![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Importance of cell body (of neuron)
|
Contains genetic and metabolic machinery for neurotransmitter synthesis and organelles. Vital.
|
|
|
Axon
|
Propagates action potentials.
|
|
|
Dendrites
|
Axons of other neurons input signaling factors and neurotransmitters to dendrites.
|
|
|
Synapse
|
Space between axon terminal and neuron or other target tissue. Can occur on cell bodies, dendrites, or axons.
|
|
|
Nomenclature for Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) cell bodies and axons
|
Cell Body = Ganglion
Axon = Nerve |
|
|
Nomenclature for Central Nervous System (CNS) cell bodies and axons
|
Cell Body = Nucleus
Axon = Tract |
|
|
All neurons in the PNS are surrounded by ________
|
Glia (Schwann cells)
|
|
|
Function of Schwann cells
|
Surrounds (wraps around) all peripheral nerve axons and cell bodies. Thick layer of phospholipids = myelination. Protective.
|
|
|
Nodes of Ranvier
|
Gaps between cells where there is no myelination.
|
|
|
What is Laminin?
Where found? |
Glycoprotein that promotes growth and regeneration of axons and glia. Found in basement membrane.
|
|
|
Which type of connective tissue surrounds:
A) whole nerve B) fascicles of nerve fibers C) surrounds individual axons |
A) Epineurium
B) Perineurium C) Endoneurium |
|
|
Forms a protein interface between Schwann cells and endoneurium.
|
Basement membrane
|
|
|
What type of cells secrete the protein matrix that makes up the basement membrane?
|
Schwann cells
|
|
|
Clusters of axons targeting single muscles or cutaneous (skin) regions are called __________
|
Nerve fascicles
|
|
|
T or F?
A single nerve has one or many fascicles that all innervate the same muscle or region. |
F
A nerve can have fascicles that separate out as individual nerves (ie femoral). But True that nerves can have one or many fascicles. |
|
|
Nervi nervorum
|
Bundles of axons innervating the CT layers of nerves (endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium)
|
|
|
Vasa nervorum
|
local blood vessels to CT, axons and glia in nerves
|
|
|
Guillain-Barre syndrome
|
Demyelination of mostly motor fibers by auto-immune response to infection, surgery or immunization. Affects the PNS.
|
|
|
A demyelination disease that affects the CNS.
|
Multiple Sclerosis
|
|
|
Negative symptoms of neuropathy
|
Loss of sensation, muscle weakness, and atrophy.
|
|
|
Positive symptoms of neuropathy
|
Parasthesia (burning, tingling, tightness, or pins and needles)
Hyperalgesia (exaggerated pain perception in response to a normally painless stimulus) |
|
|
Causes of neural disease due to damage to axons or glial cells
|
Diabetes, kidney failure, chronic alcoholism, nutritional deficiency, auto-immune disease, trauma
|
|
|
Why is painful tingling the first sign of recovery from injury due to temporary compression of nerves?
|
Slow conducting pain neurons are the first to recover from anoxia.
|
|
|
What part of the neuron is necessary for nerve regeneration?
|
Cell body.
|
|
|
Axon plus Schwann cells (but not basement membrane), distal to injury undergo __________ and ________________
|
Degeneration and Phagocytosis
|
|
|
Which part of nerve regenerates by branching ("sprouting")?
|
Axon proximal to injury
|
|
|
What guides the axons during "sprouting"?
|
Schwann cells create basement membrane tunnels (using laminin) that lead toward the target neurons. Axons sprout branches into these tunnels.
|
|
|
Why is CNS re-growth minimal?
|
Absence of basement membrane.
|
|
|
Major neurite-promoting glycoprotein component of the basement membrane that is increased on the surface of Schwann cells and the luminal face of basement membrane following injury.
|
Laminin
|
|
|
Nerve growth factor (NGF) re-establishes connections. It is secreted by _________ cells and __________ cells.
|
Schwann cells and target cells.
|
|
|
What role do macrophages play in nerve regeneration?
|
Helps to remove debris, specifically myelin and the damaged axon, from the distal injury site. Cleaning or clearing process before nerve regeneration that essentially prepares the distal stump for reinnervation.
|
|
|
The H-shaped region in the spinal cord, with cell bodies, dendrites, and proximal axons.
|
The gray matter, composed of ventral and dorsal horns.
|
|
|
What causes white color of white matter of spinal cord?
|
Myelin, the glial cells surrounding many axons, "whitens" the tissue.
|
|
|
______________ pass longitudinally along spinal cord.
|
Axons
|
|
|
The spinal nerve is composed of bundles of axons that come from _________________________.
|
Cell bodies in the ventral and dorsal horns
|
|
|
Cluster of cell bodies of sensory neurons
|
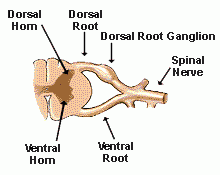
Dorsal root ganglion
|
|
|
What does pseudo-unipolar mean?
|
It contains an axon that has split into two branches; one branch runs to the periphery and the other to the spinal cord. Pseudounipolar neurons do not have dendrites.
|
|
|
Dorsal ramus innervates
|
deep back muscles and overlying skin
|
|
|
Ventral ramus innervates
|
remaining muscles, skin, etc.
|
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
|
Nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
|
|
|
What structure runs perpendicular to peripheral nerves, and is connected to peripheral nerves by gray and white rami.
|
Sympathetic ganglia
|

