![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Meth- |
1 carbon atom |
|
|
Eth- |
2 carbon atoms |
|
|
Prop- |
3 carbon atoms |
|
|
But- |
4 carbon atoms |
|
|
Pent- |
5 carbon atoms |
|
|
Hex- |
6 carbon atoms |
|
|
Alkanes |
Hydrocarbons Single bonds |
|
|
Alkanes |
Hydrocarbons Single bonds |
|
|
Alkenes |
Hydrocarbons Contain carbon-carbon double bonds C=C is their functional group |
|
|
Alkanes |
Hydrocarbons Single bonds |
|
|
Alkenes |
Hydrocarbons Contain carbon-carbon double bonds C=C is their functional group |
|
|
Alcohols |
Not hydrocarbons Like alkanes but with an OH group OH is their functional group |
|
|
Alkanes |
Hydrocarbons Single bonds |
|
|
Alkenes |
Hydrocarbons Contain carbon-carbon double bonds C=C is their functional group |
|
|
Alcohols |
Not hydrocarbons Like alkanes but with an OH group OH is their functional group |
|
|
Carboxylic acids |
Not hydrocarbons Functional group is COOH |
|
|
Alkanes |
Hydrocarbons Single bonds |
|
|
Alkenes |
Hydrocarbons Contain carbon-carbon double bonds C=C is their functional group |
|
|
Alcohols |
Not hydrocarbons Like alkanes but with an OH group OH is their functional group |
|
|
Carboxylic acids |
Not hydrocarbons Functional group is COOH |
|
|
Functional group is |
The part of a molecule which largely dictates how the molecule will react |
|
|
Alkanes are found in |
Petroleum and natural gas |
|
|
Alkanes are found in |
Petroleum and natural gas |
|
|
The first four alkanes are __________ at room temperature. The next twelve are __________ and the rest are ___________ |
Gases Liquids Solids |
|
|
Alkanes are found in |
Petroleum and natural gas |
|
|
The first four alkanes are __________ at room temperature. The next twelve are __________ and the rest are ___________ |
Gases Liquids Solids |
|
|
Since all their bonds are C—C bonds alkanes are ______ |
Saturated |
|
|
Alkanes are found in |
Petroleum and natural gas |
|
|
The first four alkanes are __________ at room temperature. The next twelve are __________ and the rest are ___________ |
Gases Liquids Solids |
|
|
Since all their bonds are C—C bonds alkanes are ______ |
Saturated |
|
|
Alkanes are generally _________ but they do ________ well in _______ |
Unreactive Burn Oxygen |
|
|
Alkanes are found in |
Petroleum and natural gas |
|
|
The first four alkanes are __________ at room temperature. The next twelve are __________ and the rest are ___________ |
Gases Liquids Solids |
|
|
Since all their bonds are C—C bonds alkanes are ______ |
Saturated |
|
|
Alkanes are generally _________ but they do ________ well in _______ |
Unreactive Burn Oxygen |
|
|
Equation for Methane burning |
CH4 (g)+ 2O2 (g) —> CO2 (g) + 2H20(l) + heat energy |
|
|
Alkanes are found in |
Petroleum and natural gas |
|
|
The first four alkanes are __________ at room temperature. The next twelve are __________ and the rest are ___________ |
Gases Liquids Solids |
|
|
Since all their bonds are C—C bonds alkanes are ______ |
Saturated |
|
|
Alkanes are generally _________ but they do ________ well in _______ |
Unreactive Burn Oxygen |
|
|
Equation for Methane burning |
CH4 (g)+ 2O2 (g) —> CO2 (g) + 2H20(l) + heat energy |
|
|
If there is not enough oxygen the alkanes undergo _______ _______. Giving off _____ ______. The equation for this is ________. |
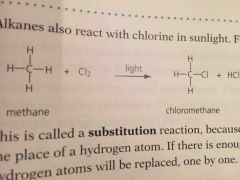
Incomplete combustion Carbon monoxide 2CH4 (g) + 3O2 (g) —> 2CO(g) + 4H2O(l) + less heat energy |
|
|
Alkanes react with _______ in ________. Give the equation using methane |
Chlorine Sunlight Methane+ chlorine —> cloromethane + HCl
|
|
|
An alkane reacting with ______ is called a _______ reaction because the chlorine atom takes the place of the _______ atom. If there is enough chlorine _____ ______ ________. The reaction is ______ it will not take place in the dark because the light energy is need to break the chlorine molecules |
Chlorine Substitution Hydrogen All hydrogen atoms will be replaced Photochemical |
|
|
Isomers are |
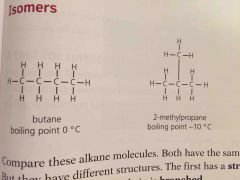
Compounds with same formula but different structures |
|
|
Since isomers have different structures they also have slightly different properties. They have ____ boiling points because the branches make it harder for molecules to get close so the attraction is less strong |
Lower |
|
|
Isomers are |
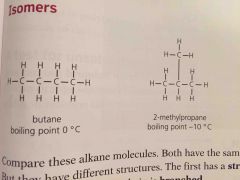
Compounds with same formula but different structures |
|
|
Since isomers have different structures they also have slightly different properties. They have ____ boiling points because the branches make it harder for molecules to get close so the attraction is less strong |
Lower |
|
|
Alkenes are ________ because they have _____ _____ bonds |
Unsaturated Double Carbon |
|
|
Isomers are |
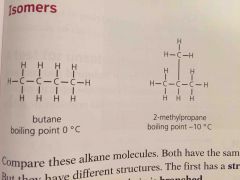
Compounds with same formula but different structures |
|
|
Since isomers have different structures they also have slightly different properties. They have ____ boiling points because the branches make it harder for molecules to get close so the attraction is less strong |
Lower |
|
|
Alkenes are ________ because they have _____ _____ bonds |
Unsaturated Double Carbon |
|
|
Alkenes are made from alkanes by ________. _______ is also produced |

Cracking Hydrogen |
|
|
Isomers are |
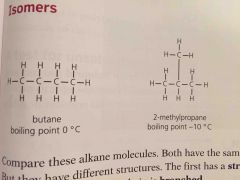
Compounds with same formula but different structures |
|
|
Since isomers have different structures they also have slightly different properties. They have ____ boiling points because the branches make it harder for molecules to get close so the attraction is less strong |
Lower |
|
|
Alkenes are ________ because they have _____ _____ bonds |
Unsaturated Double Carbon |
|
|
Alkenes are made from alkanes by ________. _______ is also produced |
Cracking Hydrogen |
|
|
Alkenes are _______ reactive than alkanes because the double bond can break to add on more other atoms |
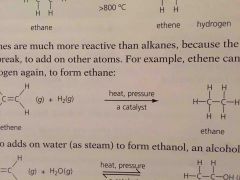
More |
|
|
Isomers are |
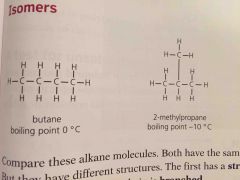
Compounds with same formula but different structures |
|
|
Since isomers have different structures they also have slightly different properties. They have ____ boiling points because the branches make it harder for molecules to get close so the attraction is less strong |
Lower |
|
|
Alkenes are ________ because they have _____ _____ bonds |
Unsaturated Double Carbon |
|
|
Alkenes are made from alkanes by ________. _______ is also produced |
Cracking Hydrogen |
|
|
Alkenes are _______ reactive than alkanes because the double bond can break to add on more other atoms |
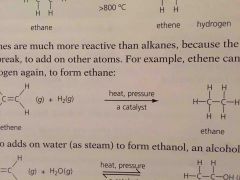
More |
|
|
Alkene molecules undergo a very useful _________ _______ where they add on to each other to form compound with very long carbon chains. |
Addition reaction |
|
|
Isomers are |
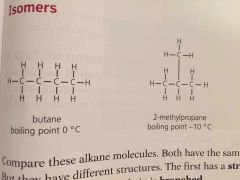
Compounds with same formula but different structures |
|
|
Since isomers have different structures they also have slightly different properties. They have ____ boiling points because the branches make it harder for molecules to get close so the attraction is less strong |
Lower |
|
|
Alkenes are ________ because they have _____ _____ bonds |
Unsaturated Double Carbon |
|
|
Alkenes are made from alkanes by ________. _______ is also produced |

Cracking Hydrogen |
|
|
Alkenes are _______ reactive than alkanes because the double bond can break to add on more other atoms |
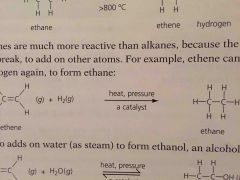
More |
|
|
Alkene molecules undergo a very useful _________ _______ where they add on to each other to form compound with very long carbon chains. |
Addition reaction |
|
|
Alkene molecules are called _______ .the long-chain compounds they form are called ______. The reaction is called ________ |
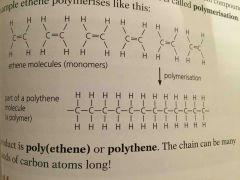
Monomers Polymers Polymerisation |
|
|
Isomers are |
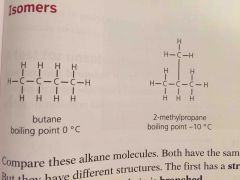
Compounds with same formula but different structures |
|
|
Since isomers have different structures they also have slightly different properties. They have ____ boiling points because the branches make it harder for molecules to get close so the attraction is less strong |
Lower |
|
|
Alkenes are ________ because they have _____ _____ bonds |
Unsaturated Double Carbon |
|
|
Alkenes are made from alkanes by ________. _______ is also produced |
Cracking Hydrogen |
|
|
Alkenes are _______ reactive than alkanes because the double bond can break to add on more other atoms |

More |
|
|
Alkene molecules undergo a very useful _________ _______ where they add on to each other to form compound with very long carbon chains. |
Addition reaction |
|
|
Alkene molecules are called _______ .the long-chain compounds they form are called ______. The reaction is called ________ |
Monomers Polymers Polymerisation |
|
|
How can you test if a hydrocarbon is unsaturated |
Bromine water if C=C is present will go from Orange to colorless |
|
|
Why does bromine water go from Orange to colorless when added to an unsaturated hydrocarbon |
An addition reaction takes place and the color disappears |
|
|
In alkenes the chains can branch in different ways and the double bonds can be in different positions. These are called _____ |
Isomers |

