![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Wolff-Kishner Reduction |
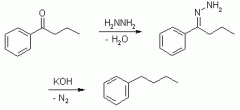
Remove carbonyl O |
|
|
Clemmensen Reduction |
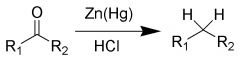
Remove carbonyl O |
|
|
Carbocation Stabilization |
-Stabilized by electron donating groups (including Halogens) ex. R, Cl, NH2 -Destabilized by electron withdrawing groups ex. C=O |
|
|
Carbanion Stablization |
-Stabilized by electron withdrawing groups ex. C=O, NO2 -Destabilized by electron donating groups including Halogens ex. Cl, R |
|
|
Electron-Withdrawing Group |
-Increases acidity because increases stability of (-) conjugate base -Increases stability of carbanions -ex. NO2, C=O, Cl (halogens are EW for acids/bases) |
|
|
Electron-Donating Group |
-Increases basicity because increases stability of (+) conjugate acid -Increases stability of carbocations -ex. R, benzene, Cl (halogens will electron donate to only carbocations and carbanions) |
|
|
Disproportionation Reaction |
Redox reaction in which the same species is both reduced and oxidized |
|
|
Halogens (Cl, Br) |
-Electron withdrawing for acids/bases -Electron donating for carbocations/carbanions because can form resonance structure out of its lone pair |

