![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the Pentateuch |
First 5 books of the Bible |
|
|
Other theories on Authorship |
Documentary hypothesis
Different names for God used therefore different authors. |
|
|
Three things that the Pentateuch has |
Narrative
Poetry
Epilogue |
|
|
Seams |
Genesis 49
Numbers 22-23
Duet 32 |
|
|
Key Questions about Pentateuch |
What subjects are addressed? What roles does faith play? What role does the law play? What roles does the land promise play?
|
|
|
Ways to look at the Pentateuch |
The Problem (Gen 1-11) The Solution (Gen 12 - Duet)
Key Text Gen 12:1-3 - Abrahams blessing |
|
|
Two Genres in the Pent |
Law - instruction for life Narrative - selective record of events |
|
|
Themes of the Pent |
God is over all and supreme Sin Grace Faith |
|
|
Unique Characteristics of Narratives |
Narrator has divine perspective
Characterization - author spends time on important attributes |
|
|
Narrative Structure |
Setting Conflict Climax Resolution Conclusion |
|
|
What is a narrative |
A selective record of events with a purpose, written in an engaging manner
|
|
|
Issues with narrative |
Historically accurate but literary dimensions Theological |
|
|
Genesis as Primeval history |
1. Author used genealogy to highlight divine origin and significance of creation 2. The author emphasized the purpose of creation (loving the creator) 3. The author shows human revolt against God as the cause of wickedness and death 4. The author stressed the promise to restore creation through a specific line |
|
|
3 things about Genealogy |
1. Shows origins 2. Shows how descendants are important 3. Spotlight a specific person |
|
|
Genesis 1 |
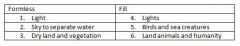
Creation Order |
|
|
Genesis 2 |
More personal name for God (covenantal)
Mans relationship with God (submission)
Mans relationship with creation (dominion) |
|
|
Genesis 3 |
Colossal Collapse
Everything is cursed |
|
|
Genesis 4 |
Cain and Abel |
|
|
Genesis 10 |
Nations descended from Noah |
|
|
Genesis 12-25 |
Story of Abraham (12) Land (15) Offspring (17) Blessing (22) |
|
|
Narrative typology |
a type of narrative that is going to be used later for something else (Gen 41-Ex 12) |
|
|
Genesis 38 |
Judah and Tamar story |
|
|
Genesis 44 |
Judah tried to sacrifice himself in place of Benjamin |
|
|
Genesis 49 |
Judah is blessed and he will have universal rule |
|
|
Structure of Exodus |
1-18 Gracious redemption of Israel 19-24 Gracious covenant with Israel 25-40 Gracious presence with Israel |
|
|
Gracious Redemption of Israel |
Exodus is the continuing fulfillment of Yahweh's promises |
|
|
Exodus 1 |
Miraculous birthrate despite slavery Midwives saving newborn boys
|
|
|
Exodus 2 |
Birth of Moses Murdered Egyptian and fled Delivered shepherds daughters Moses and Zipporah give birth to son Gershom God hears groaning of the people in slavery |
|
|
Exodus 3 |
Moses shepherding Sees burning bush not consumed Lords presence is powerful and dangerous God knows suffering of his people (Cov Promise) Moses responds with doubt God responds that He will be with him Gods divine freedom and presence |
|
|
Incurring elements of the Plagues |
Warnings Instructions Pharaohs response |
|
|
Structure of the 10 Mighty acts |
Cycle 1 - Nile to blood / Frogs / Nats Cycle 2 - Flies / Death of Livestock / Boils Cycle 3 - Hail / Locust / Darkness Climax - Death of the first born (passover) |
|
|
What does the Exodus event do |
Motivated fidelity and establishes identity (Israel belongs to God. He is their father) |
|
|
What is important about Pharaohs heart |
Personal responsibility of pharaoh and divine sovereignty |
|
|
Purpose of Leviticus |
Emphasis Gods holiness and its good news to the exodus generation
It is a guide to worship and ethics |
|
|
Structure of Leviticus |
1-16 Covenant Worship 17-27 Covenant Ethics |
|
|
Leviticus Contribution to the Bible |
It clarifies sacrifice and atonement It distinguishes between Holy and common It distinguishes between clean and unclean It shows that Israel should be Holy in its acts |
|
|
How to understand Leviticus |
Helps to have a Genesis world view (Gen1:1-2:3) Cleanliness has to do with order of creation Uncleanliness symbolizes death/sin Being Holy in actions and attitude |
|
|
Five types of offerings |
Whole burnt Grain Peace Sin (mandatory) Guilt (mandatory) |
|
|
Leviticus 10 |
Bull - sin Ram - whole burnt 2 goats -- sin offering to the Lord -- scapegoat to the wilderness |
|
|
Leviticus 16 |
Day of Atonement |
|
|
Numbers 1-13 |
Leave the mountain. Judah tribe has a spot next to the tabernacle |
|
|
Numbers 13-14 |
Leaders of each tribe are sent out to search out the land canaan.
First scouts report people are big but Caleb wants to go. |
|
|
What are other names for the Pentateuch |
The Torah The book of the Law The Book of Moses |
|
|
Deuteronomy also called |
the second law |
|
|
Key theme of Deut |
Land and the intertwining of the land with Gods presence. Gods grace is still operative |
|
|
Structure of Deut |
1-4 Retelling of Numbers 5-11 Heart |
|
|
Warnings and Dangers (Deut 7-10) |
7 - Danger of military might 8 - Danger of prosperity 9-10 Danger of self righteousness |

