![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epidemiology of maxillofacial injuries
men vs. women assualt vs. MVAs vs. accidents |
men>women
Assault>MVAs>accidents |
|

what are these 2 fractures and 1 fact about them
|
greenstick
-can occur at condyles -can prevent more serious injuries simple -bone transectted but NO DISPLACEMENT |
|

|
compound-soft tissue envelop is torn, creating a fracture which communicate with the external environemnt
communitive-shattered fracture, multiple peices, and compounded to external environment |
|
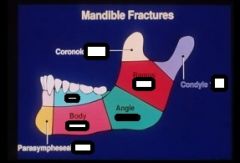
coronoid
|
|
|

|
1-left unfavo-muscle unopposed
2-right fav-muscle opposed 1-left favorable 2-right unfavorable |
|
|
Displacement of muscle groups
|
-masseter-pterygoid swing
-lateral ptrygoid disc and neck of condyle: upwards, downwards and forwards |
|
|
weak points in the mandible
|
condyle, ramus, mental foramen
|
|
|
bones of the midface
what is special about the ethmoid? |
maxillae
nasal ethmoid-include cribiform plate through which olfactory nerves travel to the anterior cranial fossa(weakness?) vomer zygomatic lacrimal cribiform plate |
|
|
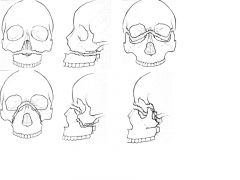
Le Fort 1
|
-horizontal
-from FRONT OF FACE to PTERYGOID PLATE -move jaw forward or backward in surgery |
|
|
Le Fort 2
|
-pyramid type of fracture
-crosses front and nasal bones -moves along inside of orbit then down and back |
|
|
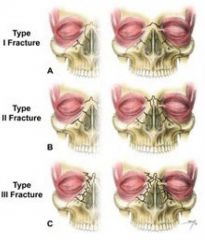
Le Fort 3
|
-frontal nasal
-through zygomatic arch and orbit -severe |
|
|
Le Fort 1,2,3
|
|
|
|
Mid-face fractures: Dentoalveolar fracture
|
includes dentition and alveolar bone
|
|
|
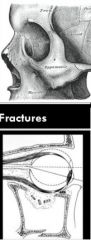
patterns in zygomatic complex and orbit
|
|
|
|
nasoethmoidal fracture patterns
|
|
|
|
how to control bleeding
|
-direct pressure
-intraoral swabs |
|
|
how to stabilize fracture
|
barton bandage(+ on head)
Bridle Wire-like a loop |
|
|
Hospital Care Management
|
Management
History medical mechanism of injury Clinical Exam Imaging surgical care |
|
|
History-essential screening questions
|
-are your teeth meeting normally
-can you open and close as before -is any part of your face numb -how is your vision -mechanism of injury-did you lose conscious! -can help determine type of fracture ex. punch = body/condyle, fall = condyle |
|
|
Physical exam
inpsect where? |
head/face: front top below
-mid face: blood clots, widening of alar nasal blades, swollen perorbital area eyes: raccoon eyes(anterior cranial fossa fracture-le Fort 2 or 3), battle's signs(manifest hrs after fracture of occiptial/temporal bone), periorbital ecchymosis, subconjunctival ecchymosis(bleeding from orbital region below conjunctiva reaching cornea) Nose: CSF rhinnorhea-nasoethmoidal fracture tears dura (has glucose/beta transferin) mouth-parasymphyseal fractures? palpation -test sensation: infraorbital nerve, IAN |
|
|
Nasoethmoidal fractures present with?
|
-widened nasal bridge
-epistasis -telecanthus -severe periorobital edema |
|
|
Orbital fractures present with?
|
-diplopia
-enopthalmus -subjunctival and periorbital ecchymosis -eye movements can be affected |
|
|
Areas to palpate?
look for? |
-mandible
-mid face * look for steps |
|
|
Imaging-areas and types?
|
Mandible
-pano -mandible series -ct Midface -CT waters, submental-vertex, occlusal |
|
|
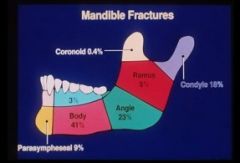
Common mandible fracture combinations
|
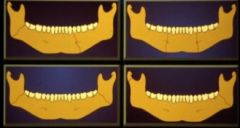
mental foramen + contralateral angle
mental foramen bilateral angle and condyle both angles |
|
|
Mandibular imaging:
-where should you look for discontinuities? -ring bone rule? |
cortical margin of whole mandible
mandible is like a pretzel that usually breaks in 2 or more places |
|
|
Fracture care
|
-reduce
-immobilize |
|
|
how to immobilize
|
-closed reduction(MMF)
-Open reduction, internal fixation(ORIF) |
|
|
latrogenic?
|
caused by surgical procedure
-jaw fractures can come from improper extractions of teeth |
|
|
do fractures tend to run along suture lines
|
-only in kids, once ossified fracture occurs less common there
|
|
|
Prehospital care
|
-stabilize spine
-secure airway-finger sweep -maintain airway-pull tongue out -many patients die from airway obstruction control bleeding -direct pressure -intraoral swab |
|
|
Mid-face imaging use?
|
CT scan!
|

