![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Needs |
Physiological or psychological deficiencies that arouse behavior |
|
|
Maslow's Need Hierarchy Theory |
-Physiological, Safety, Love, Esteem, Self-Actualization - Human needs emerge in a predictable stair-step fashion; as need is satisfied, people proceed to fulfill the next higher level need |
|
|
Alderfer's ERG Theory |
- Existence Needs - Relatedness Needs - Growth Needs |
|
|
Existence Needs |
the desire for physiological and materialistic well-being |
|
|
Relatedness Needs |
the desire to have meaningful relationships with significant others |
|
|
Growth needs |
The desire to grow as a human being and to use one's abilities to their fullest potential |
|
|
McClelland's Need Theory |
- Need for achievement - Need for affiliation - Need for power |
|
|
Need for achievement |
Desire to accomplish something difficult |
|
|
Need for affiliation |
Spend more time maintaining social relationships, joining groups, and wanting to be loved. |
|
|
Need for power |
Desire to influence, coach, teach, or encourage others to achieve |
|
|
McClelland's Need Theory: Achievement-motivated people share 3 common characteristics: |
1. Preference for working on tasks of moderate difficulty. 2. Preference for situations in which performance is due to their efforts. 3. Desire more feedback on their successes and failures. |
|
|
Herzberg's Motivator-Hygene Model |
There are two types of factors: 1. Motivators 2. Hygene factors |
|
|
Motivators |
Job characteristics associated with job satisfaction |
|
|
Hygiene factors |
job characteristics associated with job dissatisfaction |
|
|
Adams's Equity theory |
Model of motivation that explains how people strive for fairness and justice in social exchanges or give-and-take relationships. Individuals compare their job inputs (education, skills, experience) and outcomes (pay, bonuses, promotions) with those of relevant others |
|
|
Negative inequity |
Comparison where another person receives greater outcomes than you for similar inputs |
|
|
Positive inequity |
Comparison in which another person recieves lesser outcomes than you for similar inputs |
|
|
Practical lessons from Equity Theory: - No matter how fair management thinks the organization's policies, procedures, and reward system are, each employee's ___________ is what counts - Managers benefit by allowing employees to participate in __________ - Employees should be given the opportunity to _____________. - Managers can promote cooperation and teamwork among group members by ___________ |
- perception of the equity of those factors - making decisions about important work outcomes - appeal decisions that affect their welfare - treating them equitably |
|
|
Vroom's Expectancy Theory of Motivation |
holds that people are motivated to behave in ways that produce desired combinations of expected outcomes |
|
|
Motivation |
the decision of how much effort to exert in a specific task situation |
|
|
Expectancy |
Represents an individual's belief that a particular degree of effort will be followed by a particular level of performance |
|
|
Factors which influence an employee's expectancy perceptions |
- Self-esteem - Self-efficacy - Previous success at the task (prior experience) - Help received from others (support) - Information necessary to complete the task - Good materials and equipment to work with |
|
|
Instrumentality |
A performance to outcome perception |
|
|
Valence |
The positive or negative value people place on outcomes |
|
|
Outcomes |
Different consequences that are contingent on performance |
|
|
Goal |
- what an individual is trying to accomplish - object or aim of an action |
|
|
Goals... |
-Direct attention -Regulate effort -Increase persistence -foster the development and application of task strategies and action plans |
|
|
SMART Goals |
Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Results-oriented, Time-bound |
|
|
Scientific management |
That kind of management which conducts a business or affairs by standards established by facts or truths gained through systematic observation, experiment, or reasoning |
|
|
Top-Down Motivational Approaches |
- Job enlargement - Job rotation - Job enrichment |
|
|
Job enlargement |
Putting more variety into a workers job by combining specialized tasks of comparable difficulty |
|
|
Job rotation |
Moving employees from one specialized job to another |
|
|
Job enrichment |
Building achievement, recognition, stimulating work, responsibility, and advancement into a job. |
|
|
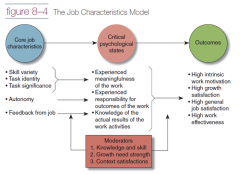
Job Characteristics Model |
|
|
|
Job crafting |
Proactive and adaptive employee behavior aimed at changing the nature of one's job |

