![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
1348
|
Black Death
|
|

1417
|
Pope Martin V elected, submitted treaty with the Holy Roman Empire, England and France.
|
|

1439
|
Council of Florence.
1. Initially the Council of Basel, convoked by Pope Martin V in 1431 during the Hussite Wars in Bohemia and the Rise of the Ottoman Empire. 2. Second phase as Council of Ferrara, convoked by Pope Eugene, drew Byzantine ambassadors to Italy. 3. Antipope Felix V moved the rival Council of Florence to avoid the plague. 4. Bridged the Great Schism and dissolved itself in 1449. |
|

1527
|
Sack of Rome:
A military event carried out by the mutinous troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in Rome, then part of the Papal States. |
|

A Secco (Fresco)
|
Watercolor on dry plaster.
Example: Technique that Michelangelo used to retouch the Sistine Chapel after its completion. |
|

Animas
|
Soul or animated life.
Example: "The Creation of Adam" on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel |
|

Annunciation
|
The announcement by the angel Gabriel to the Virgin Mary of the incarnation of Jesus Christ; often includes a dove to indicate that the virgin was conceived by the Holy Spirit.
Understanding: This is a basic term involving the life of Christ which is heavily depicted during the Renaissance. |
|

Arcade
|
A series of arches with supporting columns or piers.
Example: Basilica-style cathedrals Understanding: Popular style during the Renaissance |
|

Arch
|
A means of construction in which an opening, usually semi-circular, is spanned by a series of wedge-shaped elements.
|
|

Ascension
|

The Ascent of Christ into Heaven as witnessed by his disciples 40 days after the Resurrection.
Example: "Transfiguration" by Rafael Understanding: This is a basic term involving the life of Christ which is heavily depicted during the Renaissance. |
|

Assumption
|

The Ascent of the Virgin Mary into Heaven after her death and burial, when her soul was reunited with her body.
Example: "Coronation of the Virgin" by Lorenzo da Monaco Understanding: This is a basic term involving the life of Christ which is heavily depicted during the Renaissance. |
|
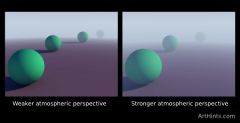
Atmospheric Perspective
|

Use of color where the sky lightens as it distances from the background.
Example: "Annunciation" by Leonardo da Vinci Understanding: Using atmospheric perspective helps make the painting look more naturalistic; a key component of Renaissance paintings. |
|

B.I.O.R.
|

Beauty, Invention, Order, Richness - key characteristics of High Renaissance Art that helped form the narrative in a painting.
Example: "The Transfiguration of Christ" by Rafael Understanding: A staple of Renaissance artwork. |
|
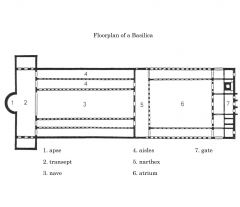
Basilica
|
A general term applied to any church that has a longitudinal nave that terminates an apse, or large semi-circular or polygonal niche, and is flanked by side aisles.
Example: St. Peter's Basilica Understanding: This style of church was popular during the Renaissance. |
|

Biblia Paupernum
|

"A Poor Man's Bible" - church wall openings were covered in images depicting Bible stories.
Example: Santi Apostoli in Firenze Understanding: Literacy rate was low during the Renaissance, so this was a way to encourage knowledge of the Church and make it more accessible. |
|
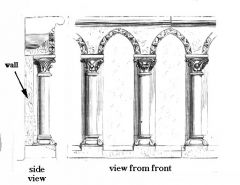
Blind Arcade
|

Arches and columns embedded into the structure of the wall instead of separate from them.
Example: Pieve in Arezzo |
|
Canon of Proportions
|

One measure used to accurately form sculptures based on real life measurements.
Example: Lysisppos' Apoxyomenos or "The Scraper" Understanding: In Classical Renaissance sculpture, an artist would use the canon of proportions as a way to search for perfection. |
|
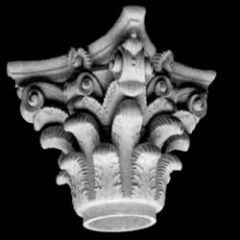
Capital
|

The decorated crowning member of a column or pilaster where the lintel or the arches of an arcade meet.
Example: Basilica style cathedrals, the Colosseum |
|
|
Castrum
Cardo Decamanus Forum |
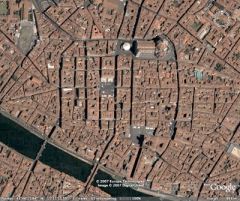
Fortified village based on a gird system where the cardo (North-South Axis/Streets) meets the decamanus (East-West Axis/Streets) at the Forum (meeting point).
Example: Piazza della Repubblica in Firenze. Understanding: This was the structure of Firenze before the Romans took over. |
|

Chiaroscuro
|

The contrast of light and shade to enhance modeling.
Example: "Maestà" by Giotto Understanding: Renaissance paintings, unlike the Gothic style before it, began to naturalize work. Modeling helped assist in creating this human-like aspect within paintings. |
|

Christus Patiens
|

"Suffering Christ"
Example: "Crucifixion" by Giotto Understanding: the transition from Christus Triumphans to Christus Patiens directly exemplifies the shift from Gothic style to Renaissance style paintings. The angle of the body shows pain, something not shown in earlier crucifixion paintings. |
|

Christus Triumphans
|

"Living Christ"
Example: Uffizi's "Christus Triumphans", some Gothic style Crucifixion paintings Understanding: the transition from Christus Triumphans to Christus Patiens directly exemplifies the shift from Gothic style to Renaissance style paintings. Gothic style shows Christ as God, not man; he sows no pain or sadness in his face or body. |
|
|
Classicism
|
The following of Greek or Roman principles in art and literature; emphasis on antiquity associated with harmony and restraint.
Understanding: One of the key principles of the Renaissance is the emphasis on Classical Rebirth |
|
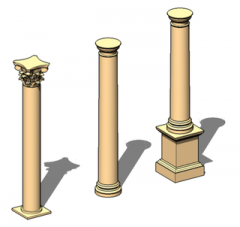
Column
|
A free-standing cylindrical support usually consisting of a base, a shaft, and a capital.
|
|

Continuous Narrative
|

The repeated use of the same figures in a moment of series of events.
Example: "Adoration of the Magi" by Gentile de Fabriano Understanding: Narrative, in general, is a key component of Renaissance work, so the use of continuous narrative to tell a story is common during this time period. |
|

Contrapposto
|

The naturalistic shape of an object where it appears more balanced.
Example: "David" by Michelangelo |
|

Crypt
|
The area beneath the presbytery of a church.
|
|

Dormition
|

Sacred slumber that shows Mary is not dead, but that she is indeed immaculate.
Example: "Coronation of the Virgin" by Lorenzo da Monaco |
|

Diptych
|
An alter piece or devotional picture consisting of two wooden panels joined together.
|
|

Domus Dei
|
"House of God"
Example: Chapels |
|

Duomo
|
"Cathedral" in which the bishop has a permanent Episcopal throne.
|
|
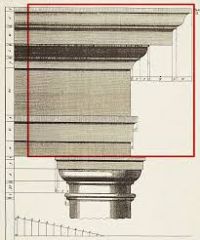
Entablature
|
The upper part of an architectural order.
|
|

Foreshortening
|

Method of rendering a specific object or figure in a picture in depth. The artist records, in varying degrees, the distortion that is seen by the eye when an object or figure is viewed at a distance or at an unusual angle.
Example: "Adoration of the Magi" by Gentile de Fabriano - the kneeling servant |
|
|
Fresco
|
A painting made on wet plaster with pigments suspended in water so that the plaster absorbs the colors and the painting becomes part of the wall.
Example: The Sistine Chapel, The Finding and Proving of the True Cross |
|

Golgotha
|
"Skull" in Aramaic, the name of the site where Jesus was crucified outside of Jerusalem.
|
|

Horror Vacui
|
The fear of open spaces.
Pre-Renaissance churches decorated from top to bottom with elaborate colors, textures, and arches. Represents shift into the High Renaissance ideal of "richness." |
|
|
Iconography
|

"Image Writing" - uses the identification of image with symbolic content.
Example: "Coronation of the Virgin" by Lorenzo da Monaco Used heavily during the Renaissance to help emphasize the narrative of a painting and underscore a deeper meaning within the work. |
|
|
Impasto
|
Raised brush strokes of thick paint.
|
|
|
Intonaco
|
Layer of smooth plaster on which a fresco is painted.
|
|
|
Isocephalic
|

Having all heads of figures in a piece on the same level.
Example: "Stefaneschi Triptych Altar Piece" by Giotto Unnatural. An attribute of Gothic style painting. As artists move towards the Renaissance style, levels become more natural. |
|
|
Languid
|

Lacking life - God gives life
Example: Adam in the "Creation of Adam" by Michelangelo in the Sistine Chapel |
|
|
Lamentation
|

The mourning of Christ's mother and his followers over the body of Christ after the descent from the cross.
Example: "The Entombment of Christ" by Caravaggio Understanding: this is a basic term involving the life of Christ which is heavily depicted during the Renaissance |
|
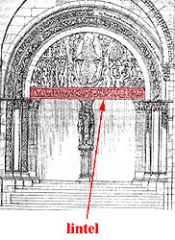
Lintel
|

The horizontal beam spanning an opening between two columns.
Example: The Colosseum |
|
|
Maestà
|

"Majesty"
Example: "Maestà" by Giotto Images of the Madonna and Child enthroned are extremely prevalent during the Renaissance, and, during this time, Maestà paintings became more naturalistic through use of modeling. |
|
|
Maniera
|
"Manner" - used to describe sophisticated, artificial, or refined style popular in the 16th century.
|
|
|
Modeling
|
The use of tinting and shading to make fabric appear as if there is an actual body underneath it.
Example: "Maestà" by Giotto Understanding: Renaissance paintings, unlike the Gothic style before it, began to humanize artwork. Modeling helped assist in creating this humanlike aspect within paintings. |
|
|
Naturalism
|
The attempt to mimic what we see.
Understanding: Renaissance art explores the idea of naturalism. Artists constantly search for a way to make their paintings more naturalistic. |
|
|
Nave
|
The center aisle of a Basilica.
|
|
|
Neoplatonism
or Neo-Platonism |

Mystical thought: a school of Greek philosophy established in Alexandria, revised by Italian humanists in the 15th century that emphasizes the philosophies of Plato and Aristotle.
Example: "Birth of Venus" by Botticelli |
|
|
Nimbus
|
"Halo"
Understanding: in Gothic style paintings, the halos were more grandiose and bold. During the early Renaissance, halos in paintings become smaller and lowly saturated. This, perhaps, shows the shifts into naturalistic of artwork. |
|
|
One-Point Perspective
|

Invented by Brunelleschi in 1413; use a vanishing point to create perspective; created by combining orthogonal (vertical) and transversal (horizontal) lines which recede into background at the vanishing point.
Example: "Battle of San Romano" by Paulo Ucello |
|
|
Patron
|

The person or group who commissions and pays for a work of art or architecture.
Example: "Doni Tondo" by Michelangelo was commissioned by the Doni family. Until the High Renaissance, when artists set the parameters of the work, the commissioner of the painting made the rules. |
|
|
Piano Noble
|
"Noble Floor" - refers to the second story of a building, intended for the owner and the noble family.
|
|
|
Prefiguration
|

The way we connect stories to one another by connecting the piece the events of the past to different events occurring at another time and place.
Example: Juxtaposition of scenes from the stories of Jesus and Moses in the Sistine Chapel. |
|
|
Putti
|

A male figure of a male baby, often winged; sometimes personified love or cupid.
Example: "Primavera" by Botticelli Cupid in Botticelli’s "Primavera" explores the mystical world of Neo-Platonic thought, a facet of the intellectual proponent of Renaissance artwork. |
|
|
Realism
|
Representation of the real world without idealization.
Less common in Renaissance art. |
|
|
Sella Gestatoria
|
Portable papal throne
Example: used on the tomb of Julius II showing him carried into the next world. |
|
|
Sfumato
|

"Smoky"
Example: "Venus of Urbino" by Titian Understanding: the dark, smoky quality of paintings is very Da Vinci esque and adds to the mystique of the Venus of Urbino painting. The painting explores a common theme in Renaissance artwork, the definition of true beauty. |
|
|
Sibyls
|
Greek and Roman prophetesses who were thought to have foretold the coming of Christ.
|
|
|
Spandrel
|
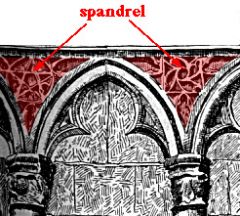
Triangular area between two adjoining arches.
Example: The Sistine Chapel |
|
|
Spolvero
|
The transfer of an image onto a wall by perforating the lines of the cartoon; or full-scale preparatory drawing on one or more sheets of heavy paper, onto the wall.
Example: The Sistine Chapel |
|
|
Stacco
|
A technique to restore frescoes by transferring the images to canvas and then transferring them back to new fresco to be repainted.
|
|
|
Stanze
|
"Room"
Example: "Stanza della Signatura" in the Vatican |
|
|
Striation
|
Web of golden lines
Example: Decoration on Byzantine icons and the Italian religious images that they inspired. |
|
|
Studio
|
"Small Study" - small decorated chambers specifically built for men in the Renaissance where books, works of art, and objects of historical and scientific interests were kept.
The "Man Cave" Example: "Venus of Urbino" by Titian |
|
|
"The Golden Legend"
|
A book published in 1266 by Jacobus de Voragine, depicting the lives of the saints.
Many martyrs are depicted in Medieval and Renaissance art. |
|
|
Tondo
|
"Circular" painting
Example: "Doni Tondo" by Michelangelo |
|
|
Transepts
|
The cross arm perpendicular to the nave on a cross-shaped church.
|
|
|
"Treatise of Terms"
|
A book published in 1435 by Leon Baptista ALBERTI.
One-point linear perspective as a quantifiable space. Example: "Battle of San Romano" by Paolo Ucello |
|
|
Triptych
|
An altar piece or devotional picture consisting of three sections.
Example: "Stefaneschi's Tryptich Alterpiece" by Giotto |
|
|
Uffizi
|
"Offices" built by Giorgio Vasari from 1565-1570.
He wrote the book which later became the basis for the organization of the Uffizi as the museum it is today. Each chapter of the book is represented by a different room. He is considered the first art historian and is responsible for the way we understand the progression of Tuscan Renaissance. |
|
|
Virgo Lactans
|
"Lactation Virgin"
The mother feeds the child with breast milk, symbolic for the church sustaining the people. |
|
|
Primary Colors
|
Red, yellow, blue
|
|
|
Secondary Colors
|
Orange, Green, Violet
|
|
|
Warm colors
|
yellow, orange, red
|
|
|
Cool colors
|
violet, blue, green
|
|
|
Neutral colors
|
White, gray, black
|
|
|
Hue
|
Pure Color
|
|
|
Tint
|
Hue + White
|
|
|
Tone
|
Hue + Gray
|
|
|
Shade
|
Hue + Black
|
|
|
Value
|
Brightness
Can be low or high |
|
|
Saturation
|
Strength, purity
Can be low or high. Low conveys serious mood. High conveys positive mood. |
|
|
Line
|
A path in space that defines the edge of a form; leads the eye around the composition and communicates info through direction.
|
|
|
Horizontal Line
|
Conveys continuation, rest, repose
|
|
|
Vertical Line
|
Conveys height
|
|
|
Diagonal Lines
|
Conveys unstable motion, dramatic movement
|
|
|
Horizontal and Vertical
|
Conveys stability, permanence, reliability
|
|
|
Curved Lines
|
conveys softening, energy, movement
|
|
|
Shape
|
Defines a 2D object in space
H + W only Often defined by lines, which provides contour for shapes |
|
|
Form
|
Defines a 3D object in space
H + W + D Basis of sculpture, furniture, and art-deco |
|
|
Geometric Shapes
|
Man-made
Conveys stability Cones, squares, etc. |
|
|
Organic Shapes
|
Irregular and asymmetrical
Natural Conveys stimulation |
|
|
Space
|
In art, a feeling of depth.
|
|
|
Positive Space
|
Area occupied by the primary objects
|
|
|
Negative Space
|
Area surrounding the primary objects
Accentuates the positive space Disproportionate negative space conveys vulnerability and isolation |
|
|
Perspective
|
Invented by Brunelleschi in 1413
One-point linear perspective: use vanishing point in one spot to create perspective Created by combining horizontal and vertical lines |
|
|
Orthogonal vs. Transversal
|
Vertical and horizontal lines, recede into background at vanishing point
|
|
|
Texture
|
The surface quality of an object that we sense through touch. All objects have a physical texture. Use color, line, and shading to imply texture in paintings. Tactile.
|
|
|
Allegory
|
Synchronization of symbols leading to a message.
|

