![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
108 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which cells cause the differentiation of odontoblasts?
|
Cells in the IEE (preameloblasts)
|
|
|
From which region do odontoblasts originate?
|
dental papilla
|
|
|
large collagen fibers and ground substance combine at the basement membrane to form what?
|
mantle dentin (large fibers are von Korff fibers)
|
|
|
What do odontoblasts secrete?
|
collagen
|
|
|
As odontoblasts secrete predentin, they move towards the _______?
|
pulp
|
|
|
Odontoblastic processes will be surrounded by predentin and then become mineralized to become ____________?
|
dentinal tubules
|
|
|
The first dentin deposited at the DEJ is called _______ dentin.
|
mantle
|
|
|
Predentin matrix allows for less invasion of HA crystals than enamel. This is why dentin is less ___________ than enamel.
|
mineralized
|
|
|
mantle dentin is (heavlily/not heavily) mineralized?
|
not heavily
|
|
|
_________________ dentin is formed a distance from the DEJ is more highly mineralized than preceeding dentin.
|
circumpulpal
|
|
|
______________ is the production of a matrix followed by mineralization by HA crystals.
|
dentinogenesis
|
|
|
radial striation of dentin is due to the __________ ___________?
|
dentinal tubules
|
|
|
Dentinal tubules form an _______________ shape.
|
S curved
|
|
|
Dentinal tubules are straighther in (root/crown) dentin?
|
root
|
|
|
Caries affecting dentin will affect pulp (apically/coronal) to the caries?
|
apically
|
|
|
_________________ are small waves in dentinal tubules.
|
Secondary curves
|
|
|
Crests of secondary curves are approx. __um apart?
|
4 (daily deposition)
|
|
|
Secondary curves represent the minor changes in ____________ movement in successive 24 hour periods.
|
odontoblastic
|
|
|
Dentinal tubule density is highest (near the enamel/near the pulp)?
|
Near the pulp (radiation of tubules)
|
|
|
Dentinal tubule density is _x higher near the _____?
|
4, pulp
|
|
|
T or F: dentinal tubules have an increase in density near the DEJ due to branching?
|
True
|
|
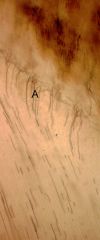
What is A?
|
dentinal tubule brancing at the DEJ
|
|
|
(Crown/root) dentin shows many side branches called ___________?
|
root, canaliculi
|
|

Is this root or crown dentin? Why?
|
root, high density of side branching
|
|
|
Which is more calcified, intertubular or peritubular dentin?
|
peritubular
|
|
|
Collagen fiber in intertubular dentin run (parallel/perpendicular) to the dentinal tubule?
|
perpendicular
|
|
|
Intertubular dentin has a (coarse/delicate) collagen matrix while peritubular dentin has a (coarse/delicate) collagen matrix?
|
coarse, delicate
|
|
|
Another name for peritubular dentin is?
|
sheath of Neumann
|
|
|
initial dentin secretion by odontoblasts is (intertubular/peritubular)?
|
intertubular
|
|
|
Peritubular dentin is secreted during ____________?
|
calcification
|
|
|
When does peritubular dentin calcify?
|
When it is secreted
|
|
|
There are three layers of dentin. What is the middle layer?
|
globular dentin
|
|
|
Interglobular dentin is (highly mineralized/has little mineralization/non-mineralized)?
|
non-mineralized
|
|
|
Interglobular dentin represents imperfections in the calcification _______?
|
front
|
|
|
Interglobular dentin exhibits _________ depressions on outer surface.
|
rounded
|
|
|
Mineralization in dentin occurs as ___________ aggregations which eventually ________.
|
sperical, fuse
|
|
|
nuclei of mineralization occur along ___________ fibers.
|
collagen
|
|
|
The granular layer of Tome's is the peripheral dentin in the (root/crown).
|
root, remember in the crown, near enamel it is the mantle layer
|
|
|
The granular layer of Tome's is composed of __________ islands of dentin and appears as dark grains near the _____?
|
uncalcified; dentino-cemento junction
|
|
|
T or F: the granular layer of Tome's is similar to the globular but smaller
|
True
|
|
|
The granules in the granular layer of Tome's have been proposed as:
|
1. uncalcified cores of large collagen fibers
2. twisted ends of dentinal tubules |
|
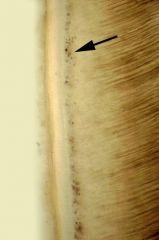
What is the arrow pointing to?
|
granular layer of Tome's
|
|
|
The imbrication lines of von Ebener correspond with what in the enamel?
|
cross striations
|
|
|
von Ebener lines are produced by _______________?
|
daily dentin deposition
|
|
|
Lines of Owen correspond with what in enamel?
|
stria of retzius
|
|
|
Lines of Owen follow the contour of the ______________?
|
pulpal surface
|
|
|
Describe the 3 theories of stimulation involving dentinal tubules.
|
1. intratubular nerves
2. odontoblasts as receptors 3. fluid movement model |
|
|
Name the 3 types of dentin.
|
1. primary
2. secondary 3. reactive (also tertiary or reparative) |
|
|
Primary dentin is deposited before completion of the ______ ___________?
|
apical foramen
|
|
|
Secondary dentin is deposited after completeion of the ________ _____________?
|
apical foramen
|
|
|
Tertiary, reparative or reactive dentin is deposited in response to an ___________?
|
irritant
|
|

What type of dentin is on the right and which on the left?
|
Primary on the left and secondary on the right
|
|
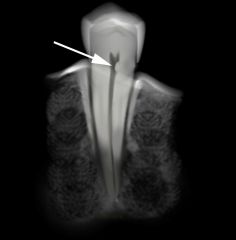
What is the arrow pointing to?
|
reparative or reactive dentin, probably due to gingival recession
|
|
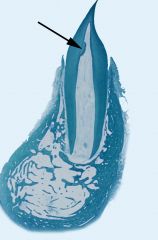
What is the arrow pointing to?
|
tertiary, reparative or reactive dentin
|
|
|
Dead tracts are tubules filled with _____?
|
air (they're empty)
|
|
|
T or F: damaged dentin still contains dentinal tubules?
|
False
|
|
|
Dead tracts will appear ______ on ground sections.
|
dark
|
|
|
Blind tracts or sclerotic dentin are (empty/filled) and are (dark/transparent)?
|
filled, transparent
|
|
|
T or F: Blind tracts and dead tracts are both due to irritation.
|
True
|
|
|
T or F: Blind tracts are due to chronic irritation?
|
True
|
|
|
T or F: Dead tracts are due to chronic irritation?
|
False
|
|
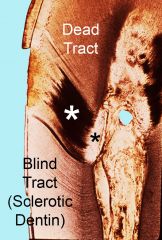
The white star is a ___________ while the black star is a _________?
|
dead tract (dark material), blind tract (white material)
|
|
|
The pulp cavity arise from what structure?
|
dental papilla
|
|
|
Pulp cavity is comprised of what type of tissue?
|
Loose CT (type I and type III collagen), cells and ground substance
|
|
|
What is the function of the pulp cavity?
|
to support odontoblasts
|
|
|
The pulp cavity has a hole at its apical end, what is it called? What enter this hole?
|
apical foramen; nerves and blood vessels
|
|
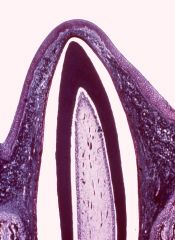
What is the layer denoted by 'A'?
|
odontoblasts with pulp cavity beneath
|
|
|
Name the 3 zones of the pulp and what they contain.
|
1. odontoblast zone - odontoblasts and von Korffs fibers
2. cell free zone of Weil - von Korffs fibers 3. cell rich zone - mainly fibroblasts, von Korffs fibers and the parietal nerve plexus of Raschkow |
|
|
What other cell types are present in the cell rich zone of the pulp besides fibroblasts?
|
mesenchymal, macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma, and eosiniphils
|
|
|
(Parasympathetic/sympathetic) nerve fibers control the blood supply within the pulp?
|
Sympathetic (thank you physiology)
|
|
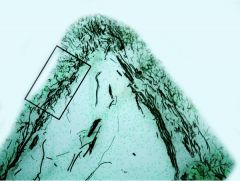
What are the black things?
|
nerve fibers (parietal nerve plexus of some russian guy)
|
|
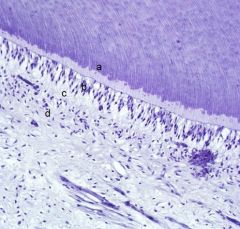
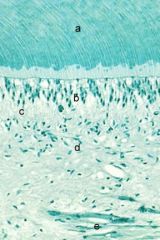
What are a-d?
|
a- mantle dentin
b- odontoblasts c- cell free zone of Weil d- cell rich zone |
|
What are a-e?
|
a- dentin
b- odontoblasts c- cell free zone of Weil d- cell rich zone e- parietal nerve plexus of Raschkow |
|
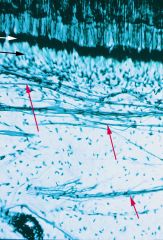
What are the arrows pointing to?
|
black- cell rich zone
white - cell free zone of Weil red- parietal nerve plexus of Raschkow |
|
|
Vascular supply in the dentin supplies what cells?
|
odontoblasts
|
|
|
Sharp pain in the pulp is mediated by __________ fibers.
|
myelinated
|
|
|
Dull, throbbing pain in the pulp is mediated by ____________ fibers.
|
unmyelinated
|
|
|
Does the pulp have lymphatic drainage?
|
Probably not
|
|
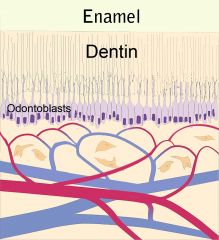
What are the blue and red lines at the bottom of the picture?
|
idk, jk, lol :)
|
|
|
What type of autonomic fibers are in the pulp and are they myelinated?
|
sympathetic, no
|
|
|
From what ganglion do the autonomic fibers start their path to the pulp?
|
super cervical ganglion
|
|
|
Sensory fibers in the pulp come from what ganlgion?
|
maxillary and mandibular branches of the trigeminal
|
|
|
Are sensory pulp fibers myelinated or unmyelinated?
|
both
|
|
|
Which fibers, (myelinated/unmyelinated) innervate odontoblasts and may extend shortly into the dentinal tubules?
|
unmyelinated
|
|
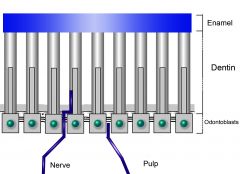
What is this picture from?
|
The first maxillay molar of R2D2, mesiobuccal cusp to be exact.
|
|
|
In a sensitive tooth, you would expect to (more/less) nerve fibers?
|
more
|
|
|
Name the two regions of the pulp.
|
Coronal and radicular
|
|
|
What is a pulp horn?
|
Its the vertical extension of the pulp into a cuspal region (or the horn looking thingy in the pulp if you prefer)
|
|
|
Where is coronal pulp located?
|
Above the cervix (of the tooth)
|
|
|
Where is radicular pulp located?
|
Below the cervix
|
|
|
What is the shape of the radicular pulp cavity?
|
conical and tapered
|
|
|
T or F: Like a mans nose, the pulp cavity increases with age?
|
False
|
|
|
T or F: the pulp cavity becomes more fibrous with age?
|
True
|
|
|
T or F: the pulp cavity becomes less cellular with age?
|
True
|
|
|
Minor pathological events result in _______________ of the pulp?
|
compression (pulp is surrounded by hard tissue)
|
|
|
T or F: compression of the pulp can lead to intense pain and death of the pulp?
|
True
|
|
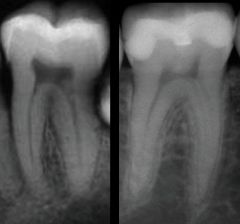
Which tooth is from an older person?
|
The one one the right (pulp cavity is smaller)
|
|
|
A true pulp stone is called a __________?
|
denticle
|
|
|
T or F: denticles are composed of dentin and have dentinal tubules?
|
True
|
|
|
Denticles are formed by interaction of what two types of cells?
|
epithelial and mesenchymal
|
|
|
False pulp stones, like true pulp stones are called ___________?
|
denticles
|
|
|
(False/true) pulp stones have concentric rings?
|
false
|
|
|
Pulp stones can be ________, __________, or ____________?
|
free, attached or embedded
|
|
|
False pulp stones are formed by calcification of ________?
|
debris
|
|
|
What am I?
|
True pulp stone
|
|
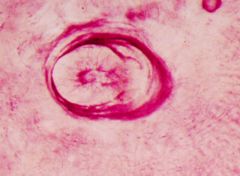
What is this?
|
True pulp stone
|
|
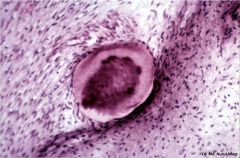
What is this?
|
True pulp stone
|
|
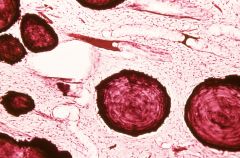
What is this?
|
false pulp stone
|

