![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
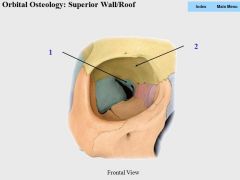
|
1. Sphenoid (lesser wing)
2. Frontal (orbital plate) |
|
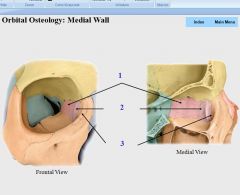
|
1. Ethmoid
2. Lacrimal 3. Maxilla (frontal process) |
|
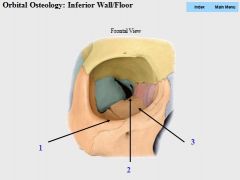
|
1. Zygomatic
2. Palatine 3. Maxilla |
|
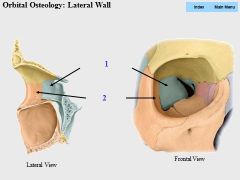
|
1. Sphenoid (greater wing)
2. Zygomatic |
|
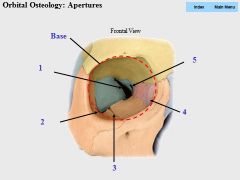
|
1. Superior orbital fissure
2. Inferior orbital fissure 3. Infraorbital groove 4. Lacrimal fossa 5. Optic canal (also the apex) |
|
|
The eyelids are covered by skin externally but by ___ internally, which is continuous with the ___ covering the ___ and ___.
These two conjunctiva layers meet at the ___. A medial fold of conjunctiva near the lacrimal lake is called the ___. |
1. palpebral conjunctiva
2. bulbar conjunctiva 3. sclera 4. cornea 5. superior and inf. fornices 6. plica semilunaris |
|
|
The ___ which lies on the anterior surface of the lens, is a thin, contractile diaphragm with a central aperature known as the ___.
|
1. iris
2. pupil |
|
|
Control of the Pupil
|
1. sphincter (constrictor) pupillae
2. dilator pupillae |
|
|
The eyelids are strengthened by dense bands of connective tissue known as the___, which are connected to the medial and lateral angles of the eye by the ___ & ___ respectively.
The ___ is a weak membrane that spans from the ___ to the margins of the orbit where it eventually becomes continuous with the ___. |
1. tarsal plates
2. medial and lateral palpebral ligaments 3. orbital septum 4. tarsal plates 5. periosteum |
|
|
5 Layers of the Eyelid
|
(superficial to deep)
1. outer skin layer 2. subcutaneous layer 3. muscular layer (orbicularis oculi & levator palpebrae superioris) 4. tarsofacial layer (tarsal glands and plate) 5. conjuctival layer (palpebral conjuctiva) |
|
|
Lacrimal Gland:
-Stimulated by? |
para/post fibers from CN VII
|
|
|
Course of Tear Drainage
|
1. Lacrimal gland
2. Lacrimal ducts 3. Superior and inferior fornix 4. Collect at lacrimal lake (modified skin @ lake = lacrimal carnucle) 5. Lacrimal punctum of lacrimal papilla 6. Lacrimal canaliculi 7. Lacrimal sac 8. Nasolacrimal duct 9. Inferior nasal meatus of nasal cavity |
|
|
Medial and Lateral Check Ligaments
-Formed By? -Function? |
-formed by expansions of fascial sheath at medial and lateral rectus ms.
-medial check lig. - limits adduction -lateral check lig. - limits abduction |
|
|
Suspensory Ligament
-Formed By? -Function? |
-formed by blending of check ligs. with fascia of inf. rectus and inf. oblique ms.
-supports eyeball and limits downward displacement |
|
|
Levator Palpebrae Superioris M.
|
I: CN III (superior division); superior tarsal m. is innervated by VE symp/post fibers
A: elevates upper eyelid O: lesser wing of sphenoid I: upper eyelid and superior tarsal plate |
|
|
Superior Rectus M.
|
I: CN III (superior div.)
A: elevates, adducts and medially rotates eyeball O: common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn) I: superior sclera |
|
|
Inferior Recus M.
|
I: CN III (inf. division)
A: depresses, adducts and laterally rotates eyeball O: common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn) I: inferior sclera |
|
|
Medial Recus M.
|
I: CN III (inf. div.)
A: adducts eyeball O: common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn) I: medial sclera |
|
|
Lateral Rectus M.
|
I: CN VI (abducens)
A: abducts eyeball O: common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn) I: lateral sclera |
|
|
Superior Oblique M.
|
I: CN IV (trochlear)
A: abducts, depresses and medially rotates eyeball O: body of sphenoid bone I: superior sclera deep to superior rectus |
|
|
Inferior Oblique M.
|
I: CN III (inf. div.)
A: abducts, elevates and laterally rotates eyeball O: anteromedial floor or orbit I: sclera inf. to lateral rectus |
|
|
CN V1:
Branch Pattern: |
passes thru sup. orbital fissure. 3 branches:
1. lacrimal 2. nasalciliary 3. frontal - 2 branches: a. supraorbital b. supratrochlear *SA cell bodies for V1 are in trigeminal ganglion |
|
|
Nasociliary N.
-Originates from? -Branches? -Changes name to? |
-originates from CN V1
-gives rise to long ciliary, posterior and anterior ethmoidal ns. -then changes name to infratrochlear n. |
|
|
CN III:
VE Para/pre Synapse? |
-passes thru sup. orbital fissure
-synapse in at ciliary ganglion |
|
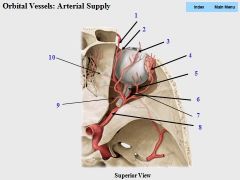
|
1. dorsal nasal
2. supratrochlear 3. supraorbital 4. lacrimal 5. long posterior ciliary 6. central artery of retina (travels through optic nerve) 7. short posterior ciliary 8. opthalmic 9. posterior ethmoidal 10. anterior ethmoidal |
|
|
Orbital Venous Drainage
|
-superior opthalmic v. drains into cavernous sinus
-inferior opthalmic v. drains into both the superior opthalmic v. and the pterygoid venous plexus |
|
|
Intrinsic Eyeball:
Fibrous Layer: -Structures? |
-cornea: anterior 1/6 of eyeball supplied by VA fibers of V1 of ciliary ns. Responsible for light refraction
-sclera: posterior 5/6 of eyeball. Responsible for attachments and shape of eye muscles |
|
|
Intrinsic Eyeball:
Vascular (Pigmented) Layer: -Structures? -Ms. that control pupil size? |
-Choroid: posterior 5/6 of eyeball; outer pigmented layer; inner highly vascularized layer
-Ciliary body: connects choroid and iris; produces aqueous humor; innervated by VE para/post fibers; controls thickness of lens -> focus -Iris: controls size of central apeture (pupil); sphincter pupillae (VE-para/post from ciliary ganglia) & dilator pupillae (VE-symp/post from long ciliary n.) |
|
|
Intrinsic Eyeball:
Inner (Retinal) Layer: -Structures? |
-outer pigmented layer
-inner neural layer with 3 types of neurons: 1. rods & cones 2. bipolar neuraons 3. gangion neurons forming CN II |
|
|
Fundus:
-Structures? |
-optic disk: blind spot caused by central retinal vessels and optic n.
-fovea centralis: area of most acute vision at center of macula lutea (yellow spot) |

