![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adam's Test (Spine) |
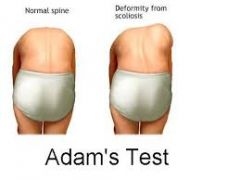
A pt with scoliosis when bending overwill have no straightening of the curve= positive. Negative= straightening |
|
|
Anterior Drawer Test (Ankle) |

Assesses instability of the ankle. Stabilize lower leg withone hand while the other cups the heel. Anterior force is appliedto the heel while attempting to move the talus anteriorly in the anklemortise. Laxity due to a sprain of the anterior talofibular ligament. |
|
|
Anterior Drawer Test (Knee)
|
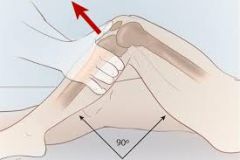
Knee flexed 90 degrees; proximal tibia ispulled forward. If soft or missing endpoint, indicates atear of the ACL. |
|
|
How to Measure Leg Length (Hip, et al) |
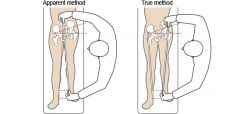
Apparent: umbilicus to medial malleolus while supine Real: ASIS to medial malleolus |
|
|
Shoulder Apprehension Test (shoulder) |
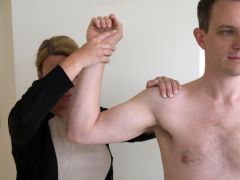
Patient supine orseated w/shoulder at 90 degrees abduction. Apply slight ant. pressure to the humerus and externally rotate arm. Apprehension @ impending subluxation/dislocation indicates anterior glenohumeral instability. |
|
|
Barlow Test (Peds Hip) |
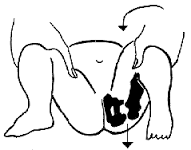
Adduct the hip (bring the thigh to midline) while extendingthe hip at the thigh (pushing the thigh posteriorly). If the hip is dislocatable thetest is positive. |
|
|
Scarf Test (shoulder)
|
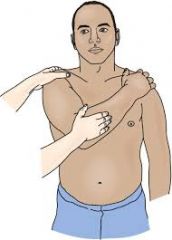
Isolatesthe acromioclavicular joint. Pt raises arm to 90degrees. Active adduction of the arm forces the acromion into the distal end of the clavicle. Pain in the area of the AC joint suggests a disorder.
|
|
|
Jobe Test AKA Empty/Full Can test (shoulder) |
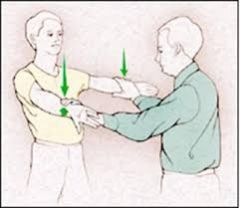
Patient forward flexes shoulder 90 degrees. The test isperformed firstly with the thumb up (supinated) and then down (pronated). The patient holds against resistance. Shoulder pain relates to impingement and weaknessof the rotator cuff. |
|
|
Finkelstein's Test (hand/wrist) |
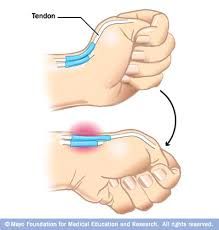
With the thumb inside the palm, the wrist and hand are flexed medially(ulnar deviation), causing pain in the abductor tendons of the thumb at theradial styloid. A positive result indicates de Ouervain's tendonitis of thewrist. |
|
|
Galleazzi Sign (Peds hip)
|
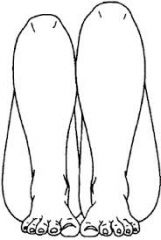
Flex legs with the knees at 90°. Observe that the length of the femur and tibia are the same. Look for adifference in height.A difference is positive Galleazzi sign. In an infant it wouldraise a concern of a dislocation of the hip on the short side. |
|
|
Hawkin's Kennedy Test (shoulder) |

Elevate the patient's arm forward to 90degrees with the elbow flexed 90° while forcibly internally rotating theshoulder. Pain with this maneuver suggests subacromial impingement orrotator cuff tendonitis. |
|
|
Lachman Test (Knee) |
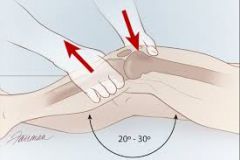
Knee flexed approximately 20 degrees, the proximal tibia ispulled forward. Excessive motion of the tibia anteriorly is indicative of atear of the ACL. This is found to be the mostaccurate clinical test for ACL tear. |
|
|
Neer Test (shoulder) |
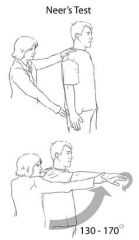
Arm in forced flexion with the arm fully pronated. The scapulashould be stabilized during the maneuver to prevent scapulothoracicmotion. Pain with this maneuver is a sign of subacromial impingement |
|
|
Ortolani's Test (Peds Hip) |
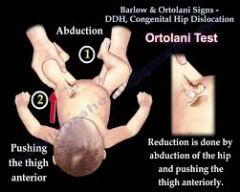
Abduct the infant's leg using thumbwhile placing anterior pressure on the greater trochanter using index and forefingers. + = 'clunk' as the femoral head relocates anteriorly intothe acetabulum. Tests for posterior dislocation of the hip. |
|
|
Patrick's Faber Test (Hip) |
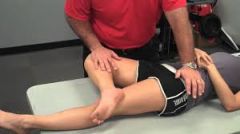
Patient supine. The knee is flexed and theexternal malleolus placed over the patella of the opposite leg. Pressure is then exerted on the flexed knee. A positive reactioncauses pain. Anterior groin pain or discomfort iselicited in hip disorders. Also in lesions of the sacroiliac ligaments, pain iselicited over the sacro-iliac joint at the site involved. |
|
|
Phalen Sign (Wrist/Hands) |
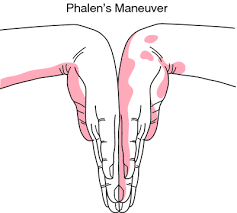
Flexion of the wrist produces the paraesthesia/pain of mediannerve compression at the wrist (carpal tunnel syndrome). The reversePhalen maneuver involves hyperextension of the wrist with the resultantmedian nerve paraesthesias. |
|
|
Posterior Drawer Test (Knee) |
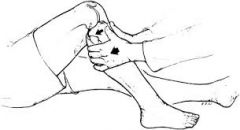
Knee flexed 90 degrees, the proximal tibia ispushed posteriorly. Excessive movement = PCL tear. |
|
|
Posterior Sag Sign (knee) |
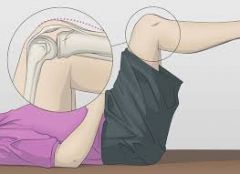
Pt supine with the hips flexed 45° and the knees flexed 90°. In this position the tibia sags backward on the femur if the posteriorcruciate ligament is torn. |
|
|
Schober Test (Spine)
|
With the patient standing, the examiner makes a mark approximately atthe level of L5. The examiner then places one finger 5cm below this mark,and another, second, finger, 10cm above this mark. The patient is askedto touch his/her toes without flexing the knee joints. By doing so, thedistance between the two fingers of the examiner increases. However, arestriction in the lumbar flexion of the patient reduces this increase; if thedistance increases less than 5 cm, then there is an indication that theflexion of the lower back is limited.
|
|
|
Straight Leg Raise (Hip) |
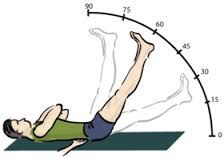
With knee extended and the patient supine, hip flexed. Pain is in the sciatic nerve distribution(buttock, posterior thigh and calf) provided that hip flexion is less than70°. |
|
|
Thomas' test (Hip)
|
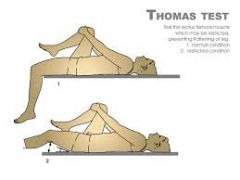
Pt supine and flexes hip. Place hand under small of back to determine that the lumbarspine has flattened out onto the bed. If the test hip remains on the bedthen there is no deformity. If test hip raises off the bed fixed flexion deformity of the hip exists equivalent to theangle the thigh makes with the bed. |
|
|
Thompson's Test (Ankle/Foot) |
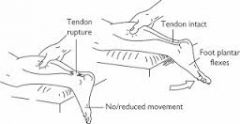
The patient is placed in a kneeling or prone position with the foot hangingfree over the end of the bed. The middle of the calf is squeezed. The test is positivewhere no ankle movement occurs and indicates a rupture of the Achilles. |
|
|
Tinel's Sign (Wrist/Hand) |
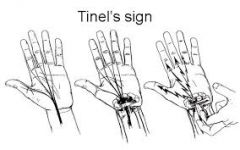
A tingling sensation w/percussion is madeover carpal tunnel. It indicates a partial lesion or thebeginning of regeneration of the nerve. |
|
|
Trendelenburg Test (Hip) |
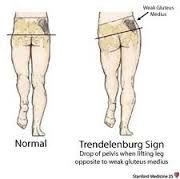
Weight is supported on affected limb x30 sec; the pelvis on thehealthy side falls instead of rising as in a normal hip. A positive test indicates gluteus medius weakness, afixed adduction contracture, short femoral neck or a dislocated hip. |
|
|
Valgus/Varus Stress Test (Knee) |
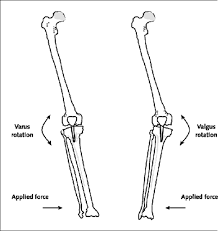
The patient is supine. Theknee is held at the ankle in 30° of flexion. With the other hand avalgising or varising force is applied to the appropriate side of the knee.Any angular giving way of the knee indicates a tear of the correspondingcollateral ligament (Valgus = medial CL; Varus = lateral CL). The knee isthen tested in full extension. |
|
|
Silfverskiold Test (knee/ankle) |
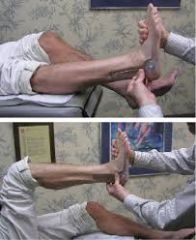
Fully extend the knee. Dorsiflex the foot, and measure the angle of dorsiflexion at the ankle. Next, flex the knee to 90 degrees and repeat the measurement. If there is less dorsiflexion when the knee is extended, this indicates a gastroc equinus, which is pulled tighter when the leg is straight. If dorsiflexion is equally limited with the knee flexed and extended, this points to either a soleal equinus or an osseous block. |
|
|
Lateral (Coleman) Block Test (Foot) |
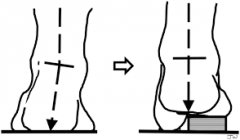
Used on varus heel to test hindfoot mobility. Patient's foot on wood block, 2.5 cm thick, with the heel and lateral border of foot on the block and bearing full weight while the first, second, & 3rd metatarsals are allowed to hang freely into plantar flexion and pronation. If the heel corrects to neutral position, the hindfoot is mobile. Thus, the deformity seen clinically is due to plantar flexion of 1st metatarsal. If the hindfoot remains in varus there is fixed hindfoot inversion deformity (or possibly spasticity of the tibialis posterior). |

