![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
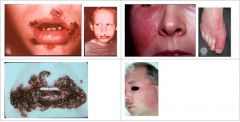
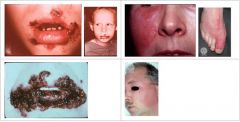
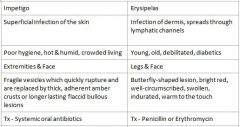
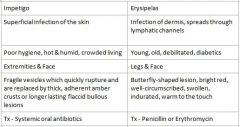
What areas are primarily affected by Impetigo?
|
Extremities & Face
|
|
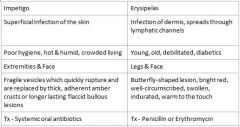
What areas are primarily affected by Erysipelas?
|
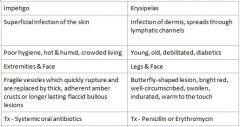
Legs & Face
|
|
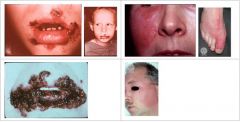
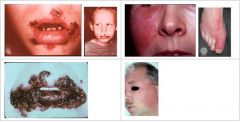
Who is at risk for Impetigo?
|
Poor hygiene, Hot & humid, Crowded living
|
|
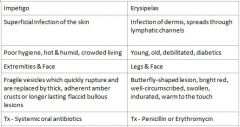
Who is at risk for Erysipelas?
|
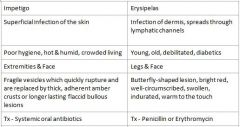
Young, old, debilitated, diabetics
|
|
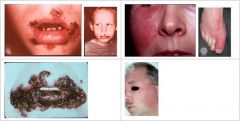
What condition manifests as fragile vesicles which quickly rupture and are replaced by thick, adherent amber crusts or longer lasting flaccid bullous lesions?
|
Impetigo
|
|
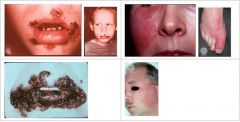
What condition manifests as Butterfly-shaped lesion, bright red, well-circumscribed, swollen, indurated, and warm to the touch?
|
Erysipelas
|
|
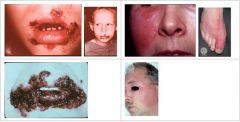
How does treating Impetigo differ from treating Erysipelas?
|
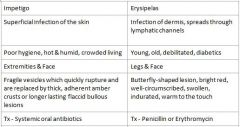
Impetigo = Systemic oral antibiotics
Erysipelas = Penicillin or Erythromycin |
|
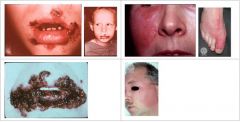
Which condition is a Superficial infection of the skin, Impetigo or Erysipelas?
|
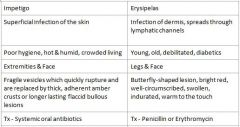
Impetigo
|
|
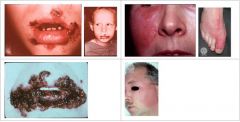
Which condition is an infection of the dermis, spreads through lymphatic channels?
|
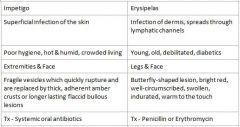
Erysipelas
|
|
|
What kind of infection is Syphilis and what is the cause?
|
Chronic infection caused by Treponema Pallidum
|
|
|
What is the primary modes of transmission for Syphillis?
|
Venereal or Mother to Fetus
|
|
|
T/F
Antibiotic therapy will cure Syphillis |
False
Antibiotic therapy may arrest clinical symptoms, but might not result in total care |
|
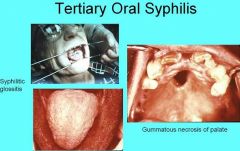
What feature of tertiary syphilis is when the tongue appears large and irregularly shaped due to diffuse atrophy and loss of dorsal tongue papillae?
|

Luetic Glossitis
|
|
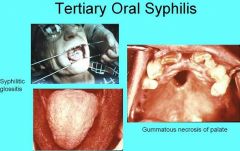
What are the most severe complications that may arise in Tertiary Syphilis?
|

Congestive Heart Failure
Dementia Death |
|
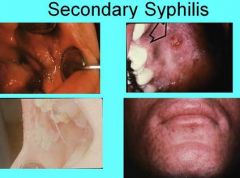
What is another term for the occasional papillary lesions found in secondary syphilis?
|

Condylomata Lata
|
|
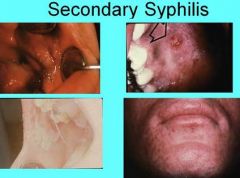
What feature of secondary syphilis is found in person with compromised immune system that results in Fever, Headache, Myalgia, Necrotic Ulcerations of the Face and Scalp, and Oral lesions?
|

Lues Maligna
|
|
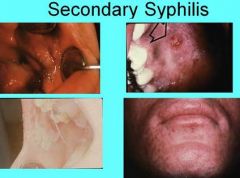
What lesions found in and/or around the mouth are common for Secondary Syphilis?
|

Diffuse, painless maculopapular cutaneous widespread rash
Mucous patches - superficial areas of irregular grayish mucosal necrosis most commonly found on tongue, lip, buccal mucosa, palate |
|
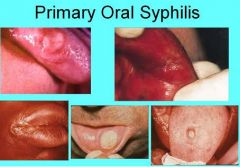
How does Primary syphilis spread throughout the body?
|

Spreads through lymphatic channels
|
|
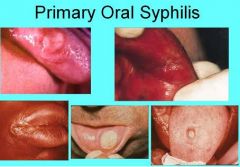
Where are the oral lesions associated with primary syphilis located?
|

Lip, Tongue, Palate, Gingiva, & Tonsils
|
|
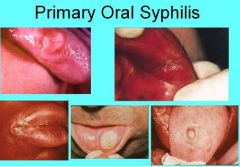
Describe the clinical appearance of oral lesions due to primary syphilis
|

Oral lesions may be painless, clean-based ulcerations or vascular proliferations
|
|
|
How long can Syphilis become latent for?
|
May last 1-30 years
|
|
|
What is included in Hutchinson's triad due to Congenital Syphilis?
|
Hutchinson's teeth
Interstitial keratitis Eigth nerve deafness |
|
|
What are the properties of primary tuberculosis?
|
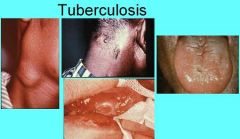
1. Occurs in previously unexposed people
2. Localized fibrocalcified nodule at initial site of involvement 3. Vital organisms remain dormant in nodule for years 4. Usually asymptomatic |
|
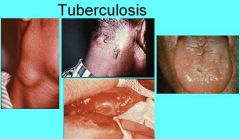
What do oral lesions from Tuberculosis look like?
|
Nodular, granular, ulcerated or firm leukoplakic areas
|
|
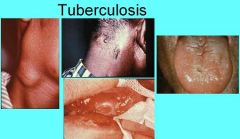
Where do oral lesions from primary tuberculosis manifest?
|
Primary - Gingiva, Mucobuccal fold, Areas adjacent to teeth, and extraction sites
Secondary - Tongue, Palate, Lip |
|
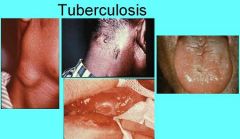
Where do oral lesions of Secondary Tuberculosis Manifest?
|
Primary - Gingiva, Mucobuccal fold, Areas adjacent to teeth, and extraction sites
Secondary - Tongue, Palate, Lip |
|
|
What is the most common life-threatening fungal infection in AIDS patients?
|
Cryptococcosis
|
|
|
How might Cryptococcosis manifest?
|
1. Cryptococcal menigitis characterized by headache, fever, vomiting, stiff neck
2. Cutaneous lesions develop in 10-20% of patients with disseminated disease 3. Erythematous papules or pustules that may ulcerate 4. Deep fungal infection associated with poor immunosuppression |
|
|
What is the most common pattern of HSV-1 infection?
|
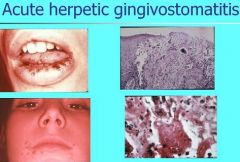
Acute Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
|
|
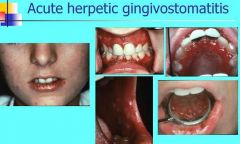
What age range is most commonly affected by Acute Herpetic Gingivostomatitis?
|
6 months - 5 years
|
|
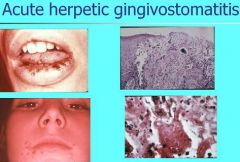
What are the clinical features of Acute Herpetic Gingivostomatitis?
|
Pinhead vesicles, collapse to form small red lesions which develop ulceration
Movable and attached oral mucosa can be affected Gingiva enlarged, painful, extremely erythematous |
|
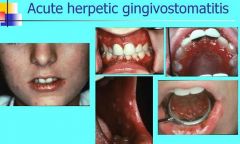
How long should Acute herpetic gingivostomatits last for?
|
5-7 days (mild)
2 weeks (severe) |
|
|
What lesions do Herpes Simplex Virus cause on the tonsils?
|
Pharyngotonsillitis
Primary infection in adults Vesicles on tonsils and posterior pharynx Vesicles rupture and form shallow ulcerations |
|
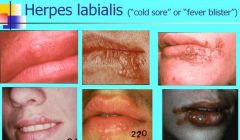
Where is the most common site of Herpes labialis (cold sore or fever blister)?
|
Most common site is vermilion border and adjacent skin of lips
|
|
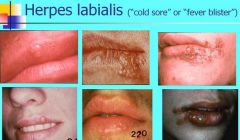
When do prodromal symptoms of herpes labialis occur before the lesion develops?
|
6-24 hours prior to lesion development
|
|
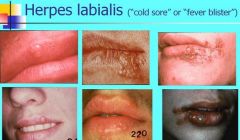
How does Herpes Labialis present clinically?
|
Small erythematous papules form clusters of fluid-filled vesicles
Vesicles rupture within 2 days, healing occurs within 7-10 days |
|
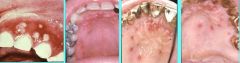
What is shown here?
|
Recurrent Intraoral Herpes
|
|
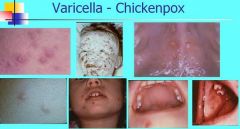
What are the symptoms of Varicella?
|
Primary infection with VZV
Rash Malaise Fever Oral lesions may precede skin lesions |
|
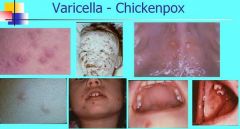
What are two major complications of chickenpox?
|
Reye's syndrome
Encephalitis |
|
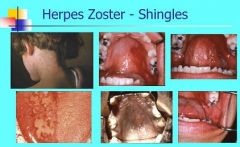
Who is at risk for Herpes Zoster?
|
Immunosuppression, Radiation, Malignancies, Old Age
Pain normally present 1-4 days before development of cutaneous or oral lesions. Lesions resolve within 2-3 weeks in healthy individuals |
|
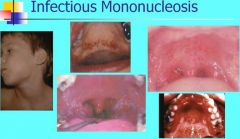
What causes Infectious mononucleosis?
|
Epstein Barr Virus
|
|
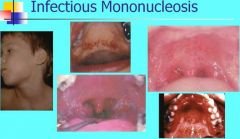
What are the symptoms for Infectious Mononucleosis?
|
1. Fever, lymphadenopathy, pharyngitis, tonsillitis
2. Petechiae on hard or soft palate, disappear 24-48 hours 3. Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis 4. Chronic fatigue syndrome 5. Resolves in 4-6 weeks |
|
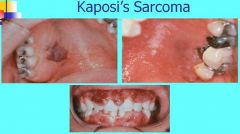
What is Kaposi's Sarcoma?
|
1. Multifocal neoplasm of vascular endothelial origin
2. Begins with lesions of skin or oral mucosa, hard palate, and gingiva 3. Plaques or Nodules 4. Progressive malignancy that may disseminate |
|
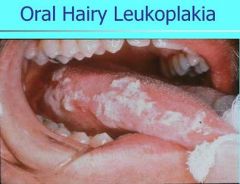
What causes hairy leukoplakia, which presents with hyperkeratosis and epithelial hyperplasia on lateral border of tongue?
|
Epstein Barr Virus
|
|
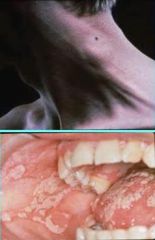
What are common manifestations of HIV infection?
|
1. PGL persistent generalized lymphadenopathy - present for more than 3 months, involves 2+ extrainguinal sites
2. Candidiasis is the most common oral manifestation, often the presenting sign leading to diagnosis |
|
|
What family do Entero viruses belong to and what diseases does it cause?
|
Coxsackie Virus Family
1. Herpangina 2. Hand Foot and Mouth Disease 3. Acute Lymphonodular Pharyngitis (NOT vesicles) |
|
|
What fungal infection is found in insulin-dependent diabetics with poor control as well as immunosuppressed patients that may involve the nose and maxillary sinus?
|
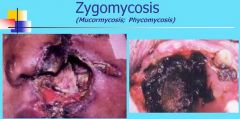
Zygomycosis
1. Nasal obstruction, bloody discharge, headache, swelling, cellulitis, facial paralysis 2. Maxillary sinus involvement may present as intraoral swelling of maxillary alveolar process or palate 3. Palatal ulceration may evolve with significant tissue destruction 4. Sinus may appear opaque on radiographs |
|
|
What condition occurs when Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis extends to involve adjacent soft tissue and adjacent bone?
|
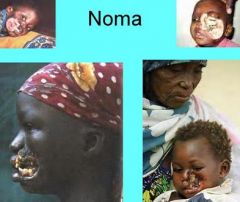
Noma (Necrotizing Stomatitis, Gangrenous Stomatitis, Cancrum Oris)
|
|
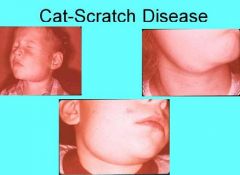
Explain mechanism of Cat Scratch Disease
|
1. Organism enters through scratch or other trauma
2. Papule or pustule develops along scratch 3. Lymph node changes in 3 weeks 4. Self limiting; usually resolves in 4 months 5. Must be considered in differential diagnosis of patients with unexplained symptomatic lymphadenopathy |
|
|
What other disease could Cat Scratch Disease be mistaken for?
|
Red or purple skin lesions resemble Kaposi's sarcoma
Oral lesions also resemble Kaposi's sarcoma |
|
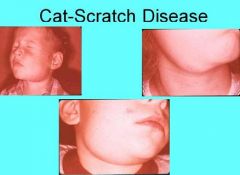
What other disease could Cat Scratch Disease be mistaken for?
|
Red or purple skin lesions resemble Kaposi's sarcoma
Oral lesions also resemble Kaposi's sarcoma |
|
|
What are two forms of common streptococcal disease in the mouth and how does it manifest?
|
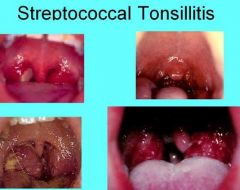
Streptococcal Tonsillitis and Pharyngitis
Sore throat, dysphagia, tonsillar hyperplasia, redness of the oropharynx and tonsils, palatal petechiae, cervical lymphadenopathy and yellowish tonsillar exudate. |
|
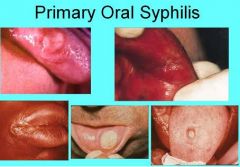
Where does Primary Syphilis manifest?
|
Chancre develops at site of inoculation after 2-3 weeks
Oral lesions may be found on: 1. Lip 2. Tongue 3. Palate 4. Gingiva 5. Tonsils |
|
|
What ailment is known as the great imitator?
|
Syphilis
|
|
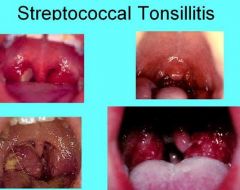
What are the symptoms of Streptococcal Tonsillitis and Pharyngitis?
|
1. Sore Throat
2. Dysphagia 3. Tonsillar Hyperplasia 4. Redness of the oropharynx and tonsils 5. Palatal Petechiae 6. Cervical lymphadenopathy 7. Yellowish tonsillar exudate |
|
|
What condition is most common in children ages 3-12. It affects the tonsils, softpalate, pharynx becomes erythematous and edematous.The rash looks like a sunburn with goose pimples. After rash clears desquamation of the skin. Also can have white or red strawberry tongue.
|
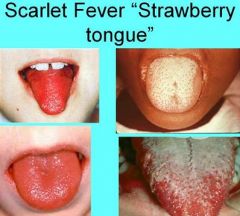
Scarlet Fever
|
|
|
What manifestation of Scarlet Fever is during the first 2 days the dorsal surface of tongue has white coating through which only the fungiform papillae can be seen?
|
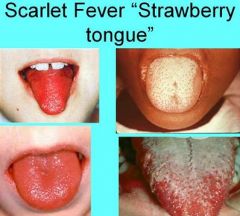
White Strawberry Tongue
|
|
|
What manifestation of Scarlet Fever is by day 4 or 5, white coating desquamates to reveal erythematous dorsal surface with hyperplastic fungiform papillae?
|
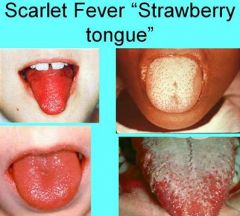
Red Strawberry Tongue
|
|
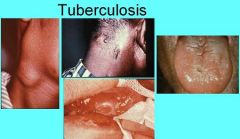
What are the symptoms and oral manifestations of Tuberculosis?
|
Productive cough, fever, malaise, anorexia, weight loss, night sweats, consumption.
Miliary tuberculosis - diffuse dissemination through vascular system Scrofula - tuberculosis from drinking infected milk Oral lesions involve gingiva, mucobuccal fold, areas adjacent to teeth and extraction sites while oral lesions of secondary tuberculosis present on tongue, palate or lip |
|
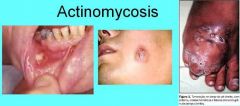
How does Cervicofacial Actinomycosis occur?
|
Actinomyces ssp. enters through area of prior trauma, direct extension through soft tissue, may extend to surface to form fistula
Sulfur granules - discharge large yellowish flecks representing colonies of bacteria |
|
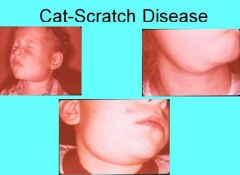
What is the causative organism for Cat-Scratch Disease?
|
Bartonella Henselae
|
|
|
What are the manifestations and causes of Pseudomembranous Candidiasis (Thrush)?
|
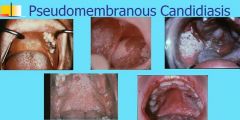
Adherent white plaques (resembling cottage cheese) on tongue, palate, buccal mucosa.
Plaques can be removed by scraping Burning sensation, bad taste May present as a result of exposure to broad spectrum antibiotics (rapid development) Longstanding form result of immunosuppression (leukemia, HIV infection) |
|
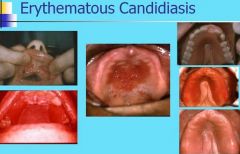
What are some presentations of Erythematous Candidiasis?
|
Acute Atrophic Candidiasis (antibiotic sore mouth)
Central papillary atrophy (median rhomboid glossitits) Chronic Multifocal Candidiasis Angular Cheilitis (involvement of angles of mouth) Denture stomatitis (erythema localized to denture-bearing areas removable dental prosthesis) |
|
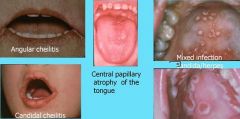
What is the common agent for all of these conditions?
|
Candidiasis
|
|
|
What condition is also referred to as Candidal Leukoplakia
|
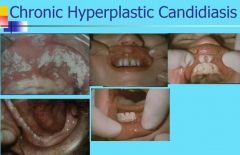
Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis
|
|
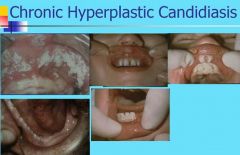
What are the features of Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis?
|
White patch cannot be removed by scraping
Mucocutaneous candidiasis Severe oral candidiasis as component of immunologic disorder |
|
|
What is the most common Systemic fungal infection in U.S.?
|
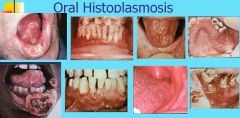
Histoplasmosis
|
|
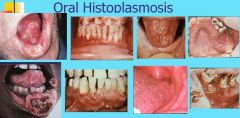
How does Histoplasmosis present?
|
Solitary, painful ulceration of tongue, palate, or buccal mucosa
Lesion has firm, rolled margins, may be clinically indistinguishable from malignancy Most oral lesions of histoplasmosis occur with the disseminated form of the disease |

