![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
176 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
This 12 year old girl complained of fatigue, nose-bleeds, and pain and bleeding from her gingiva. This patient is probably suffering from which of the following.
a) Hyperparathyroidism b) Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus c) Leukemia d) Sickle cell anemia e) Thalassemia |
Leukemia
|
|
|
The patient was a 56 year old male, who was a heavy user of tobacco and alcohol. The lesion of the lateral border of the tongue was described as indurated and rapidly growing. This lesion is Most likely which of the following?
a) Traumatic ulcer b) Basal cell carcinoma c) Chancre d) Verrucous carcinoma e) Squamous cell carcinoma |
SCC
|
|
|
The right photograph is a close-up of the lateral skull film projected on the left. This radiographic appearance is usually associated with which of the following disease entities?
a) Thalassemia b) Paget disease c) Sickle cell disease d) All of the above e) A & C only |
E
|
|
|
The solitary exophytic soft tissue mass observed on this patient's lip is most consistent with a diagnosis of which of the following?
a) Irritation/traumatic fibromas/fibrous hyperplasia b) Verrucous carcinoma c) Papilloma d) Papillary hyperplasia e) Proliferative verrucous hyperplasia |
Papilloma
|
|
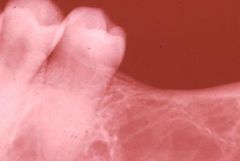
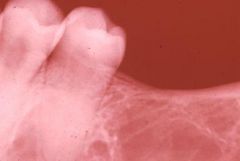
This 16 year old Black Male complains he is always tired and can not "keep up" in gym class. Based upon the projected radiograph and the accompanying Hx, this young man should be worked-up for which of the following conditions?
a) Sickel cell anemia b) Iron deficiency anemia c) McCune-Albright syndrome d) Addison disease e) Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia |
Sickle cell anemia
|
|
|
This solitary exophitic mass was described as firm in consistency and it had been present for over a year with little increase in size. From the disease processes listed below, it is most likely which of the following?
a) Lipoma b) Irritation (traumatic) fibroma/fibrous hyperplasia c) Pyogenic granuloma d) Mucocele e) Osseous choristoma |
Irritation (traumatic) fibroma/fibrous hyperplasia
|
|
|
The major concern for a dentist when treating a patient with Sturge-Weber syndrome is which of the following?
a) Sever infections b) Spontaneous ulcerations c) Gingival hemorrhage d) Epithelial desquamation e) The need for premedication |
Spontaneous ulcerations
|
|
|
Which of the following is true for von Recklinghausen disease?
a) It is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait b) Patients may have multiple cafe au lait macules c) Patients have gingival fibromatosis d) Patients have polyostotic fibrous dysplasia e) No known risk exists for malignant transformation of the skin lesions |
Patients may have multiple cafe au lait macules
|
|
|
A patient who manifests anemia and has "step-ladder" trabeculations visible in his jaw radiographs should be worked up for which of the following diseases?
a) Squamous cell carcinoma b) Pernicious anemia c) Lymphoma d) Sickle cell anemia e) Iron deficiency anemia |
Sickle cell anemia
|
|
|
The hair-on-end effect on skull radiographs is more commonly associated with patients with which of the following disease entities?
a) Osteomalacia b) Multiple myeloma c) Thalassemia d) All of the above e) A and C only |
Thalassemia (also sickle cell anemia)
|
|
|
Which of the following is true of sickle cell anemia?
a) It occurs as the result of a point mutation b) Weakness, shortness of breath and fatigue are common symptoms c) A hair on end radiographic appearance may occur d) All of the above e) A & C only |
I think that this is only
Weakness, shortness of breath and fatigue are common symptoms |
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of Langerhans cell disease?
a) Lesions may appear as multiple "punched out" areas of radiolucency b) A "tooth floating in air" radiographic appearance has been reported in Langerhans c) The eosinophilic granuloma subtype has only bony lesions d) All of the above e) A & C only |
A "tooth floating in air" radiographic appearance has been reported in Langerhans
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of fibrous dysplasia?
a) Fibrous dysplasia is typically slow growing b) Fibrous dysplasia is typically painful c) Fibrous dysplasia typically occurs in patients under the age of 25 years d) All of the above e) A & C only |
A & C only
|
|
|
Which of the following types of oral leukoplakia is Most Likely to undergo malignant transformation?
a) Smooth, thin leukoplakia b) Thick, fissured leukoplakia c) Granular leukoplakia d) Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia |
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
|
|
|
Which of the following is the site predilection for oral squamous cell carcinoma?
a) Tongue, lateral border b) Soft palate c) Gingiva d) Buccal mucosa e) Floor of mouth |
Tongue, Lateral border
|
|
|
Which of the following clinical features is More Consistent with a diagnosis of Recurrent Aphthous Ulcers, Minor Type than with recurrent herpes simplex infection?
a) Lesions occur most frequently on keratinized tissue b) Lesions usually occur as single ulcers c) Initial lesion begins as a vesicle d) All of the above e) A & C only |
Lesions usually occur as single ulcers
|
|
|
Which of the following is the Most common Oral Cancer?
a) Mucoepidermoid carcinoma b) Basal cell carcinoma c) Squamous cell carcinoma d) Verrucous carcinoma e) Fibrosarcoma |
SCC
|
|
|
Which of the following malignant tumors is composed of plasma cells and characterized by a monoclonal spike on immunoelectrophoresis?
a) Melanoma b) Multiple myeloma c) Leukemia d) Lymphoma e) Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
Multiple Myeloma
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most frequent intraoral site for metastatic tumors?
a) Buccal mucosa b) Gingiva c) Soft palate d) Tongue e) Mandible |
Mandible
|
|
|
Symmetric widening of the periodontal ligament space around a tooth is closely associated with which of the following?
a) Osteosarcoma b) Fibrous dysplasia c) Scleroderma d) All of the above e) A & C only |
All of the above
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of peripheral odontogenic fibromas?
a) Most commonly appear as multilocular radiolucencies of the posterior mandible b) Most commonly appear as unilocular radiolucencies of the posterior mandible c) Most commonly appear as mixed (RL/RO) lesions of the anterior mandible d) Most commonly appear as swellings of the facial gingiva of the mandible e) Most commonly appear as mixed (RL/RO) lesions of the posterior mandible |
Most commonly appear as mixed (RL/RO) lesions of the posterior mandible
This is different from the Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma |
|
|
Which of the following is the most appropriate term used for this adherent, white lesion associated with an ill-fitting denture?
a) Leukoedema b) Leukoplakia c) Leukokeratosis mucosae oralis d) Verrucous carcinoma e) Frictional keratosis |
Frictional keratosis
|
|
The patient's chief complaint was pain and swelling in the floor of his mouth. In palpating the region you noted a bony hard mass. Observing the projected lateral oblique radiograph, you notice a bony hard mass. Observing the projected lateral oblique radiograph, you notice an opacity near the inferior border of the mandible. This is most likely which of the following?
a) An osteoma b) An osseous choristoma c) A sialolith d) A condensing osteitis e) A torus mandibularis |
A sialolith
|
|
|
Which of the following is the Best clinical diagnosis of this adherent white lesion observed in a 58 year old male, who used tobacco and alcohol heavily?
a) Leukoedema b) Lichen planus c) Frictional keratosis d) Pseudomembranous candidiasis e) Leukoplakia |
Leukoplakia
|
|
|
This red and white pattern was observed bilaterally on the buccal mucosa during routine examination of an apprehensive 23 year old male. Close examination of the white component showed ragged tags of tissue. This condition is Most likely which of the following?
a) Erythroleukoplakia b) The result of chronic cheek chewing c) Candidiasis d) Ectopic geographic tongue e) Erosive lichen planus |
The result of chronic cheek chewing
|
|
|
The patient's chief complaint was pain and swelling in the floor of his mouth. In palpating the region you noted a bondy hard mass. Observing the projected lateral oblique radiograph, you notice a bony hard mass. Observing the projected lateral oblique radiograph, you notice an opacity near the inferior border of the mandible. This is most likely which of the following?
a) An osteoma b) An osseous choristoma c) A sialolith d) A condensing osteitis e) A torus mandibularis |
A sialolith
|
|
|
Which of the following is the Best clinical diagnosis of this adherent white lesion observed in a 58 year old male, who used tobacco and alcohol heavily?
a) Leukoedema b) Lichen planus c) Frictional keratosis d) Pseudomembranous candidiasis e) Leukoplakia |
Leukoplakia
|
|
|
This red and white pattern was observed bilaterally on the buccal mucosa during routine examination of an apprehensive 23 year old male. Close examination of the white component showed ragged tags of tissue. This condition is Most likely which of the following?
a) Erythroleukoplakia b) The result of chronic cheek chewing c) Candidiasis d) Ectopic geographic tongue e) Erosive lichen planus |
The result of chronic cheek chewing
|
|
|
The multiple separate radiolucencies observed in this young patient are Most consistent with which of the following diagnoses?
a) Multiple myeloma b) Metastatic carcinoma c) Langerhans cell disease d) Paget disease e) Fribrous dysplasia |
Multiple Myeloma
|
|
|
The red lesion observed in the center of the dorsal surface of this middle aged man's tongue is asymptomatic and stationary. Which of the following statements is True of this condition?
a) It is more common in adults than children b) It has been called central papillary atrophy of the tongue c) It has been associated with a fungal infection d) All of the above e) A and C only |
A & C only
|
|
|
This slow growing lesion with rolled borders and an ulcer in its center is Most likely which of the following?
a) Adenoid cystic carcinoma b) Basal cell carcinoma c) Condyloma accumatium d) Dermatofibroma e) Seborrheic karatosis |
Basal Cell carcinoma
|
|
|
The white lesion of the tongue seen in this slide which had no apparent cause, was adherent. From the following, which is the Most likely clinical diagnosis?
a) White sponge nevus b) Leukoplakia c) Squamous cell carcinoma d) Lichen planus e) Leukoedema |
I think this is Leukoplakia
White lesions that occur on the lateral of the tongue include: Frictional keratosis, Acute Pseudomembranous Candidiasis, Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis, cinnamon oil allergy, transient lingual papillitis, Reticular and Plaque-like leukoplakia, Hairy Leukoplakia |
|
|
The patient in this case indicated that his father had similar nodular masses. Upon examining the patient you notice that he has cafe au lait spots. Which of the following conditions does this patient Most likely have?
a) Neurofibromatosis type I b) Paget disease c) Sturge-Weber syndrome d) Peutz-Jeghers syndrome e) Gardner syndrome |
Neurofibromatosis type I
|
|
|
This firm, slowly developing mass has been present for "well over a year". It is most likely which of the following?
a) Papilloma b) Neurofibroma c) Fibroma/traumatic fibroma/irritation fibroma d) Mucocele e) Verrucous carcinoma |
Fibroma/ traumatic fibroma/ irritation fibroma
|
|
|
This slow developing lesion was described as soft in consistency. It is Most liklely which of the following?
a) Fibroma b) Mucocele c) Sebaceous cyst d) Ranula e) Lipoma |
Lipoma
|
|
|
This cauliflower-like lesion had been present for over two years and was slowly increasing in size. Which of the following statements is Most likely true of the lesion?
a) It is a papilloma and papillomas have been closely associated with EBV b) It is a papilloma and papillomas have been closely associated with HPV c) It is a papilloma and papillomas have been closely associated with HHV-8 d) It is a granular cell tumor and these lesions have been closely associated with EBV e) It is a squamous cell carcinoma and these lesions are caused by tobacco usage |
It is a papilloma and papillomas have been closely associated with HPV
(Specifically HPV viral subtypes 6 & 11) |
|
|
This rapidly developing, ulcerated and indurated lesion was noted in a long-time smoker and alcohol abuser. The lesion is Most likely which of the following?
a) Adenoid cystic carcinoma b) Basal cell carcinoma c) Squamous cell carcinoma d) Verrucous carcinoma e) Traumatic ulcer |
Squamous cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
This whitish lesion showing some areas of hemorrhage has been slowly enlarging over the past few months. It is indurated and was discovered in a long-time tobacco chewer. It is Most likely which of the following?
a) Basal cell carcinoma b) Verrucous carcinoma c) Melanoma d) Papillary hyperplasia e) Verruca vulgaris |
Verrucous carcinoma
|
|
|
The flat brown lesions like these on this patient's back are commonly observed in which of the the following?
a) McCune-Albright syndrome b) Behcet syndrome c) Von Recklinghausen disease d) All of the above e) A & C only |
A & C only
|
|
|
This ulcer has recurred for the third time in this particular area only to heal in a week or two. It is most likely which of the following?
a) Appthous ulcer b) Traumatic ulcer c) Herpetic ulcer d) A chancre e) A squamous cell carcinoma |
Herpetic ulcer
|
|
|
Which of the following should head a list of differential diagnoses knowing that this persistent, indurated lesion occurred in a long-time alcohol and tobacco abuser?
a) Adenoid cystic carcinoma b) Basal cell carcinoma c) Lymphangioma d) Squamous cell carcinoma e) Granular cell tumor |
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
This spreading, indurated blue/black/brown lesion is most characteristic of which of the following?
a) Amalgam tattoo b) Blue nevus c) Melanoma d) Varix e) Mucocele |
Melanoma
|
|
|
This fluctuant, bluish lesion arose to its present size rather rapidly. It is considered an example, i.e. occuring in the floor of the mouth, of which of the following lesions?
a) Hemangioma b) Mucocele c) Lymphoepithelial cyst d) Dermoid cyst e) Epidermoid cyst |
Mucocele
|
|
|
Which of the following should be considered in the differential diagnosis of this solitary, red, ulcerated mass?
a) Pyogenic granuloma b) Eplis fissuratum c) Peripheral giant cell granuloma d) All of the above e) A & C only |
A & C only
|
|
|
These ulcerative lesions began as blisters, which then ruptured. The patient indicates that they have occurred previously but healed uneventfully in a week or two. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
a) Recurrent aphthous ulcers b) Behcet syndrome c) Recurrent herpes simplex infection d) Traumatic ulcers e) Erythema multiforme |
Recurrent herpes simplex infection
|
|
|
Which of the following is the Most likely diagnosis of the rough lesions observed in the palate of this long-time denture wearer?
a) Epulis fissuratum b) Papillary hyperplasia c) Verruca vulgaris d) Multiple papillomas e) Hairy leukoplakia |
Papillary hyperplasia
|
|
|
The patient first noted this solitary, painful, lesion shortly after brushing his teeth to get ready for a dental appointment. This lesion is most likely which of the following?
a) Aphthous ulcer b) Herpetic ulcer c) Herpangina d) Traumatic ulcer e) Erythema multiforme |
Traumatic ulcer
|
|
|
Which of the following is the Best course of managing the exophytic mass observed in the vestibule of this denture wearer?
a) Surgical excision b) Surgical excision with histologic examination of the excised tissue c) Surgical excision with histologic examination of the tissue coupled with either remaking or relining the denture d) Remake the denture only and the tissue will recede itself e) Incise and drain |
Surgical excision with histologic examination of the tissue coupled with either remaking or relining the denture
|
|
|
This solitary pigmented macule had been present for at least 10 years with no change in size, shape, or color. The patient has no other medical conditions. The macule is most likely which of the following?
a) A pigmented spot associated with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome b) A pigmented spot associated with Addison disease c) An amalgam tattoo d) A labial melanotic macule e) A melanoma |
A labial melanotic macule
|
|
|
The adherent white lesion of the buccal mucosa was seen bilaterally and would disappear upon stretching the mucosa. It is Most likely which of the following?
a) Leukoplakia b) Leukoedema c) Lichen planus d) White sponge nevus e) Lekomoid reaction |
Leukoedema
|
|
|
The adherent white lesion associated with this ill-fitting maxillary denture is best termed which of the following?
a) Leukoedema b) Leukoplakia c) Frictional keratosis d) Smokeless tobacco keratosis e) Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia |
Frictional keratosis
|
|
|
Which of the following is considered the most common cause of this rapidly-developing, blue, soft, fluctuant, lesion, which could not be emptied by digital pressure?
a) Traumatic severance or rupture of a salivary gland duct b) Ductal dilation secondary to ductal obstruction with a sialolith c) Agenesis of the salivary gland duct d) Neoplastic obstruction of a salivary gland duct e) Bacterial invasion of a salivary gland |
Traumatic severance or rupture of a salivary gland duct
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most common salivary gland neoplasm?
a) Squamous cell carcinoma b) Pleomorphic adenoma c) Mucoepidermoid carcinoma d) Basal cell adenocarcinoma e) Warthin tumor |
Pleomorphic adenoma is by far the most common salivary gland neoplasm
|
|
|
Which condition is most often seen on the buccal mucosa?
a) Nicotine stomatitis b) Papillary hyperplasia c) Fibroma/ fibrous hyperplasia d) Retrocuspid papilla e) Minor salivary gland tumors |
Fibroma/ fibrous hyperplasia
|
|
|
The tongue is the site of predilection for which of the following?
a) Peripheral giant cell granuloma b) Granular cell tumor c) Papillary hyperplasia d) Lichen planus e) Epulis fissuratum |
Granular cell tumor has a strong predilection for the dorsum of the tongue
|
|
|
Which of the following is a type of squamous cell carcinoma that appears as a slow growing exophytic mass that rarely metastasizes?
a) Adenoid cystic carcinoma b) Verrucous carcinoma c) Chondrosarcoma d) Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma e) Ameloblastic carcinoma |
Verrucous carcinoma
|
|
|
Which of the following is a Malignant salivary gland tumor?
a) Adenoid cystic carcinoma b) Basal cell adenoma c) Mucoepidermoid carcinoma d) All of the above e) A & C only |
A & C only
|
|
|
Which of the following is the Most common site of occurrence of intraoral squamous cell carcinoma?
a) alveolar mucosa b) lateral border of the tongue c) buccal mucosa d) soft palate e) floor of the mouth |
lateral border of the tongue
|
|
|
Which condition is Not associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)?
a) Infectious mononucleosis b) Burkitt lymphoma c) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma d) Herpangina e) Hairy leukoplakia |
Herpangina
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most common form of recurrent herpes simplex infection?
a) Herpetic whitlow b) Herpes labialis c) Herpes zoster d) Herpangina e) Angular cheilitis |
Herpes labialis
|
|
|
The most common intraoral location for salivary gland tumors is which of the following?
a) Lower lip b) Upper lip c) Junction of hard and soft palate d) Alveolar mucosa e) Floor of mouth |
Don't know
Parotid gland tumors are the most common salivary gland tumor followed by minor salivary gland tumors which are most frequently on the Palate. Next most common is the lip. The Upper Lip is most frequent for lip salivary gland tumors (as opposed to the mucocele on the lower lip) |
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of epulis fissuratum?
a) Typically, is observed at the borders of ill-fitting dentures b) Is more common in male patients c) Is much more common in adults than children d) All of the above e) A and C only |
A and C only
|
|
|
Which of the following is true of mucoceles?
a) Mucoceles occur most commonly on the lower lip b) Mucoceles usually occur as the result of blockage of a salivary gland duct by a stone c) If mucoceles do not rupture on their own, local surgical excision is treatment of choice d) all of the above e) A and C only |
A & C only
They are typically caused by traumatic severance of the salivary gland excretory duct |
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of the oral papilloma?
a) Is caused by EBV b) Often undergoes malignant change c) Has a rough, warty (cauliflower-like) appearance d) Often invades adjacent tissues e) All of the above are true of oral papillomas |
Has a rough, warty (cauliflower-like) appearance
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of the oral irritation (traumatic) fibroma?
a) Treatment of choice is conservative surgical excision b) Site predilection is the anterior portion of the tongue c) Most are considered to be reactive hyperplasias rather than true neoplasms d) All of the above e) A & C only |
A & C only
|
|
|
Which oral lesion has the greatest malignant potential?
a) A keratotic white lesion of the buccal mucosa at the bite line b) A white patch on an edentulous ridge c) A white patch adjacent to a fractured amalgam d) A red patch related to trauma e) A velvety red patch with no known cause |
A velvety red patch with no known cause
|
|
|
Which of the following defines the term epulis?
a) Any benign neoplasm associated with ill-fitting dentures b) A benign neoplasm of epithelium c) Any "tumor" of the gingiva or alveolar mucosa d) A neural tumor of Schwann cells e) A tumor-like growth of microscopically normal tissue in an abnormal location |
Any "tumor" of the gingiva or alveolar mucosa
|
|
|
Which of the following is most commonly associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome?
a) Melanin spots on the oral mucosa b) Port-wine stain or nevus flammeus c) Multiple papillomas d) Multiple odontogenic keratocysts (OKCs) e) Supernumerary teeth |
Port-wine stain or nevus flammeus
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of pyogenic granulomas?
a) Have female gender predilection b) Often are red and may bleed easily due to their high degree of vascularity c) Conservative surgical excision is treatment of choice d) All of the above e) A & C only |
All of the above...pregancy tumor
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of the peripheral ossifying fibroma?
a) Most commonly appear as a radiopacity of the anterior mandible b) Most commonly appears as a multilocular radiolucency of the posterior mandible c) Occurs exclusively on the gingiva d) Most commonly apears as a mixed RL/RO lesion of the posterior mandible e) Is seen only the maxilla |
Occurs exclusively on the gingiva
|
|
|
The oral effects of smokeless tobacco include which of the following?
a) Gingival recession b) Oral cancer c) Cervical (tooth) erosion d) all of the above e) A & C only |
All of the above
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of pemphigus vulgaris?
a) Skin lesions rarely occur if at all b) Most patients are under 20 years of age and are males c) Oral lesions may precede skin lesions and are often persistent thus are described as the "first to show and last to go" d) Perilesional tissue characteristically shows subepithelial clefting (separation) e) Most patients present with hypermobility of their joints |
Oral lesions may precede skin lesions are are often persistent thus are described as the "first to show and last to go"
(equal frequency in both men and women) |
|
|
Which of the following has the Greatest malignant transformation potential?
a) Smooth leukoplakia b) Erythroplakia c) Thick leukoplakia d) Nicotine stomatitis e) Frictional keratosis |
Erythroplakia
|
|
|
Severe epithelial dyplasia, carcinoma-in-situ or squamous cell carcinoma is discovered in approximately what percentage of the oral leukoplakic lesions?
a) 5% b) 25% c) 50% d) 75% e) 95% |
You got me
I found 5-25%, but both of those options are present |
|
|
Which of the following appears to be Most closely associated with the development of oral leukoplakia and oral cancer?
a) Alcohol b) HPV infection c) Candida albicans d) Tobacco e) Trauma |
Tobacco
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true concerning the treatment of oral hemangiomas?
a) Many hemangiomas undergo involution so management often consists of "watchful neglect" b) Sclerotherapy alone may be sufficient for smaller lesions c) Larger vascular malformations may be treated by surgical excision d) All of the above e) A & E only |
All of the above
|
|
|
Deficiency states reported to produce glossitis include which of the following?
a) Plummer-Vinson syndrome b) Vitamin B complex deficiencies c) Iron deficiency anemia d) All of the above e) A & C |
All of the above
|
|
|
All of the following lesions would be expected to have a rough surface except?
a) Papilloma b) Neurofibroma c) Verrucous carcinoma d) Seborrheic keratosis e) Verrucae vulgaris |
Neurofibroma
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most common oral malignancy?
a) Adenoid cystic carcinoma b) Osteosarcoma c) Melanoma d) Fibrosarcoma e) Squamous cell carcinoma |
SCC
|
|
|
Which of the following is often regarded as the earliest sign of asymptomatic oral cancer?
a) Induration b) Ulcer c) Erythroplakia d) Leukoplakia e) Swelling |
Erythroplakia
|
|
|
Which of the following is Not a sequellae of xerostomia?
a) Dysphagia b) Oral cancer c) Dental caries d) Atrophic mucositis e) Oral candidiasis |
Oral cancer
|
|
|
Which of the following soft tissue lesions would have a predilection for patients over the age of 40 years?
a) Metastatic carcinoma b) Acute leukemia c) Hemangioma d) All of the above e) A & C only |
Metastatic carcinoma
|
|
|
T/F
Fibrous dysplasia is a precancerous lesion occurring mostly in the elderly |
False non-cancerous and 18-22 year old males
|
|
|
Multiple myeloma is a malignant tumor composed of which of the following?
a) Langerhans cells b) Plasma cells c) Lymphocytes d) Epithelial cells e) Osteoblasts |
Plasma cells
|
|
|
Leukemia may cause which of the following?
a) Incomplete formation of tooth crowns b) Partial or complete destruction of the cortices of the tooth crypts c) Enlargement of tooth crypts with failure of bone d) All of the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
Differential diagnosis of small rough-surfaced exophytic lesions would include which of the following?
a) Papilloma b) Keratoacanthoma c) Verruca vulgaris d) All of the above e) A & C |
All of the above
|
|
|
Differential diagnoses of small rough surfaced exophytic lesions would include which of the following?
a) Papilloma b) Keratoacanthoma c) Verruca vulgaris d) All of the above e) A & C |
All of the above
|
|
|
Any pathologic growth that projects above the normal contours of the oral surface would best be termed which of the following?
a) Hyperplasia b) Hypertrophy c) Exophitic lesion d) Neoplasm |
Exophitic lesion
|
|
|
Which of the following is an inflammatory hyperplasia observed at the borders of an ill fitting denture?
a) Verrucous carcinoma b) Epulis fissuratum c) Torus d) Pulp Polyp |
Epulis fissuratum
|
|
|
A ____ is defined as a deep crater that extends through the entire thickness of surface epithelium and involves the underlying connective tissue.
a) Vesicle b) Bullae c) Erosion d) Ulcer |
Ulcer
|
|
|
T/F
The aphthous ulcer is by far the most common oral mucosal ulcer |
False
Traumatic ulcer is most common |
|
|
Differential diagnosis for white sponge nevus would include which of the following
a) Lichen planus b) Leukoedema c) Leukoplakia d) All of the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
T/F
Leukoplakia is considered a common variation and occurs in more than 50% of adult patients |
False
Leukoedema |
|
|
Nicotine stomatitis has a site predilection for which of the following areas of the oral cavity?
a) Anterior portion of the floor of the mouth b) Buccal mucosa c) Lower lip d) Dorsal surface of the tongue e) Palatal mucosa |
Palatal mucosa
|
|
|
The etiologic factors of leukoplakia include which of the following?
a) Tobacco products b) Alcohol c) Sharp edges of prostheses or teeth d) All of the above e) A & C |
I think that this is only Tobacco products, although I am not positive regarding the trauma aspect.
|
|
|
Which of the following terms is used for a chronic sustained elevation in the number of erythrocytes and level of hemoglobin?
a) Polycythemia b) Erythema multiforme c) Leukemia d) Leukocytosis |
Polycythemia
|
|
|
Calcareous (radiopaque) deposits in the ducts of the major or minor salivary glands or within the glands themselves are given which of the following terms?
a) Rhinoliths b) Sialoliths c) Antroliths d) Phleboliths |
Sialoliths
|
|
|
Pink smooth-surfaced lesion. Described as firm, nonfluctuant, slowly increasing in size and present for several years. The most likely diagnosis is?
a) Fibroma/irritation fibroma b) Parulis c) Myxoma d) Osteoma e) Lipoma |
Fibroma/irritation fibroma
|
|
|
Asymptomatic, speckled red and white patch in the floor of the mouth was found in an elderly man who admitted heavy tobacco and alcohol use of several years duration. The lesion was firm to palpation. The most likely diagnosis is?
a) Lichen planus b) Traumatic erythema c) Atrophic candidiasis d) Squamous cell carcinoma e) Osteosarcoma |
SCC
|
|
|
Rough papillary lesion was discovered by the middle-aged man 6 months ago and has not enlarged since that time. The lesion is not painful. The patient denies the use of tobacco and alcohol. The best management for this lesion would be
a) Evaluate the lesion again when you see him in six months b) Make an intralesional corticosteroid injection c) Perform exfoliative cytology d) Perform an excisional biopsy e) Place the patient on antibiotic therapy |
Perform an excisional biopsy
|
|
|
A 30 year old HIV positive male presented the projected white plaques on the lateral border of his tongue. The condition is?
a) Leukoedema b) Leukoplakia c) Erythroleukoplakia d) Hairy leukoplakia e) Hairy Tongue |
Hairy leukoplakia
|
|
|
This patient's complaint is a swelling of the palate. The mass has been enlarging slowly over the past several months. The lesion is firm and painless. Which of the following is likely to be the diagnosis of this lesion?
a) Palatal torus b) Palatal abscess c) Malignant minor salivary gland tumor d) Necrotizing sialometaplasia e) Pleomorphic adenoma |
Pleomorphic adenoma (benign minor salivary gland tumor)
|
|
|
The whitish lesions shown in this projection occurred bilaterally in a 32 year old male. He indicated that his father had similar lesions and that the lesions had been present since he was young. The most likely diagnosis is?
a) Leukoedema b) Leukoplakia c) White sponge nevus d) Candidiasis e) Aspirin burn |
White sponge nevus
|
|
|
This white lesion was observed bilaterally. The asymptomatic lesion could not be rubbed off and it disappeared when the tissue was stretched. The most likely diagnosis is?
a) White sponge nevus b) Leukoedema c) Leukoplakia d) Lupus erythematosus e) Candidiasis |
Leukoedema
|
|
|
This patient noticed the asymptomatic yellow spots in the buccal mucosa and became concerned. Which of the following represents the diagnosis, nature of the spots and treatment required?
a) Lipoma, benign neoplasm of adipose tissue, surgical excision b) Buccal fat pad, normal adipose tissue, no treatment required c) Fordyce's granules, sweat glands, surgical excision d) Fordyce's granules, sebaceous glands, no treatment/reassurance e) Linea alba, hyperkeratosis, antiviral |
Fordyces granules, sebaceous glands, no treatment/reassurance
|
|
|
Which of the following lesions would NOT be described as fluctuant?
a) a cyst b) an abscess c) a fibroma d) a ranula e) A mucocele |
Fibroma
|
|
|
Which of the following has been defined as a persistent velvety red patch that cannot be identified as any other specific lesion?
a) Traumatic macule b) Candidiasis c) Aphthous ulcer d) Erythroplakia e) Erythema multiforme |
Erythroplakia
|
|
|
What term means any pathologic growth that projects above the normal contours of the oral surface?
|
Exophytic
|
|
|
Which of the following would be the more common location for minor salivary gland tumors?
a) Gingivae b) Junction of the hard and soft palate c) Anterior hard palate d) Ventral surface of the tongue e) Buccal mucosa |
Junction of the hard and soft palate
|
|
|
Which of the following brownish, bluish, or blackish lesion is malignant?
a) Melanoplakia b) Melanotic macule, labial or oral c) Melanoma d) Junctional nevus e) Blue nevus |
Melanoma
|
|
|
Lesions with smoothly contoured shapes, as a general rule, originate:
a) Only from bone b) From the stratified squamous epithelium c) Only from adipose tissue d) In the deeper tissues and are below and separate from the overlying epithelium e) Only from salivary gland |
In the deeper tissues and are below and separate from the overlying epithelium
|
|
|
Which of the following would most likely present with a rough surface?
a) Lipoma b) Papilloma c) Mucocele d) A & C e) All of the above |
Papilloma
|
|
|
The most common oral malignancy is?
a) Osteosarcoma b) Papilloma c) Melanoma d) Fibrosarcoma e) Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
SCC
|
|
|
Which of the following is often regarded as the earliest sign of asymptomatic oral cancer?
a) Induration b) Ulcer c) Erythroplakia d) Leukoplakia e) Swelling |
Ulcer
(actually I think this is erythroplakia) |
|
|
Epulis fissuratum
a) Is caused by EBV b) Is most common in the midline of the palate c) Is of bacterial origin d) Has a buccal or labial vestibule site predilection e) Is malignant |
Has a buccal or labial vestibule site predilection
|
|
|
Which of the following lesions would not be included in the sloughing, pseudomembranous, necrotic white lesion group?
a) Chemical burns b) Traumatic ulcers c) Candidiasis d) Leukoplakia |
Leukoplakia
|
|
|
Differential diagnoses for palatine petechiae include:
a) Trauma from severe vomiting or coughing b) Prodromal sign of infectious mononucleosis c) Prodromal sign of hemostatic disease d) A & C e) All of the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
Young female who fell down and bit her lip last evening. The bluish, exophytic lesion you observe now is soft, fluctuant and cannot be emptied. The most likely diagnosis is?
a) Varix b) Amalgam tattoo c) Mucocele d) Blue nevus e) Eruption cyst |
Mucocele
|
|
|
The lesion you observe in the vestibule of this 57 year old female denture wearer has been present for over two years. She indicates that it developed slowly and has remained static for many months. The lesion is firm to palpation and non-tender. The most likely diagnosis is?
a) SCC b) Pyogenic granuloma c) Tramatic neuroma d) Parulis e) Epulis fissuratum |
Epulis fissuratum
|
|
|
This 53 year old male patient discovered the projected pigmented lesion a few months ago. The lesion has since rapidly increased in size and has become darker in color. This lesion most likely will be a?
a) Oral melanotic macule b) Cafe au lait spot c) Melanoma d) Amalgam tattoo e) Area of racial pigmentation |
Melanoma
|
|
|
This roughened lesion was noted by the patient four months ago. It has not changed in size or appearance since it was discovered. The lesion is most likely a
a) neuroma b) fibroma c) papilloma d) lipoma e) benign salivary gland tumor |
Papilloma
|
|
|
This red/blue lesion is soft fluctuant and blanches upon pressure. The most likely diagnosis is
a) myxoma b) mucocele c) hemangioma d) fibroma e) torus |
Hemangioma
|
|
|
This firm exophytic lesion has enlarged slowly over several years. The lesion is NOT painful. The lesion is most likely
a) torus b) fibroma c) mucocele d) papilloma e) hemangioma |
fibroma
|
|
|
Squamous cell carcinoma is a synonymous term for:
a) Basal cell carcinoma b) Epidermoid carcinoma c) Osteosarcoma d) Verrucous carcinoma e) Any of the above |
Epidermoid carcinoma
|
|
|
All of the following are true of leukoedema except
a) Cause is unknown b) May be present in Caucasians c) Generally asymptomatic d) When stretched, it can disappear e) Has a predilection for the palate |
Has a predilection for the palate
|
|
|
Traumatic ulcers, which are the most common type of ulcer, may result from
a) Ill-fitting dentures b) Biting c) Cotton roll injury d) Pizza burn e) All of the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
The site with the best prognosis for oral/paraoral epidermoid carcinoma is the
a) Floor of mouth b) Lip c) Tongue d) Hard palate e) Gingiva |
Lip
|
|
|
What is the cause of nicotinic stomatitis?
a) A pinch of snuff placed in the buccal vestibule b) Heat from a pipe or cigar c) Nitrosonornicotine d) Inflammatory response to physical trauma e) Alcohol |
Heat from a pipe or cigar
|
|
|
Oral hyperkeratosis (clinical leukoplakia) may be caused by
a) A fractured restoration b) Cheek biting c) Smokeless tobacco d) Friction from a denture e) All of the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
Hyperkeratosis of the oral cavity results in a ___ lesion usually caused by ________.
a) Red, acanthosis b) Red, increased keratin c) White, fibrosis d) White, necrosis e) White, thickening of the epithelial keratin |
White thickening of the epithelial keratin
|
|
|
Approximately, what percentage of the oral leukoplakic lesions in the US are malignant or will become malignant if left untreated?
a) 10% b) 25% c) 50% d) 75% e) 90% |
10%
|
|
|
Approximately, what percentage of the oral Erythroplakia (erythroplasia) will be premalignant or malignant upon initial examination?
a) 10% b) 25% c) 50% d) 75% e) 90% |
90%
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a peripheral oral exophytic lesion?
a) Mucocele b) Fibroma c) Papilloma d) Hemangioma e) Oral melanotic macule |
Oral melanotic macule
|
|
|
Which of the following best describes the meaning of the term induration?
a) white b) firm/hard c) fluctuant d) soft e) rough |
Firm/Hard
|
|
|
A lesion could appear white in the oral cavity for all of the following reasons except
a) The epithelium may be thicker than normal due to hyperplasia b) The epithelium may have a thicker keratin layer c) The epithelial cells may be edmatous d) There is a marked increase in hemoglobin concentration |
There is a marked increase in hemoglobin concentration
|
|
|
Which of the following is the method advocated for the treatment of oral hemangiomas?
a) surgical removal b) sclerosing solutions c) embolization d) radiation therapy e) all of the above have been used in trained hands to treat oral hemangiomas |
All
|
|
|
Which of the following is Least likely to be included in the differential list for oral melanoma?
a) Nevus b) Amalgam tattoo c) Superficial mucocele d) Oral melanotic macule e) Focal hemosiderin deposit |
Superficial mucocele
|
|
|
The prognosis of aral squamous cell carcinoma is dependent upon
a) Size of the primary lesion b) Location of the primary lesion c) Histologic grade of the primary lesion d) All of the above e) A & C only |
All of the above
|
|
|
Most mucoceles result from?
|
Mucous duct breakage and spillage
|
|
|
A ranula is best considered
a) a mucocele of the palate b) a mass of fibrous connective tissue c) a mass of granulation tissue d) a mucocele of the labial mucosa e) a mucocele on the floor of the mouth |
A mucocele on the floor of the mouth
|
|
|
A pregnancy tumor is probably a
a) Myxoma b) Fibroma c) Pyogenic granuloma d) Ossifying fibroma e) Peripheral giant cell granuloma |
Pyogenic granuloma
|
|
|
A swelling which contains effused blood is a
a) Hamartoma b) Hemangioma c) Varicosity d) Ecchymoses e) Hematoma |
Hematoma
|
|
|
What is the most common oral mucosal ulcer?
|
Traumatic ulcer
|
|
|
A smooth firm dome shaped mass developed slowly in the palate of this 47 year old femal patient. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of this lesion?
a) palatal torus b) Benign salivary gland tumor c) Mucocele d) Squamous cell carcinoma e) Papillary hyperplasia of the palate |
Benign salivary gland tumor
|
|
|
Which of the following questions would be most helpful in arriving at a clinical working diagnosis of the keratotic white lesion observed in the buccal mucosa of this patient?
a) Did you place an aspirin in this area b) Do you use smokeless tobacco c) Do you chew your cheeks d) Do you smoke e) Are you pregnant |
Do you use smokeless tobacco
|
|
|
Which of the following questions would be most helpful in arriving at a clinical working diagnosis of this red and white (adherent) lesion seen in this middle-aged patient?
a) Did you place an aspirin in this area b) Do you use smokeless tobacco c) Do you chew your cheeks d) Do you smoke e) Are you pregnant |
Do you chew your cheeks
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of the soft fluctuant bluish swelling which arose rapidly in the right floor of the mouth?
a) Oral melanotic macule b) Hemangioma c) Ranula d) Melanoma e) Melanocytic nevus |
Ranula
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of the rough lesion observed in the palate of this patient?
a) An ulcerated salivary gland neoplasm b) A torus palatinus c) A fibroma d) A pyogenic granuloma e) A papilloma |
A papilloma
|
|
|
Which of the following should be included in the differential diagnosses of this red lesion of the maxillary gingiva/alveolar ridge?
a) Peripheral giant cell granuloma b) Mucocele c) Pyogenic granuloma d) All of the above e) A & C only |
A & C only
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of the solitary reddish ulcerated lesion observed in this projected photograph?
a) Traumatic fibroma b) Pyogenic granuloma c) Parulis d) Papilloma e) Pulp polyp |
Pyogenic granuloma
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of the projected solitary, firm, smooth mass of the buccal mucosa?
a) Traumatic (irritation) fibroma b) Peripheral ossifying fibroma c) Papilloma d) Hemangioma e) Lipoma |
Traumatic (irritation) Fibroma
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of this rapidly growing, indurated, brown, red, black lesion of the palate?
a) Melanocytic nevus b) Melanoma c) Oral melanotic macule d) Amalgam tattoo e) Hematoma |
Melanoma
|
|
|
This rough, brownish black lesion of this elderly patient's face had been present for several years now. On palpation of the lesion pieces of it crumbled away and were greasy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of this lesion?
a) Keratoacanthoma b) Basal cell carcinoma c) Squamous cell carcinoma d) Melanocytic nevus e) Seborrheic keratosis |
Seborrheic keratosis
|
|
|
Lesions, such as the ones seen at the corners of the mouth, in this elderly female patient have been associated with which of the following?
a) Deficiency of riboflavin b) Loss of vertical dimension c) Infection with Candida albicans d) All of the above e) A & C only |
All of the above
|
|
|
Using the two projected photographs, what is the most likely diagnosis of the red lesion of the left labial mucosa?
a) Hematoma b) Mucocele c) Hemangioma d) Labial melanotic macule e) Mucous cyst |
Hemangioma
|
|
|
Which of the following has been defined as a white patch or plaque on a mucous membrane that cannot be identified clinically as any other specific lesion?
a) Leukomoid reaction b) Leukoedema c) Leukoplakia d) Leukemia e) Lichen planus |
Leukoplakia
|
|
|
Which term describes the earliest presentation of most cases of asymptomatic oral cancer?
a) Area of induration b) Area of swelling c) An ulcerated area d) A leukoplakia e) An erythroplakia |
Erythroplakia
|
|
|
Which of the following is most likely to mimic a mucocele during its early stage?
a) Melanoma b) Nevus c) Low grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma d) Oral melanotic macule e) Smokers melanosis |
Low-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma
|
|
|
All of the following are true of leukoedema except one. Which is the exception?
a) Predilection for the hard palate b) Is more common in blacks than whites c) Generally is asymptomatic d) When stretched, it can disappear e) Is not a precancerous lesion |
Predilection for the hard palate
|
|
|
Which of the following types of oral leukoplakia has the highest malignant transformation potential?
a) Smooth thin leukoplakia b) Smooth thick leukoplakia c) Granular leukoplakia d) Thick fissured leukoplakia e) Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia |
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most common salivary gland neoplasm
a) SCC b) Pleomorphic adenoma c) Mucoepidermoid carcinoma d) Basal cell adenocarcinoma e) Warthin tumor |
Pleomorphic adenoma
|
|
|
The oral papilloma is most closely associated with which of the following?
a) Alcohol b) Symphilis c) HPV d) Tobacco e) Candida albicans |
HPV
|
|
|
Which of the following is true of pemphigus vulgaris?
a) Intraoral lesions generally precede skin lesions b) No treatment is necessary c) Is associated with a positive Nikolsky sign (test) d) All of the above e) A & C only |
A & C only
|
|
|
All of the following lesions would be expected to be painful except?
a) An infected cyst b) An aphthous ulcer c) A pleomorphic adenoma d) An acutely inflamed tissue e) a Traumatic ulcer |
Pleomorphic adenoma
|
|
|
Which of the following disease entities is most commonly associated with cafe au lait spots?
a) Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome b) Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome c) Von Recklinghausen disease d) Gardner syndrome e) CREST syndrome |
Von Recklinghausen disease
|
|
|
Which of the following is an example of an oral inflammatory hyperplastic lesion that is one that is a reactive hyperplasia related to tissue injury
a) Addison disease b) Squamous cell carcinoma c) Papilloma d) Neurofibroma e) Pyogenic granuloma |
Pyogenic granuloma
|
|
|
37 year old female complains of parotid enlargement, dry eyes and dry mouth. This clinical picture is most consistent with?
a) Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome b) Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, type I c) Behcet syndrome d) Sturge-Weber syndrome e) Sjogren syndrome, either primary or secondary depending upon whether the patient also manifests another associated autoimmune disease |
Sjogren syndrome, either primary or secondary depending upon whether the patient also manifests another associated autoimmune disease
|
|
|
Which of the following conditions has been associated with Epstein-Barr virus?
a) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma b) Burkitt lymphoma c) Oral hairy leukoplakia d) All of the above e) A & C only |
All of the above
|
|
|
Which of the following lesions could be soft and fluctuant?
a) Abscess b) Ranula c) Hemangioma d) All of the above e) A & C only |
All of the above
|
|
|
Which of the following lesions is benign?
a) Pleomorphic adenoma b) Verrucous carcinoma c) Melanoma d) All of the above e) A & C only |
Pleomorphic adenoma
|
|
|
Which of the following types of melanoma does not have a radial (lateral) growth phase?
a) Acral lentiginous melanoma b) Lentigo maligna melanoma c) Nodular melanoma d) Superficial spreading melanoma |
Nodular melanoma
|
|
|
A hemangioma would best be classified as which of the following?
a) Malignant neoplasm b) Benign neoplasm c) Choristoma d) Developmental "tumor" or hamartoma e) Hyperplasia |
Developmental tumor or hamartoma
|
|
|
Kaposi's sarcoma is most common seen at which oral site?
a) Buccal mucosa b) Palatal mucosa c) Gingiva d) Floor of mouth e) Tongue |
Palatal mucosa
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of pyogenic granulomas?
a) Have femal gender predilection b) Often are red and may bleed easily due to their high degree of vascularity c) Conservative surgical excision is treatment of choice d) All of the above e) A & C only |
All of the above
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of the peripheral ossifying fibroma?
a) Most commonly appears as a radiopacity of the anterior mandible b) Most commonly appears as a multilocular radiolucency of the posterior mandible c) Occurs exclusively on the gingiva d) Most commonly appears as a RL/RO lesion of the posterior mandible e) Is seen only the maxilla |
Occurs exclusively on the gingiva
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true of pemphigus vulgaris?
a) Oral lesions may precede skin lesions and are often persistent thus are described as the "first to show and last to go" d) Perilesional tissue characteristically shows subepithelial clefting (separation) e) Most patients present with hypermobility of their joints |
Oral lesions may precede skin lesions and are often persistent thus are described as the first to show and the last to go.
|

