![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
HBr
|
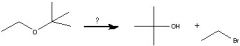
What Reagent?
|
|
|
In a Williamson ether synthesis
1)what kind of molecule is made in the first step? 2)How is it made? |
1) Alkoxide
2) Adding an alcohol to Na, K, or NaH |
|
|
In a Williamson Ether Synthesis, what occurs if a secondary halide or tosylate is used?
|
Creates a possibility for an E2 Reaction to occur, which competes with the desired SN2, reaction usually sucks.
|
|
|
What does MCPBA do as a reagent?
|
Breaks an Alkene into an epoxide.
|
|
|
1)What kind of substance is MCPBA and CH3COOOH?
2)What do they do as reagents? |
1)Peracids
2)Break alkenes into epoxides |
|
|
What does CH3COOOH do as a reagent?
|
Breaks an Alkene into an epoxide
|
|
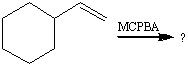
What Product?
|
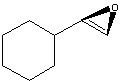
.
|
|
|
HI
|
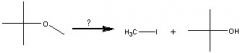
What Reagent?
|
|

What Reagent?
|
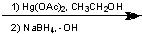
.
|
|
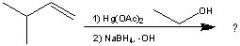
What Product?
|
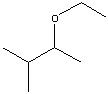
.
|
|
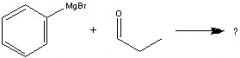
What Product?
|
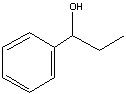
.
|
|
|
What hybridization are all carbons in a benzene ring?
|
sp2
|
|
|
1)What bond angle are all carbons in a benzene ring?
2)What shape does the ring take because of this? |
1)120
2)Flat |
|
|
What is the molecular mass of benzene?
|
78
|
|
|
Is a double bond or single bond longer?
|
Single
|
|
|
What bonds are longer in a benzene ring?
|
All benzene bonds stretch to the same size
|
|
|
What happens in an aromatic to allow resonance stabilization?
|
P-orbitals line up parallel to allow electrons to move freely from one to the other
|
|
|
What is the kekule structure?
What does it symbolize? |
Constant resonance
|
|
|
How stable is benzene? How reactive?
|
Very Stable. Very unreactive.
|
|
|
Define Aromaticity
|
High Stability, usually due to resonance stabalization
|
|
|
How do you determine if a molecule is aromatic?
|
1)Cyclic
2)Planar compound - must have all atoms in ring in sp2 hybridization 3)Must have Huckel # of pi electrons |
|
|
What is the Huckel Rule?
|
In order to be aromatic the ring must have 4n+2 pi electrons where n=0,1,2...
|
|
|
What are the first four Huckel Numbers?
|
2,6,10,14...
|
|
|
How do you know if a compound is anti-aromatic?
|
Must be cyclic and planar, but no huckel number of pi electrons exists. Has 4n Pi electrons
|
|
|
What is a heteroatom?
|
N, O, P, S..
|
|
|
What does the atomic number signify in a neutral atom
|
The number of protons in the nucleus and the number of electrons surrounding it
|
|
|
What does the mass number signify in a neutral atom
|
Sum of the number of protons and neutrons in nucleus
|
|
|
What does the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle state?
|
The exact location of an electron can never be determined, but the orbital defines where there is a high probability of finding an electron with a certain energy.
|
|
|
Explain the arrangement of electron density of a 2s orbital.
|
Has a small region of high electron density close to the nucleus, but most of the electron density is farther from the nucleus, beyond a node, or region of zero electron density.
|
|
|
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
|
There are a maximum of 2 electrons in each orbital (spins must be paired)
|
|
|
What is the Aufbau Principle?
|
Electrons "build up" the orbitals from lowest energy to highest energy.
|
|
|
What is Hund's Rule?
|
Electrons "build up" or "fill" one orbital at a time in a sublevel and then pair.
|
|
|
How is the major contributor of a molecule with resonsance determined?
|
1) As many octets as possible
2) As many bonds as possible 3) Any negative charges on the more electronegative atoms 4) As little charge seperation as possible |
|
|
Arrhenius Acid
|
substance that ionizes/dissociates in water to give a hydronium ion
|
|
|
Arrhenius base
|
substance that dissociates in water to give a hydroxide ion
|
|
|
How is pH calculated?
|
pH = -log[H3O+)
|
|
|
Bronsted-Lowry Acid
|
any species that can donate a proton
|
|
|
Bronsted-Lowry Base
|
any species that can accept a proton
|
|
|
Lewis base
|
an electron pair donor, nucleophile
|
|
|
Lewis acid
|
an electron pair acceptor, electrophile
|
|
|
degenerate orbitals
|
orbitals with identical energies
|
|
|
conjugate acid
|
acid that results from the protonation of a base
|
|
|
conjugate base
|
base that results from the deprotonation of an acid
|
|
|
constitutional isomers
|
isomers that are connected differently, differing in bonding sequence
|
|
|
structural isomers
|
isomers that are connected differently, differing in bonding sequence
|
|
|
stereoisomers
|
isomers that differ only in how their atoms are arranged in space
|
|
|
cis/trans isomers
|
stereoisomers that differ in their cis-trans arrangement on a ring or a double bond
|
|
|
geometric isomers
|
stereoisomers that differ in their cis-trans arrangement on a ring or a double bond
|
|
|
axial bond
|
one of six bonds (three up and three down) on the chair conformation of the cyclohexane ring that are parallel to the "axis" of the ring
|
|
|
The most stable conformation of cyclohexane
|
Chair conformation
|
|
|
cracking
|
heating large alkanes to cleave them into smaller molecules
|
|
|
equatorial bond
|
one of the six bonds (three down and three up) on the cyclohexane ring that are directed out toward the "equator" of the ring.
|
|
|
spirocyclic conformation
|
bicyclic compounds in which the two rings share only one carbon atom
|
|
|
The first propagation step is ____ for bromination but ____ for chlorination.
|
endothermic, exothermic
|
|
|
The transition states forming the primary and secondary radicals for the ____ ____ have a larger energy difference than those for the ____ ____.
|
endothermic bromination
exothermic chlorination |
|
|
In a ____ reaction, the transition state is closer to the products in energy and in structure.
|
endothermic
|
|
|
In a ____ reaction, the transition state is closer to the reactants in energy and in structure.
|
exothermic
|
|
|
Hammond postulate
|
Related species that are closer in energy are also closer in structure. The structure of a transition state resembles the structure of the closest stable species.
|
|
|
Name of a benzene with an -OH
|
Phenol
|
|
|
Name of a benzene with an -NH2
|
Aniline
|
|
|
Name of a benzene with a -CH3
|
Toluene
|
|
|
Name of a benzene with an -OCH3
|
Anisole
|
|
|
Name of a benzene with a -COOH
|
Benzoic Acid
|
|
|
Name of a benzene with a -COH
|
Benzaldehyde
|
|
|
What kind of substituent configuration does ortho represent?
|
1,2
|
|
|
What kind of substituent configuration does meta represent?
|
1,3
|
|
|
What kind of substituent configuration does para represent?
|
1,4
|
|
|
What does a benzene ring require to proceed in a substitution reaction?
|
Super strong electrophile
|
|
|
What does the halogenation of a benzene require?
|
Lewis acid catalyst
|
|
|
What catalyst is required for the chlorination of a benzene?
|
FeCl3 or AlCl3
|
|
|
What catalyst is required for the brominatino of a benzene?
|
FeBr3
|
|
|
How would you brominate benzene? How would you chlorinate?
|
Br2, FeBr3
Cl2, FeCl3 or AlCl3 |
|
|
What hybridization does the reactive carbon have in its intermediate state of an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction?
|
sp3
|
|
|
What hybridization does an aromatic carbon have? What hybridization is the end product of the carbon after electrophilic aromatic substitution?
|
sp2, sp2
|
|
|
How do you iodinate an aromatic?
|
I2, HNO3
|
|
|
What reagents are required for the nitration of an aromatic?
|
HNO3, H2SO4
|
|
|
How does HNO3 and H2SO4 act as reagents to nitrate an aromatic?
|
H2SO4 is a much stronger acid so it donates a proton to the less stronger acid, HNO3. The HNO3 acts as a base and accepts the proton. H2NO3 loses water and NO2 is formed, which reacts in the substitution.
|
|
|
What can be used to reduce nitrobenzene to aniline?
|
Zn, Sn.. , HCl
|
|
|
How is an aromatic sulfonated?
|
SO3, conc. H2SO4
|
|
|
An electron withdrawing substituent on an aromatic ring is:
activating/deactivating ortho/meta/para director |
deactivating
meta director |
|
|
An electron donating substituent on an aromatic ring is:
activating/deactivating ortho/meta/para director |
activating
ortho/para director |
|
|
A halogen on an aromatic ring is:
activating/deactivating ortho/meta/para director |
deactivating
ortho/para director |
|
|
2,4-dimethylpentanol
Structure? |
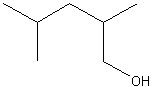
Name?
|
|
|
cyclohex-3-en-1-ol
Structure? |
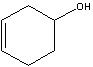
Name?
|
|
|
6-bromo-5-methyl-2,3-hexandiol
Structure? |
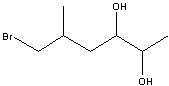
Name?
|
|
|
It is a general principle that reactions proceed towards ___ reactive species.
|
Less
|
|
|
What is the stability of the following starting with the most stable to least stable?
CH3CH2O- ClCH2CH2O- CH3O Cl3CCH2O- |
Cl3CCH2O-
ClCH2CH2O- CH3O- CH3CH2O- |
|
|
What is the reactivity of the following starting with the most reactive to least reactive?
CH3CH2O- ClCH2CH2O- CH3O Cl3CCH2O- |
CH3CH2O-
CH3O- ClCH2CH2O- Cl3CCH2O- |
|
|
3 > 1 > 2
|
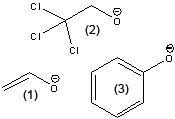
Number from most to least stable
|
|
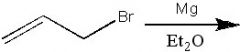
What product?
|

.
|
|
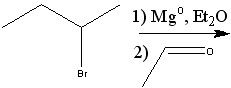
Product?
|
.
|
|

What reagent(s)?
|
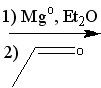
.
|
|
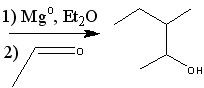
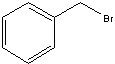
What starting material?
|
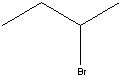
.
|
|
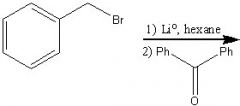
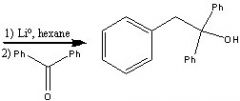
What product?
|
.
|
|

What reagents?
|
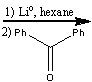
.
|
|
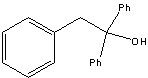
What starting material?
|
.
|
|
|
What product is formed when combining a grignard reagent and an aldehyde?
|
Secondary alcohol
|
|
|
What product is formed when combining a grignard reagent and a ketone?
|
Tertiary alcohol
|
|
|
What product is formed when combining a grignard reagent and formaldehyde?
|
Primary alcohol
|
|
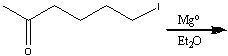
What product?
|
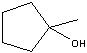
.
|
|
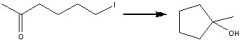
What reagents?
|
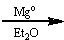
.
|
|
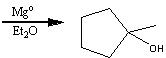
What starting material?
|

.
|
|
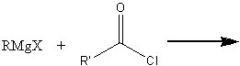
What product?
|
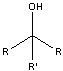
.
|
|
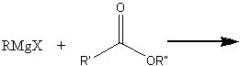
What product?
|
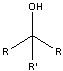
.
|
|
|
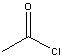
In order to get a tertiary alcohol from a grignard reagent and an acid chloride, what must occur?
|
Grignard reagent must react twice with the acid chloride.
|
|
|
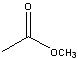
In order to get a tertiary alcohol from a grignard reagent and an ester, what must occur?
|
Grignard reagent must react twice with the ester.
|
|
|
What kind of product(s) are formed when a grignard reagent is reacted with an ester?
|
A tertiary alcohol and a primary alcohol
|
|
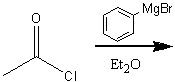
What product?
|
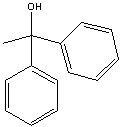
.
|
|
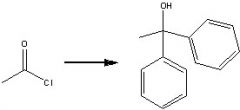
What reagents?
|
.
|
|
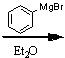
What starting material?
|
.
|
|
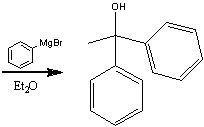
What product?
|
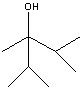
.
|
|

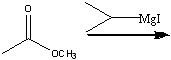
What reagents?
|
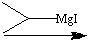
.
|
|
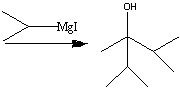
What starting material?
|
.
|
|
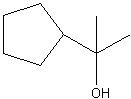
Synthesize with:
a)grignard reagent and a carbonyl. b)organolithium and a carbonyl c)grignard reagent and acid chloride |
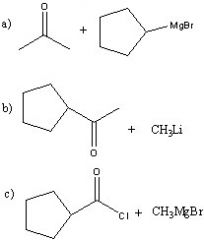
.
|
|
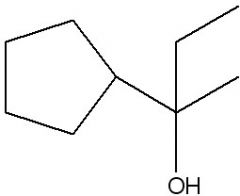
Synthesize.
|
.
|
|
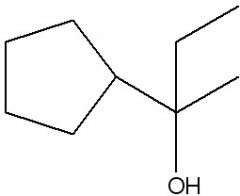
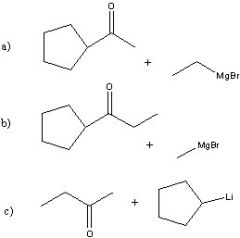
Synthesize with:
a)Grignard reagent (2 ways) b)Organolithium |
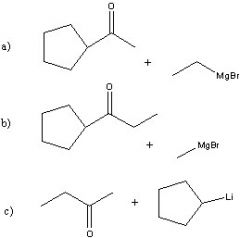
.
|
|
|
1)Grignard chemistry will not work with a molecule with these functional group(s).
2)This will happen instead of the grignard reaction 3)This happens because |
1) Hydroxyl, sulfhydryl, -NH
2) Acid/Base reaction. The Reactive group from the grignard reagent will remove the H from the acidic O, S, or N, and the acidic atom that lost the proton will bond with the organometallic. 3)It takes less energy |
|
|
Define Oxidation
|
Addition of O content or removal of H
|
|
|
Define Reduction
|
Addition of H content or removal of O
|
|
|
When a molecule is in its most oxidized state it is ____ to reduce.
|
difficult
|
|
|
If you wanted to reduce a ketone or aldehyde what could you use?
|
LAH or NaBH4
|
|
|
If you wanted to reduce a carboxylic acid what could you use?
|
LAH
|

