|
When a tooth moves mesially
|
|
|
What causes bone remodeling in the tooth socket?
|
movement or pressure
|
|
|
In bone remodeling of the tooth socket, what is the first bone to be broken down?
|
bundle bone, it is right next to cementum
|
|
|
In bone remodeling a cavity is formed and then later filled by new bone. What type of bone is this?
|
bundle bone
|
|
|
In bone remodeling, what type of fibers must be re-anchored?
|
PDL
|
|
|
T or F: bone remodeling applies only to horizontal movement and not rotational movement?
|
False, it applies to both
|

