![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
somatic dysfunction definition
|
change in function diagnosed by texture, asymmetry, restriction of motion,and tenderness (TART)
|
|
|
what is required to move the restiction of barrier from the physiologic barrier to the anatomic barrier
|
passive ligamentous stretch
|
|
|
How do you name a somatic dysfunction?
|
by its freedom of motion
|
|
|
A lesion is C3 F Sl Rl. What does this mean?
|
C3 is flexed, sidebent to the left, and rotated to the left on C4
|
|
|
Fryette's Type I dysfunction- definition
|
group curves of more than one vertebra - rotation is opposite to the side bending
|
|
|
Fryette's Type II dysfunction- definition
|
dysfunction of one vertebra -
rotation is the same direction as side bending |
|
|
Cervical spine lesions are Type I or II
|
type II
|
|
|
myofascial technique - definition
|
gentle stretching or use of physiologic muscle reflexes through guided patient muscle contraction
|
|
|
counterstrain technique - definition
|
"tender points" are identified and eliminated by positioning of the body part
|
|
|
facilitated positional - definition release
|
joint or muscle is placed into its ease-of-motion position, held, and then released
|
|
|
High velocity, low amplitude technique - definition
|
joint is placed agaist restrictive barrier and a thrust moves the barrier
|
|
|
myofascia release - definition
|
placed against or away from barrier until release of tension or restriction
|
|
|
Right vertebral rotation and sidebending - palpation finding
|
the right transverse process becomes more prominent posteriorly
|
|
|
Vertebra flexion causes right vertebral rotation and sidebending - why
|
the vertebra turns away from a flexion restriction to allowable freedom of motion -right SB, and right rotation
|
|
|
Name the dysfunction when the left transverse process of T3 is most prominent in flexion
|
T3 E Rl Sl
|
|
|
In muscle energy technique, what are the restriction barriers in a C4 E Sr Rr lesion
|
flexion, and L SB and L Rot
|
|
|
Muscle energy technique for C4 E Sr Rr lesion
|
Patient is placed into C4 flexion, L SB & L Rot. Patient moves in the opposite direction of the restrictions against operator's resistance.
|
|
|
Direct technique - definition
|
Direct technique moves into the restrictive barrier
|
|
|
Indirect technique - definition
|
Indirect technique moves away from the restrictive barrier
|
|
|
Spinal levels with distinct intersegmental evalation operator positions
|
OA to C2-7, T1-4, T5-T12, Lumbar, etc
|
|
|
OA to C2-7 intersegmental evalation operator position
|
Operator seated at head of table, elbows on table palpating and cupping neck
|
|
|
T1-4 intersegmental evalation operator position
|
Operator behind and to one side. Hand on head. Fingers span vertebra.
|
|
|
T5-T12 intersegmental evalation operator position
|
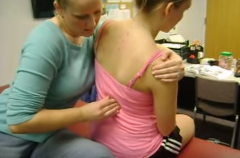
Operator behind and to one side. Hand on opposite shoulder. Fingers span vertebra.
|
|
|
Thoracolumbar regional testing patient and operator position
|
Patient standing. Operator behind patient introducing flexion extension, SB, rotation. Add hip drop.
|
|
|
Lumbar intersegmental evalation patient and operator position
|
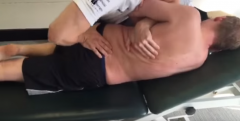
Patient lateral recumbent. Operator facing patient. Palpates transverse processers.
|
|
|
Cervical spine gross motor testing
|
Operator standing introducing flexion extension, SB, & rotation.
|
|
|
OA dysfunction technique. OA F Sr Rl
|
Operator standing introducing
extension, L SB, & R rotation. Patient moves against resistance at these restrictive barriers. |
|
|
AA joint dysfunction treatment. Joint is pure rotation.
|
Operator seated palpating AA. Carry head to rotation restrictive barrier and have patient resist.
|
|
|
Cervical Vertebral Dysfunction C2-7 - ex. C4 E Sr Rr - treatment? gets worse more prominent with extension then it is an extension lesion
|
Operator seated palpating C4. Introduces flex, L SB, L Rot. Patient moves against operator's malar hand resistance away from this barrier.
|
|
|
Thoracic Spine Vertebral Dysfunction T1-4 ex. T4 E Sr Rr - treatment?
|
Operator standing behind and to side. Hand on chin. Palpating T4. Introduces flex, L SB, L Rot. Patient moves against operator's hand on chin resistance away from this barrier.
|
|
|
Thoracic Spine Vertebral Dysfunction T1-4 ex. T4 E Sr Rr - treatment? |
Sit on the side you want to rotate towards “listening hand” on transverse processes Stabilizing hand across chest to opposite shoulder Sidebend towards you Rotate towards you |
|
|
Thoracic Spine Vertebral Dysfunction T5-12 ex. T12 E Sr Rr - treatment?
|
Operator standing behind and to side. Arm spans shoulder on side of motion barrier. Palpating T12. Introduces flex, L SB, L Rot. Patient moves against operator's shoulder resistance away from this barrier.
|
|
|
Lumbosacral examination for intersegmental dysfunction.
|
Patient prone. Operator applies firm, equal pressure in a ventral direction. Ex. ease of R. ventral motion means R restrictive barrier.
|
|
|
Lumbosacral examination for intersegmental dysfunction.
|
Patient lateral recumbent, Operater facing. Palpates lumbar vertebrae. Introduces flexion. Introduces SB by raising upper leg.
|
|
|
Lumbosacral Spine Vertebral Flexion Dysfunction ex. L3 F SL RL - flexed, prominent transverse process on left - lat recumbent with prominence ( left ) to table
treatment? |
L lateral recumbent. (L posterior transverse process to table.) R shoulder back. Operator facing. Palpates L3. Introduces L SB by raising R leg. Patient moves R ankle to floor against operator's resistance.
|
|
|
Lumbosacral Spine Vertebral Extension Dysfunction ex. L3 E Sl Rl - treatment?
|
L lateral SIMS position. (R posterior transverse process away from table.) Upper shoulder flexed forward. Operater facing. Palpates L3. Introduces R SB by raising ankle. Patient moves ankle to ceiling against operator's resistance.
|
|
|
Lumbosacral Spine Vertebral FLEXION Dysfunction - treatment
|
Posterior transverse process DOWN to table. R shoulder BACK. Patient moves legs DOWN against resistance
|
|
|
Lumbosacral Spine Vertebral EXTENSION Dysfunction- treatment
|
Posterior transverse process UP away from table. R shoulder FORWARD. Patient moves legs UP against resistance
|
|
|
Lumbosacral Group Curve Dysfuction - tx
|
lateral recumbent with concavity to floor. flex, SB to apex. Patient pushes his feet to floor against resistance.
|
|
|
Thoracic Treatment
|
Patient inhales then exhales. Operator presses down on rib as the patient takes a breath.
|

