![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why is life carbon-based?
List the 5 reasons. |
1) Tetravalent (i.e. four bonds which allows carbon-based molecules to have 3-D shape for life's building blocks)
2) C-C bonds are strong 3) C-X bonds are possible 4) Carbon makes double and triple bonds 5) Exchange reactions (e.g. AB + CD > AC + BD) |
|
|
Define "Atom"
|
Atom:
The basis for organic molecules |
|
|
List the three types of atoms and its composition.
|
1) Neutral:
p+ = e- 2) Cation: p+ > e- 3) Anion p+ < e- |
|
|
Define "orbital"
|
Orbital:
The standing wave around nuclei where the e- can be found. |
|
|
Heisenberg Principle
|
An e-''s location OR trajectory can be identified, but not both at the same time.
|
|

|
Draw an "s-orbital".
How many types are there? |
|

|
Draw a "p-orbital"
How many types is/are there? |
|
|
List the "principal quantum numbers"
|
Principle quantam numbers: n, l, ml, ms
|
|
|
Define principle quantum number "n".
|
Principle quantum number "n":
Tells you the size and energy of the e-. |
|
|
What does the principle quantum number "l" describe?
What is its equation? |
describes: shape of the orbital
l = 0,1,2....(n-1) |
|
|
Define "n".
|
"n" = principal quantum #
Tells you the size and energy of the e-. |
|
|
Define "electron selection rules".
|
Electron selection rules:
Determines what orbital an e- is in. |
|
|
How many types of d-orbitals are there?
|
There are 5 types of d-orbitals.
|
|
|
Define "l"
|
Principal quantum "l":
Angular momentum. Tells you the shape ofthe orbital. |
|
|
When "n" equals the following what does "l" equal? Identify what types of orbitals are in each.
n=1 n=2 n=3 |
n=1 L = 0
"s" orbital n=2 L= 0, 1 "s" and "p" orbitals n=3 L=0, 1, 2 "s", "p", "d" orbitals |
|
|
Can "n" equal zero? Why/why not?
|
Principal quantum "n" cannot equal zero because it describes the size and energy of the e-. Size and energy of an e- cannot equal zero.
|
|
|
What does principal quantum "m(l)" describe?
What is its equation? |
Principal quantum "m(l)" describes the orientation {i.e. p(x), p(y), p(z)} of the e-.
equation: -L...0...+L |
|
|
When "m(L)" equals the following, what does each mean?
m(L) = -1 m(L) = 0 m(L) = +1 |
"m(L) = -1" means the e- can be found on the "p(x)" axis.
"m(L) = 0" means the e- can be found on the "p(y)" axis. "m(L) = +1" means the e- can be found on the "p(z)" axis. |
|
|
What does it mean when "m(L)" equals the following?
|
"m(L) = -2, -1, 0, +1, +2" describes the location of the e- within the 5 different types of d-orbitals.
|
|
|
Describe each:
1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 3d 3d |
"1s"
n=1, L=0, m(L) = 0, m(s) = -1/2 and +1/2 "2s" n = 2, L=0, m(L) = -1, 0, +1, m(s) = -1/2 and +1/2 "3s" |
|
|
Pauli Exclusion Principal
|
Pauli Exclusion Principal:
No two e-'s can have the same set of principal quantum numbers {i.e. n, l, m(L), m(s)}. |
|
|
What are the two atom bonding types? Describe each.
|
Atom bonding types:
1) Ionic: Complete charge separation of atoms. (e.g. Na+ and Cl-) The electrostatic attraction between the positive and negative atoms hold the atoms together. 2) Covalent: Sharing of e-'s. 2) |
|
|
Define "formal charge".
|
"Formal charge":
The observed charge on each atom within the molecule. |
|
|
How do you calculate "formal charge"?
|
(# of valence e-'s) - ({# of bonded e-'s} / 2) - (# of e-'s within lone pairs)
|
|
|
Go online to practice calculating "formal charges" until it becomes second nature.
|
..
|
|
|
Define "electronegativity".
What is its trend in the periodic table? |
Electronegativity:
The degree by which an atom wants to attract e-'s. Electronegativity trend: 1) Diagonally toward Fluorine: increasing electronegativity 2) Upward: Increasing 3) Downward: Decreasing 4) Away from fluorine: Decreasing |
|
|
Fill in the blanks:
____(1)_____ is important for breaking and formation of _____(2)____ because it leads to ___3___ and ____(4)___ . |
____(1, Electronegativity)_____ is important for breaking and formation of _____(2, covalent bonds)____ because it leads to ___(3, polarity)___ and ____(4, dipole moments)___ .
|
|
|
What is the symbol for dipole moments?
|
Greek letter "mu".
|
|
|
Define "hybridization".
|
Hybridization:
A phenomenon observed why leads to a molecule's geometry. |
|
|
Why do atoms want to hybridize?
|
To lower energy.
|
|
|
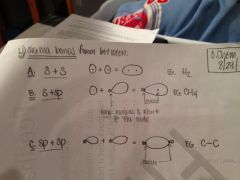
How many sigma bonds are there?
What types of orbitals are in each? |
Types of sigma bonds:
3 types Orbitals found in each type of sigma bond: 1) s+s 2) s+sp 3) sp+sp |
|
|
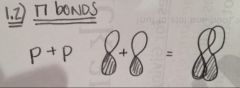
How many types of pi bonds are there?
What types of orbitals are in each? |
Number of pi bonds:
There is only one type of pi bond. Orbitals within a pi bond: p + p |
|
|
Find hybridization problems online and practice until they become second nature.
|
..
|
|
|
What is a function of antibonding orbitals?
|
Antibonding orbitals help lock the geometry of a molecule in place.
|
|
|
Explicitly draw each type of pi bond.
|
|
|
Explicitly draw each type of sigma bond.
|
|

|
Draw each of the d-orbitals.
|
|
|
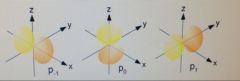
Draw all of the p-orbital orientations.
|

