![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
?
|
-Origin:
-Insertion: -Innervation: -Blood supply: -Action: |
|
|
splenius capitis
|
-Origin: nuchal ligament, supraspinous ligament, spinous processes of C7-T4
-Insertion: mastoid process and occipital bone -Innervation: dorsal rami -Blood supply: dorsal branch of posterior intercostal arteries -Action: |
|
|
splenius cervicis
|
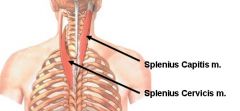
-Origin: spinous processes of T3-T6
-Insertion: transverse processes of C1-C3 -Innervation: dorsal rami -Blood supply: dorsal branch of posterior intercostal a. -Action: |
|
|
Transversospinal muscle group
|
-semispinalis, multifidus, rotatares
-Origin: transverse processes -Insertion: spinous processes, except semispinalis, which inserts onto the nuchal line of skull -Innervation: dorsal rami -Blood supply: dorsal branch of posterior intercostal a. -Action: contralateral rotation |
|
|
Multifidus
|
-Origin: sacrum, ilium, transverse processes of C4-C7
-Insertion: spinous processes of above vertebra, spanning 2-4 spinal segments -Innervation: dorsal rami -Blood supply: dorsal branch of posterior intercostal a. -Action: |
|
|
trapezius
|
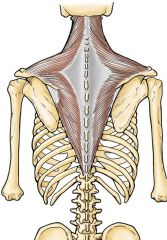
-Origin: external occipital protuberance, superior nuchal line, nuchal ligament, spinous processes of C7-T12
-Insertion: spine of scapula, acromion, lateral 1/3 of clavicle -Innervation: motor: CN 11 (spinal accessory nerve) sensory: proprioception via C3-C4 spinal nerves -Blood supply: superficial branch of transverse cervical a. -Action: elevates and depresses scapula, adducts/retracts scapula, rotates scapula upward & outward |
|
|
latissimus dorsi
|

-Origin: spinous processes of T7-T12, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, ribs 9-12
-Insertion: floor of bicipital/intertubercular groove -Innervation: thoracodorsal/middle subscapular nerve (C6 mainly,7,8); branches from posterior cord of the brachial plexus -Blood supply: thoracodorsal a. (a branch of subscapular a.) -Action: extends, adducts and medially rotates |
|
|
Levator scapulae
|
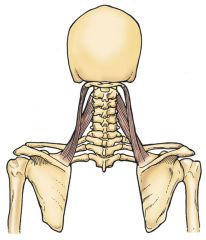
-Origin: transverse processes of C1-C4
-Insertion: medial boarder of scapula, superior to scapular spine -Innervation: C3-C4 anterior rami and dorsal scapular nerve -Blood supply: deep branch of transverse cervical a. -Action: elevates scapula, tilts glenoid fossa inferiorly by rotating scapula, extends neck, laterally flexes neck |
|
|
rhomboid minor
-origin -insertion ... rest rhomboid major |
-Origin: spinous processes of C7-T1
-Insertion: root of spine of scapula |
|
|
rhomboid major
|
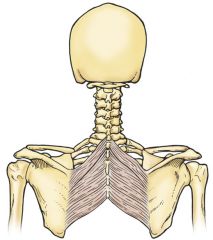
-Origin: T2-T5
-Insertion: medial border of scapula -Innervation: dorsal scapular nerve -Blood supply: deep branch of transverse cervical a./dorsal scapular a. -Action: retracts and elevates scapula, (w/help from other muscles rotates lateral aspect inferiorly) |
|
|
serratus posterior superior
|
-Origin: lower part of ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes of C7-T3
-Insertion: ribs 2-5 -Innervation: intercostal nerves T2-T5 -Blood Supply: -Action: elevates ribs (during forced inspiration) |
|
|
serratus posterior inferior
|
-Origin: spinous processes of T11-L3
-Insertion: ribs 9-12 -Innervation: intercostal nerves T9-T12 -Blood Supply: -Action: stabalizes lower ribs against diaphragm contraction |
|
|
Deltoid
|
Proximal attachment:
Lateral 1/3 of clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula Distal attachment: Deltoid tuberosity of humerus Innervation Axillary nerve Blood Supply: Deltoid branch of thoracoacromial artery Posterior humeral circumflex artery Action: Abducts, flexes, extends, internal and external rotation |
|
|
Supraspinatus Muscle
|
Proximal attachment:
Supraspinous fossa Distal attachment: Greater tubercle of humerus Innervation: Suprascapular nerve Blood supply: Suprascapular artery Main action: Initiates abduction of upper limb (*critical for first 15 degrees) Holds head of humerus in the glenoid cavity during arm elevation (flexion, abduction) |
|
|
Infraspinatus Muscle
|
Proximal attachment:
Infraspinous fossa of scapula Distal attachment: Middle facet on greater tubercle of humerus Innervation: Suprascapular nerve (C5 and C6) Blood supply: Suprascapular artery & scapular circumflex artery Main Actions: Laterally rotates humerus Holds head of humerus in glenoid fossa during arm movements |
|
|
Teres Minor Muscle
|
Proximal attachment:
Superior part of lateral border of scapula Distal attachment: Inferior facet on greater tubercle of humerus Innervation: Axillary nerve Main Actions: Laterally rotates the humerus Blood Supply: Scapular circumflex |
|
|
Subscapularis Muscle
|
Proximal attachment:
Subscapular fossa Distal attachment: Lesser tubercle of humerus Innervation: Upper and lower subscapular nerves (C5, C6 and C7) Main Actions: Medially rotates the humerus Blood Supply: Subscapular artery |
|
|
Teres Major Muscle
|
Proximal attachment:
Posterior surface of inferior angle of scapula Distal attachment: Medial lip of intertubercular groove of humerus Innervation: Lower subscapular nerve Blood supply: Circumflex scapular a. Main Actions: Medially rotates the humerus (opposite to teres minor) Adducts and extends the humerus |
|
|
Serratus Anterior M:
-NN -Main actions |
-Innervation
Long thoracic nerve (C5, C6 and C7) Innervated by anterior rami -Main actions Protracts the scapula Holds scapula against body wall Assists in rotating scapula during abduction of upper limb |
|
|
Pectoralis Minor Muscle:
|
Proximal attachment is 3rd-5th ribs near their costal cartilages.
Distal attachment is to the coracoid process of the scapula. Innervated by the medial pectoral nerve (anterior rami C8 and T1) Main action is to stabilize the scapula during upper limb movements. |
|
|
Subclavius Muscle:
|
Arises from the 1st rib near its costal cartilage.
Attaches to the inferior surface of the middle 3rd of the clavicle. Innervated by the nerve to the subclavius (mainly C5, and C6) Nerve comes off superior trunk of the brachial plexus Main action – to anchor and stabilize the clavicle |
|
|
Brachialis
|
Lies deep to the biceps brachii
Origin – Distal half of anterior surface of humerus Insertion – Coronoid process & ulnar tuberosity Innervated by the musculocutaneous n., C5 & C6 (and small lateral component-radial n., C7) Main Actions Most powerful forearm flexor, all elbow positions. Isometric contraction allows controlled forearm extension |
|
|
Gluteus Maximus
|
Proximal attachment
Ilium posterior to the posterior gluteal line, sacrum, coccyx, and sacrotuberous ligament. Distal attachment gluteal tuberosity of the femur and the iliotibial tract Innervated by the inferior gluteal nerve (L5,mainly S1, mainly S2) Extends thigh (and assists with lateral rotation |
|
|
Tensor Fascia Lata
|
Proximal attachment: anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) and anterior part of iliac crest
Distal attachment: iliotibial tract to the lateral condyle of the tibia Innervated by the superior gluteal nerve (mainly L4,mainly L5,S1) Abducts and medially rotates the thigh (active along with gluteus medius to stabilize the pelvis during unilateral stance). Helps flex the thigh |
|
|
Gluteus Medius
|
Proximal attachment: External surface of the ilium between the anterior and posterior gluteal lines
Distal attachment lateral surface of the greater trochanter of femur Innervated by the superior gluteal nerve Abducts thigh, keep pelvis level during unilateral stance phase of gate Anterior fibers medially rotate thigh |
|
|
Gluteus Minimus
|
Proximal attachment: Ilium between anterior and inferior gluteal lines
Distal attachment: Anterior surface of the greater trochanter of the femur Innervated by the superior gluteal nerve Abducts and medially rotates the thigh, helps keep pelvis level during unilateral stance phase of gate |
|
|
Positive Trendelenburg Gait/Sign:
Hip abductors keep the pelvis level during unilateral stance phase of gait. If one of the ___ muscles is weak (perhaps due to ___ nerve injury) then the pelvis will drop on the ___ side.. This is called a Trendelenburg gait pattern or a gluteus medius gait if observed while the patient is walking. If the pelvis drops when you ask a patient to raise one foot off the floor during an examination then it is called a positive Trendelenburg sign |
-gluteus medius
-superior gluteal -contralateral |
|
|
Piriformis
|
Proximal attachment: anterior surface of the sacrum and sacrotuberous ligament
Distal attachment: superior border of greater trochanter of the femur Innervated by branches of anterior rami of mainly S1,S2 Laterally rotates thigh, abducts the thigh from the flexed position |
|
|
Quadratus Femoris
|
Proximal attachment: lateral border of ischial tuberosity
Distal attachment: Quadrate tubercle on intertrochanteric crest of femur Innervated by nerve to quadratus femoris (L5,S1) Laterally rotates thigh and stabilizes femoral head in the acetabulum |
|
|
Obturator internus
|
Proximal attachment: obturator internus originates from the obturator membrane, margin of the obturator foramen
Distal attachment: medial aspect of the greater trochanter Innervated by the nerve to obturator internus Laterally rotates thigh |
|
|
Obturator externus
|
Proximal attachment: external surface of obturator membrane and adjacent bone
Distal attachment: trochanteric fossa Innervated by the obturator nerve It is an external rotator of the femur |
|
|
Hamstrings
-attachments |
Proximal attachment is the ischial tuberosity
Distal attachments Biceps femoris lateral side of the head of the fibula Semitendinosus medial surface of superior part of tibia Semimembranosus Posterior part of medial condyle of tibia (Oblique popliteal ligament) |
|
|
Sartorius
|
Proximal attachment: Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS)
Distal attachment: superior part of medial surface of tibia Innervated by the femoral nerve Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates the thigh at the hip joint, and flexes the leg at the knee joint |
|
|
Adductor Magnus (adductor part)
|
Proximal attachment: Adductor part - ischiopubic ramus
Distal attachment: posterior surface proximal femur, linea aspera medial supracondylar line Innervated by the obturator nerve Adducts thigh, aids medial rotation |
|
|
Adductor Magnus (hamstring part)
|
Hamstring part :
Proximal attachment: ischial tuberosity Distal attachment: adductor tubercle of femur and supracondylar line Innervated by the tibial division of sciatic n. |
|
|
Adductor Longus and Brevis
|
Proximal attachment: pubis
Distal attachment: linea aspera Innervated by obturator nerve Adducts thigh |
|
|
Pectineus
|
Proximal attachment: pectineal line of pubis
Distal attachment: femur inferior to lesser trochanter to the linea aspera Innervated by femoral nerve (even though its in the medial compartment) Adducts and flexes thigh |
|
|
Gracilis
|
Proximal attachment: Pubis (body and inferior ramus)
Distal attachment: superior part of medial surface of tibia Innervated by obturator nerve Adducts thigh Flexes leg and helps rotate leg medially at the knee joint |
|
|
Obturator externus
|
Proximal attachment: external surface of obturator membrane and adjacent bone
Distal attachment: trochanteric fossa Innervated by the obturator nerve It is an external rotator of the femur |

