![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lab exercises? |
mixed dentition case analysis, removable posterior bite plate, removable hawley retainer, fixed appliances and molar uprighting spring, fixed lingual retainer, fixed lingual retainer, essix-type retainer |
|
|
definition of orthodontics & dentofacial orthopedics? |
the dental specialty which includes the diagnosis, prevention, interception, guidance and correction of malrelationships of the developing or mature orofacial structures. |
|
|
dentition & development? |
primary dentition, early mixed dentition, late mixed dentition, permanent dentition. |
|
|
primary dentition?
we want? |
20 primary teeth, deciduous dentition erupts between 6 months and 2.5 years, incisors are the first to be shed around age 7.
we want? normal eruption sequence, anterior spaces, 20 teeth, healthy.
|
|
|
Deciduous dentition-eruption? |
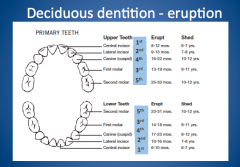
|
|
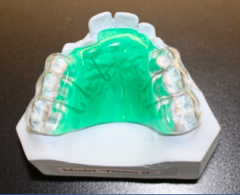
|
removable posterior bite plate |
|
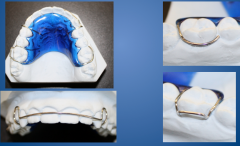
|
removable hawley retainer |
|

|
fixed appliances and molar uprighting spring |
|
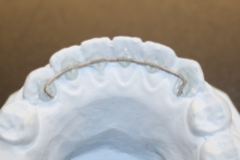
|
fixed lingual retainer |
|
|
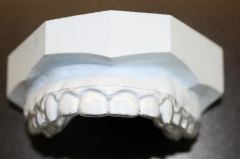
Essix-type retainer |
|
|
Early mixed dentition? |
chronological age: 6-9yo, permanent incisors and first molar present, deciduous canines and molars remain. |
|
|
Late mixed dentition? |
chronological age: 10-13yo, deciduous canines and molars are being replaced by permanent teeth |
|
|
Lee way space? |
definition: the difference in size between the primary canine and molars and their permanent successors (premolars). maxillary e space: 1.5mm per side mandibular e space: 2mm per side
leeway space =C+D+E-(3+4+5) E space= E-5 |
|
|
Permanent dentition? |
chronological age: after ~13 years of age permanent teeth have replaced all primary teeth. third molars erupt at age 17-35 years. |
|
|
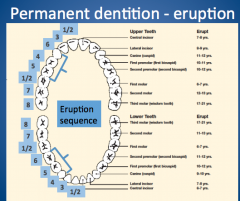
permanent dentition eruption? |
|
|
|
Eruption phenomenon-concerted action of 4 events? |
a) elongation of the permanent tooth root b) resorption of the primary tooth c) increase in alveolar height d) movement of the permanent tooth in the correct path through bone |
|
|
what is the responsibility of a GP? |
recognize malocclusion/eruption probs/parafunctional habits. prevent development of probs. intervene or refere to tx prob. |
|
|
ortho tx is 4 things? |
1) preventative-prevent development of malocclusion 2) interceptive-to intercept a developing prob 3) comprehensive- to tx malocclusion with fixed appliances, may include functional appliances. 4) limited- ortho tx with a limited objective, not involving the entire dentition. |
|
|
1) preventative ortho- examples? |
-space maintenance after early primary tooth loss -extraction of retained primary teeth to prevent impaction/ ectopic eruption. -dental restorations (interproximal caries). |
|
|
2) interceptive ortho? |
-habit discontinuation -recovery of space loss -correction of dental crossbite |
|
|
3) comprehensive ortho? |
the coordinated dx and tx leading to the improvement of a pt's craniofacial dysfxn and/or dentofacial deformity including anatomical, functional and esthetic relationships. -fully banded and bonded tx |
|
|
4) limited ortho- example? |
simple crossbite tx |
|
|
What is malocclusion? results from? |
definition: a deviation from the functionally and anatomically correct occlusion or a deviation in intramaxillary and/or intermaxillary relations of teeth from normal occlusion.
results from interplay of HEREDITY & ENVIRONMENT. |
|
|
symptoms of malocclusion? |
impaired oral fxn, poor facial aesthetics, dysfxn of the tmj articulation, susceptibility to dental caries, susceptibility to pdl dis, impaired speech due to malpositions of the teeth. |
|
|
etiologic factors for malocclusion classification system: Graber--2 types: general extrinsic factors & local intrinsic factors. |
Graber classification- general factors: heredity, congenital defects, environment, predisposing metabolic climate and disease, diet, abnormal pressure habits, posture, trauma. local factors: congenital absence of teeth, anomalies of tooth size, anomalies of tooth shape, abnormal labial frenum, premature loss of deciduous teeth, supernumerary teeth. |
|
|
classification of malocclusion: |
inherited=genetic predetermined. acquired= environmental, epigenetic (altering the activity of genes, not their structure). |
|
|
Heredity? |
for each individual there is a basic pattern or blue print for dentofacial development. -racial and familial characteristics repeat. -affected by heredity: tooth size, arch length and width, height of palatal vault, crowding/spacing, overbite/overjet, position and configuration of muscles, tongue size and shape, character of the oral mucosa. |
|
|
Environmental factors contributing to the development of malocclusion? prenatal: |
prenatal: trauma, maternal diet (deficiency diseases, beri beri, scurvy, ricketts), maternal alcohol&drugs, maternal metabolism and diseases ( Gachers dis, acute febrile dis (ex: measles, mumps, chicken pox), dis of muscle dysfxn (muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy, poliomyelitis), endocrine disorders (pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid).... fetal posture (Pierre Robin Sequence). |
|
|
Environmental factos contributing to the development of malocclusion? postnatal:
craniofacial complex is? |
postnatal: birth injuries, TMJ injuries, accidents, fractures, avulsion/displacement of teeth, posture-unimportant-may contribute, seldome a primary cause
The craniofactial complex is continuously adapting to the environment within its genetic disposition. |
|
|
examples of congenital defects? |
clefts of the lip and palate, cerebral palsy, crouzons syndrome, cleido-cranial dysostosis, cranial synostosis. |
|
|
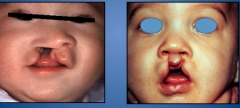
clefts of the lip and palate? |
through the area of the LI, often associated with supernumerary teeth or congenital absence, underdeveloped and constricted maxilla, anterior and posterior crossbites, hypernasality due to velopharyngeal insuff, 1/3 to 1/2 have previous fam hx, occurence 1/800. |
|
|
unilateral cleft then bilateral cleft |
|
|
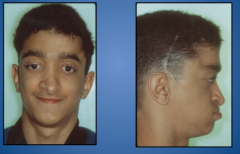
caused by genetic mutation, AD, early fusion of cranial sutures, midface deficiency, beaked nose, exophthalmus, hypertelorism (wide set eyes), class 3 malocclusion, anterior crossbite |
|
|
Dental etiologic factors? |
anomalies of tooth size, anomalies of tooth shape, hypodontia, abnormal labial frenum, premature loss of deciduous teeth, hyperdontia, delayed eruption of permanent teeth, abnormal eruptive path (ectopy), ankylosis of deciduous teeth, proximal caries, improperly contoured restorations. |
|
|
anomalies of tooth size? |
Bolton ratio-compares size of mand to max teeth. macrodontia/microdontia. |
|
|
anomalies of tooth shape? |
peg LI, mulberry molar and Hutchinson's incisor, fusion of roots, gemination-fusion of crowns, shovel shaped incisor |
|
|
Hypodontia (Tooth Agenesis)? indicates? |
def: congenital absence of a few teeth. prevalence: 2-4%, often bilateral, may be associated with systemic disease (ectodermal dysplasia), etiology: polygenic multifactorial model, can be hereditary.
hypodontia in primary dentition indicates absence of the respective permanent teeth as the primary tooth buds give rise to the permanent tooth buds. permanent teeth more frequently affected. generally the missing tooth is the most distal tooth of any given type: 3rd m 20%, 2nd PM 3.4%, mx LI 2.2%. |
|
|
hypodontia: problems associated with? -retained primary teeth? -absent LI often linked to? |
problems associated with tooth agenesis. retained primary teeth-> ankylosis. absent LI are often linked to: small LI and impacted canine on contralateral side. |
|
|
Abnormal labial frenum? |
thick fibrous and low attachment, may extend to the lingual papilla, may cause midline spacing (diastema), space may close as permanent cuspids erupt, may require surgery (frenectomy). |
|
|
Premature loss of deciduous teeth: causes, results, intervention? |
-causes= decay, pd dis, trauma. -results=movement of teeth and loss of arch length, blocked out permanent teeth, tipping of neighboring teeth, extrusion of opposing teeth. -intervention= missing primary second molar?=place space maintainer. missing primary first molar?=observe. if in doubt, place space maintainer. |
|
|
where is the best space maintainer for an unerupted permanent tooth? |
the overlying primary tooth. |
|
|
Hyperdontia? |
supernumary teeth, full-size teeth or amorphous composites of enamel and dentin. prevalence 1%. order of freqency: mx LI, mesiodens, PM, molars, lower incisor. may be impacted. can cause diastema, crowding, prevent eruption of other teeth. |
|
|
causes of delayed eruption of permanent teeth? |
meds, systemic dis, overall delayed development/puberty, sclerotic bone, ankylosed deciduous tooth, lack of space (due to early loss of deciduous tooth), supernumerary teeth, primary failure of eruption.. |
|
|
eruption is expected to proceed as long as? when does eruptive force cease? |
as long as the roots have not fully formed. eruptive force ceases as root formation is completed.
eruptive forces ceases as root formation is completed. |
|
|
ectopic eruption? |
tooth develops or erupts in an abnormal position. ex: mx M1 erupting too far mesially. md PM2 erupting too far distally. mx can erupting buccally or transposed.
causes: trauma, retained primary tooth, supernumary tooth, abnormal position in crypt
teeth erupt in the path of least resistance. |
|
|
Ankylosed primary teeth? |
ankylosis=calcification of the PDL resulting in abnormal fixation of a tooth. primary tooth ankylosis results in infraocclusion and eruption delays. primary molars |
|
|
what can caries and improperly contoured restorations cause? |
-can cause loss arch length=space loss. -teeth must be restored to full dimension to preserve space for erupting permanent teeth. |
|
|
Habits: definition? |
definition: a frequently repeated negative activity that may alter the normal development of the teeth or bones.
thumb or finger sucking. foreign objects. tongue thrusting. lip or cheek biting. mentalis muscle strain. |
|
|
Thumb sucking: tx? |
expansion & habit control. |
|
|
tongue crib/rake? |
habit appliance. fixed to upper or lower molarbands. |
|
|
bluegrass appliance? |
habit appliance. fixed. |

