![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
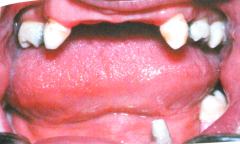
Ectodermal Dysplasia - A group of inherited conditions in which 2 or more ectodermally derived anatomical structures fail to develop.
- Deacreased # of sweat glands (intolerance to heat) - Fine, sparse hair; possible periocular wrinkling and hyper pigmentation; possible midface hypoplasia Oral - Marked decrease in number of teeth (hypodontia) - Abnormal shape of teeth, tapered anterior crowns - In most severe cases, cuspids and 1st molars are present but usually abnormal n shape |
|
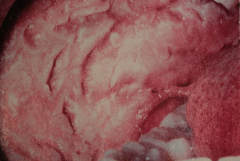
Autosomal dominant transmitted condtions (due to defect of normal keratinization)
|
White Sponge Nevus - Discussed under epithelial lesions
usually bilateral Histo - epithelium shows acanthuses and hyperparakeratosis biopsy to confirm - no malignant transformation |
|
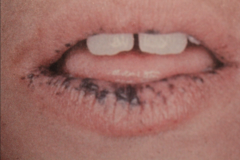
|
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (see pigmented lesions)
- Childhood onset, familial condition - Oral perioral melanotic macules - intestinal polyposis - Pigmentation of 1-5 mm found around lips, eyes, nose... - Oral pigmentation includes buccal mucosa, gingiva, palate (seldom tongue) - Polyps may cause abdominal pain and cause obstruction due to intussusception. |
|
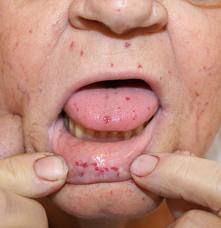
|
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber Disease) [soft tissue lesions lecture]
- Autosomal dominant - tend to undergo repeated hemorrhage - Epistaxis may be an early sign - Pt. may suffer from anemia, but not usually life threatening. |
|
|
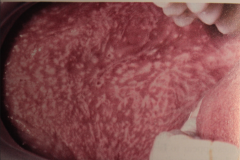
Lichen Planus - Reticular Form- Lacy-like pattern (have Stiae of Wickham) - MOST common type
- seldom has symptoms, Often bilateral Location: - Buccal mucosa - 80% - tongue - 65% - Lips - 20% HISTO: Hyperkeratosis in reticular type. |
|
|
Relatively common, chronic dermatologic disease that affects the oral mucosa. Unknown etiology, but appears to me a cell-mediated immune process. Severity may parallel pt's stress level in some cases.
|
Lichen Planus (seen in 1-2% of population)
- F:M = 3:2 (but Dr. T says 90% female) - Primary symptoms = pruritis - Small papules (a few mm in diameter) - Seen in flexor surfaces. wrist, knees, inner thigh... Most pt.s have oral lesions. If pt. has oral lesion, 20-40% chance of having a skin lesion. - several patterns seen |
|
|
Names the patterns of Lichen planus and which is most common.
|
Reticular form - mentioned above
Plaque form - may resemble Leukoplakia - usually dorsum of tongue. Atrophic form - smooth, poorly defined red areas (may be seen in conjunction w/ reticular or erosive types). Vesicle and bulla formation (rare) Erosive Type - (granular and erythematous) Ulcerative type, painful. May have radiating striae around ulcer MAIN TWO ARE: Reticular and Erosive. |
|
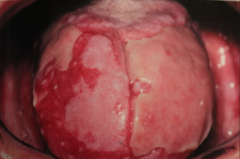
|
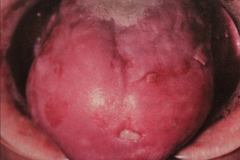
Erosive lichen planus - same pt. after systemic corticosteroid therapy.
Erosive lochen planus cont. (not necessary this pt.) - many pts also have secondary oral candidiasis - Can be confused w/ pemphigoid or pemphigus - Touching areas during an exam may produce pain and bleeding. |
|
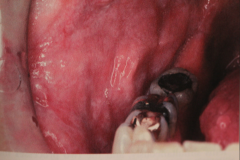
|
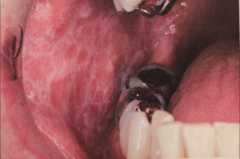
Lichen planus - Lichenoid mucositis w/ superimposed candidiasis. - same pt. 2 weeks after antifungal therapy
HISTO for lichen planus: - "Saw toothed" rete ridges - Basilar cell degeneration - Infiltrating of lymphocytes under basement membrane - Thin band of eosinophilic coagulum |
|
|
What is desquamative gingivitis?
|
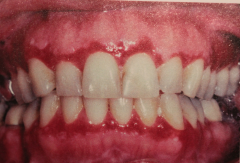
Describes gingival epithelium that spontaneously sloughs or can be removed w/ minor manipulation.
- should be biopsied b/c mucous membrane pemphigoid and pemphigus vulgarism may appear in a similar fashion. - seen here w/ erosive lichen plans. |
|
|
Treatment for Lichen planus
|
Palliative - not a cure
- Reticular type often does not require treatment. Topical application of steroids - Kenalog and orabase: put on lesions & swish for 2 min. - .05 Fluocinonide (lidex): (3X a day in severe cases) - don't take for a long time b/c causes adrenal suppression - Dexamethasone (Decadron) elixir swish around - Clobetasol (Temovate) - one of the strongest topical steroids must also use topical antifungal. Systemic steroids Antifungal meidcation Vitamin A analogues Standard of care is that all lichen planus pt.s should be biopsied. |
|
|
serious cicatricial skin disease characterized by the appearance of vesicle and bullae that develop in cycles
|
Pemphigus Family
- Possible Autoimmune - Ab. to intercellular cementing substance (autoantibodies against desmosomes) - Usually adults (esp. Jews) (average age = 50) - 1-5 per million diagnosed each year. Start with rapid bullae (or vesicles) Rupture - leave ulcerations Painful |
|
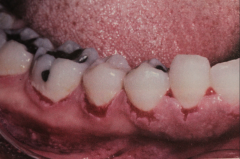
|
Pemphigus Vulgaris (most common type - and the one we discuss) (other types are P. foliaceous, p. megatons, p. erythamatosus - the are rarely oral)
- Seldom before 30 - Skin lesion may be accompanied by fever or malaise - Nikolsky's sign - pressure of friction causes bullae or vesicle - mainly affects torso |
|
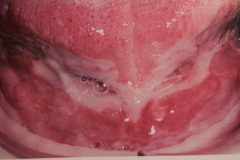
Oral - Often first manifestation (50% of cases)
|
Pemphigus Vulgairs
- All sites can be affected orally - Painful - cannot eat HISTO: - Acantholysis -loss of cohesiveness between cells lying in vesicular space (epithelial cells lying free w/in bulla). - "Tzanck cells" - the cell called Tzanck cell undergoes changes that include swelling of nuclei and hyperchromatin staining - Supravasilar vesicles or intraepithelial vesicles(above basal layer) - "Rows of tombstones" |
|
|
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pemphigus Vulgaris
|
Standard biopsy
Direct immunofluorescence - best way to confirm - Long term steroid therapy has improved prognosis, still 5-10% of cases are possibly fatal. - Corticosteroirds -high doses cause remission - Steroids used w/ non-steriod immunosuppresant drugs such as azathioprine. |
|
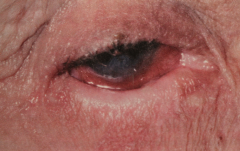
Location - oral mucosa, skin, genetalia, and ocular involvement (25% of the time)
|
Benign Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid (Cicatricial Pemphigoid) (BMMP)
- Twice as common as pemphigus vulgarism. - Autoimmune - Deposits of immunoglobulins and complement are found along the basement membrane ocular involvement (important) (25%) - Conjuctivitis - adhesions - scarring - blindness (30%) |
|
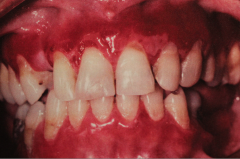
|
BMMP - oral involvment
- seen in most cases - mainly gingiva (may be misdiagnosed as desquamative gingivitis); also palatal mucosa - Vesicles thick-walled - last longer before rupture - leave bleeding surface - gingiva may show persistent erythema for weeks - + Nikolsky's sign - pushing on gingiva and a blister will form in a few min. |
|
|
Differential Diagnosis for Benign Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
|
- Pemphigus
- Bullous pemphigous - Erythema Multiforme - Chronic desquamative gingivitis |
|
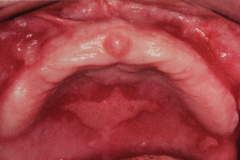
Antibodies attacking the basement membrane (sub-epithelial)
|
BMMP
- hemidesmosome is involved - No acantholysis 2:1= Female: Male 50-60 yrs old. Treatment - use of steroids, both local and systemic (may use custom tray) - Lack of oral hygiene often aggravates gingival condition, cholorodexidine may be useful. |
|
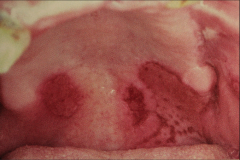
|
Bullous Pemphigoid (many fetures similar to BMMP)
- Rash on libs, many weeks before bullae - Bullae are thick-walled (sub-epithelial) - No acantholysis Oral involvem - Less frequent than BMMP - occurs in 10-45% of cases. Treat w/ corticosteroids, may have spontaneous remission. |
|
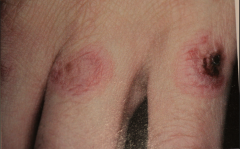
"target" or "Iris" lesion - peripheral gets larger as central area undergoes healing.
|
Erythema Multiforme (EM)
- An ulcerative and blistering mucocutaneous condition caused by a hypersensitivity reaction (probably to drugs/food/pollen) - some may appear spontaneously - Viral lesions may trigger disease ( up to 50%) - Other precipitating factors are GI condition such as chron's dz, malignancies, radiation therapy, vaccinations. - Usually rapid onset w/ prodromic period or 3-7 days with headache, fever, malaise |
|
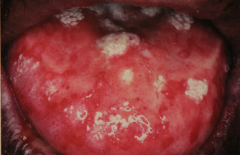
|
Erythema Multiforme
- oral lesions are less common than skin (hands, arms, feet, face, neck...) - Painful, and my involve any area of the mouth - Macules, papules or skin vesicles may become eroded and bleed There are two main forms, mild and chronic. Chronic is the mildest and may have continuos lesions for more than a year. |
|
|
What is one of the very noticeable oral manifestations of EM
|
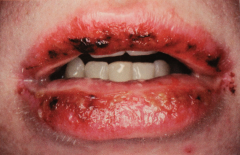
Bloody crusty lips.
No specific treatment - self limiting but may have chronic episodes. |
|
|
What are the associated syndromes of EM?
|
Stevens-Johnson syndrom (EM major) -sever
- Skin 10% of total body affected, and oral cavity - eyes - conjunctivitis (may lead to reccurent infection and blindness. - genitalia (urethritis) Toxic Epidermal Necrosis (TEN) - Very Bad - Blistering over more than 20% of body - High mortality rate. |
|
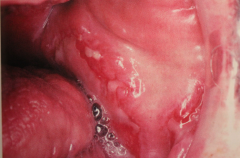
An immunologically mediated condition that presents in one of serval forms, and affects skin, CT and specific internal organs
|
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (L.E.)
- there are two other forms Chronic cutaneous LE and subacute cutaneous LE. - average age is 30-40 w/ a 8:1 female predilection - common findings are: fever, weight loss, arthritis, & general malaise. - butterfly rash is seen in 50% of pt.s - Kidney is affected in 50% of pt.s - oral lesion in 5 - 40% of cases - appear as lichenoid areas - cardiac condition are common. |
|
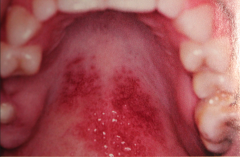
oral lesion in 20% of cases
|
Chronic cutaneous LE
- Few or no symptoms, sun exposure affects - Pts have scaly, erythematous patches on skin, also may have butterfly rash over nose. |
|
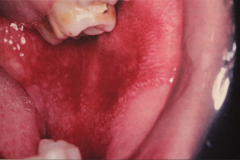
|
Chronic cutaneous LE
- oral lesions appear similar to lichen planus (leukoplakic areas with or without ulcerations) Diagnosis - microscopic, direct immunofluorescence, Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs) - For systemic LE 5 year survival is 95% and 15 yr is 75% - overall prognosis depends on organ involvement - For chronic 50% resolve after several years. |
|
|
Skin disease affecting 2% of population, with positive Auspitz sign. Oral lesions are uncommon and if there are any, they appear as whit or red plaques and possible ulceration.
|
Psoriasis
- symmetrical scaly papules of extensor surface, face, back, chess, scalp, elbows (Erythromatous plaque coved by silvery scales). Plaques bleed if picked off - positive Auspitz sign -12 % have arthritis Rx - sunlight, steroids, tar soaps, calcipotriene ( Vit D3 analog) tazarotene (a Vit A compound) |
|
|
Inherited blistering mucocutaneous disorder, that in the severe form is not compatible with life.
|
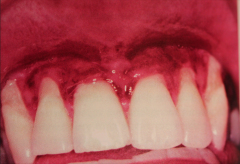
Epidermolysis Bullosa
- Vesicles form in mild areas of trauma |
|
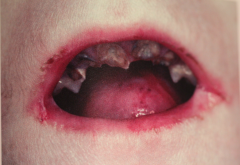
|
Epidermolysis Bullosa
- Severe caries associated with a soft cariogenic diet (less trauma to oral tissue) - Whole body is affected, fingernails may be lost. Oral manifestation inclued: - Gingival erythema - anodontia - Enamel hypoplasia - Bulla and vesicle formation. |
|
|
Fixation of dermis due to excess dense collagen deposition - hands become stiff and skin cannot wrinkle
|
Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis)
- Face looks mask like - Organs involved lead to organ failure - Raynaud's phenomenon of hands, face, and trunk - Neuralgia and parasthesia develops Oral involvement mostly in tongue, soft palate, larynx. lips become rigid. |
|
|
Uncommon dermatologic condition that has striking skin lesions along with subtle oral mucosal lesion.
Altered epithelial cells - build up a lot of keratin |
Darier's Disease (keratosis Follicularis)
- Numerous erythematous papules on skin (esp. trunk and scalp) - Palms and soles exhibit pits and keratoses - stinks Oral lesion consists of white flat papules and are seen in 50% of pts. Kind of a cobblestone looking appearance on palate. |
|
|
An uncommon solitary lesion on the skin or mucosa hisopathologically identical to Darier's disease. But just one leison
|
Warty Dyskeratoma
- Seen in pts older than 40 - roughed surface - less and 5 mm - no symptoms. |
|
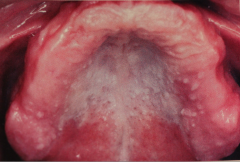
|
Darier's Disease
|
|
|
Immunologically mediated condition that may be triggered by one of several infectious agents in a susceptible person.
Has a classic triad of signs |
Reiter's syndrome (Reactive Arthritis)
Classic triad of signs - Nongonococcal urethritis - Arthritis - Conjuctivitis - usually seen in young men, and develops 1-4 weeks after an episode of dysentery or venereal disease. May develop skin lesion on penis - 20% may have oral lesions such as erythematous papules and ulcerations. |

