![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Two Parts of the Oral Cavity
|
1. Vestibule: narrow interval b/w lips/cheeks and teeth/ginigivae
2. Oral Cavity Proper: posterior and medial to the upper and lower dental arches |
|
|
Lips
Structure? Contents? Muscle? |
Covered by skin externally, mucous membrane internally.
B/W Obicularis Oris(CN 7) and mucous membrane there are labial salivary glands |
|
|
Cheeks
Structure? Contents? Muscle? Nerve? |
Covered by skin externally, mucus membrane internally.
Parotid Duct open on the parotid papilla opposite of 2nd max. molar Buccal Salivary glands b/w buccinator(CN7) and mucus membrane Sensory SA via long buccal(V3) |
|
|
Gingivae
Structure? Innervation? |
Fibrous tissue covered with mucous membrane
SA from: superior alveolar, greater palatine, nasopalatine, long buccal, inferior alveolar, lingual, mental |
|
|
Innervation for teeth
|
Max Molars: Posterior Superior Alveolar
Max Premolars: Middle Superior Alveolar Max Anteriors: Anterior Superior Alveolar Mandibulars: Inferior Alveolar nerve |
|
|
Hard Palate Formation
|
Horizontal Plate of the Palatine Bone,
Palatine process of the Maxillary bone |
|
|
Hard Palate Foramina
|
Incisive: Nasopalatine nerves, septal br. of sphenopalatine artery(anastomosis with great palatine a.)
Greater Palatine Foramen: Transmits palatine nerve and vessels to the hard palate Less Palatine Foramen: less palatine nerve and vessels to soft palate |
|
|
Hard Palate
|
Covered by mucous membrane(connected to periosteum)
Deep to Mucosa, mucus secreting palatine glands(VE Para/Post from PPG via greater palatine nerve) |
|
|
soft Palate
Location? Fxn? |
Extends posterioinferiorly from hard palate, ends into free margin conical process called UVULA.
Fxn: close off nasopharynx during swallowing, suckling, oral speech |
|
|
Soft Palate Contents?
|
Fold of mucous membrane enclosing:
aponeurosis, muscles, palatine glands(VE Para Post via PPG via Lesser Palatine N.), vessels, nerves |
|
|
Soft Palate Pillars
|
Anterior: Palatoglossal arch/fold
Posterior: Palatopharyngeal arch/fold |
|
|
Soft Palate Fauces
|
Aperature by which the mouth communicates with oropharynx(M shaped).
bound superiorly by soft palate, inferiorly by dorsum of tongue, laterally by palatoglossal arch. |
|
|
Muscles of the Soft Palate Innervation
|
Tensor Veli Palatine -V3
Levator veli palatini-XI via X Palatoglossues- XI via X Palatopharyngeus- XI via X Musculus uvulae-XI via X |
|
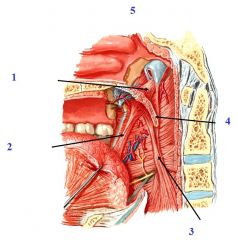
|
1. Levator Veli Palatini
2. Palatoglossus 3. Palatopharyngeus 4. Musculus uvulae 5. Tensor Veli Palatini |
|
|
Tensor Veli Palatini
|
Origin: Scaphoid of Spehnoid, Spine of Sphenoid, auditory tube cartilage
Insert: Palatine aponeurosis Nerve: V3(from m. pterygoid that goes through otic ganglion) Action: tenses soft palate, opens auditory tube during swallowing/yawning |
|
|
Musuclus uvulae
|
O: Posterior nasal spine, palatine aponuerosis
I: mucosa of uvula Nerve: 11 via 10(pharyngeal plexus) Action: shorters uvula and pulls it superiorly |
|
|
Palatopharyngeus
|
Origin: Palatine Aponeurosis
Insert: Lateral Wall of Pharynx Nerve: CN 11 via 10 (pharyngeal plexus) Action: pulls wall of pharynx superiorly, anteriorly & medially during swallowing |
|
|
Palatoglossus
|
Origin: palatine aponeurosis
Insert: Lateral Margin of the Tongue Nerve: 11 via 10 Action: elevates posterior part of tongue and depresses soft palate |
|
|
Levator Veli Palatini
|
Origin: Auditory Tube Cartilage,Petrous part of temporal B.
Insert: CN 11 via 10 Action: elevates soft palate during swallowing & yawning |
|
|
SA for Hard palate(gingiva and mucus membrane)
|
Greater Palatine Nerve +Nasopalotine Nerves
SA via V2 VE Para Post to Palatine Glands Symp Post |
|
|
SA for soft palate
|
Lesser Palatine(SA from V2)
VE Para Post to Palatine Glands Symp Post |
|
|
Blood Supply to Palate
|
Greater and Lesser Palatine Arteries
which are branches of descending palatine artery |
|
|
2 Parts of the Tongue
|
1. oral part-ant. 2/3
2. pharyngeal part-posterior 1/3 |
|
|
Tongue Parts Division
|
Boundaries between parts indicated by anterior pillars(palatoglossal arches)
and a V-shaped groove called Sulcus Terminalis whose apex projects posteirorly and ends in a median pit called the foramen cecum |
|
|
Oral Part of Tongue
|
1. Vallate+Foliate+fungiform papillae contain taste buds
2. Filiform-snesory nerve endings for touch |
|
|
Pharyngeal Part and Lingual Tonsils
|
Mucus membrane thick and contains lymphatic nodules--> lingual tonsils
Also contains taste resceptors |
|
|
Inferior Surface of Tongue
|
Reflects onto lingual gingvae and floor of mouth.
Mucosa is elevated into a fold called frenulum of the tongue |
|
|
Extrinsic Tongue Muscles:
|
Genioglossus
hyoglossus styloglossus Innervated via CN12 |
|
|
Styloglossus
|
Origin: styloid process of temporal bone
Insert: side of tongue, interdigitating with hyoglossus Nerve: CN12 Action: Retracts tongue, curls up sides of tongue |
|
|
Hyoglossus
|
Origin: greater horn/body of hyoid
Insert: interior aspect of lateral part of tongue Nerve: CN12 Action Depresses Tongue |
|
|
Genioglossus
|
Origin: Superior genial tubercle of mandible
insert: entire dorsum of tongue, some attach to hyoid Nerve: CN12 Action: Protrudes and depresses tongue |
|
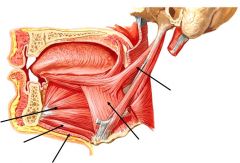
|
Left-->Right
Genioglossus Geniohyoid Mylohyoid Hyoglossus Styloglossus |
|
|
Tensor Veli Palatini
|
Attachments: Auditory Cartilage, Spine/Scaphoid of Sphenoid, Palatine Aponeurosis
N: V3 FXN: Tense soft palate, open auditory tube during swallowing/yawning |
|
|
Levator Veli Palatini
|
A: auditory cartilage, petrous part of temporal bone, palatine aponeurosis
N: CN12 FXN: Elevate soft palate during swallowing and yawning |
|
|
Palatopharyngeus
|
A:Palatal aponeurosis, lateral pharynx
N: CN12 FXN: Draws pharynx Anterior,medial, superior during swallowing |
|
|
Palatoglossus
|
A: Palatal Aponeurosis, Lateral tongue
N: CN12 FXN: Raises posterior tongue, depress soft palate |
|
|
Muscle of Uvulae
|
A: Posterior nasal spine, palatine aponeurosis, mucosa of uvula
N: CN12 FXN: shorters uvula and pulls it superiorly |
|
|
Hard Palate Mucosal Innervation
|
SA via Nasal Palatine(V2), Greater Palatine(V2)
Para/Post to palatine glands Symp Post to arteries |
|
|
Soft Palate Mucosal innervation
|
SA via Lesser Palatine(V2)
Para/Post to Palatine glands Sympost to arteries |
|
|
Palate Blood Supply
|
Greater Palatine A.
Lesser Palatine A. these are branches of descending palatine |
|
|
tongue, 2 divisions?
|
Oral Part: Anterior 2/3, anterior to sulcus terminalis
Pharyngeal Part: Posterior 1/3 posteior to sulcus terminalis |
|
|
tongue Features
|
Taste: fungiform, foliate, vallate
Sensory: filiform |
|
|
Inferior Surface of Tongue
|
Reflects onto floor of mouth and midline.
Muscosa elevated into a fold called the frenulum of the tongue |
|
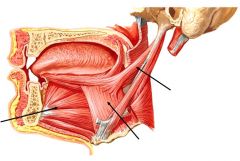
|
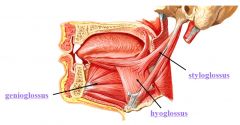
|
|
|
Genioglossus
|
A: Genial tubercles, spans to dorsum of tongue
N: CN12 FXN: Protrude, depress tongue |
|
|
Hyoglossus
|
A: greater horn + body Hyoid bone, lateral inferior tongue
N: CN12 FXN: Depress tongue |
|
|
Styloglossus
|
A: Styloid Process, Lateral surface of tongue, interdigitating with hyoglossus
N: CN12 FXN: retract tongue, rolls up lateral side of tongue |
|
|
Intrinsic Muscles
|
superior/inferior longitudinal
Tranverve Vertical FXN: change shape of tongue |
|
|
Arteries for Tongue
|
Lingual branch of external carotid A.
Branches: Deep Lingual: tip Sublingual: under tongue Dorsal Tongue: Dorsum |
|
|
Innvervation of the tongue
|
Anterior 2/3 : CN 7 SS, V3 SA
Posterior 1/3: CN 9 SS, VA Posterior: CN10 SS, VA |
|
|
Tongue Veins
|
Lingual Vein(from IJV)
Branches: Deep Lingual: tip Sublingial: inferior surface of tongue Dorsal Lingual: dorsum |
|
|
Sublingual Gland
|
superior to mylohyoid
8-20 ducts which open into the mouth plica sublingualis(sublingual fold) |
|
|
Connection of tongue to epiglottis
|
Lateral Glossepiglottic Fold
Medial Glossoepiglottic Fold Vallecula |
|
|
Innervation of teeth
|
Maxillary: SA via superior alveolar nerves(posterior, middle, anterior) via V2
Mandibular: SA of inferior alveolar(V3) |
|
|
Lymph Drainage
|
Anterior 2/3 Tip: Sub Mental
Anterior 2/3 Middle: Deep Cervical Anterior 2/3 Lateral: Submandibular Posterior 1/3: Deep Cervical |
|
|
Blood supply to teeth
|
Maxillary: Superior Alveolar arteries
(posterior-->V2, middle, anterior via infraoribital a.) Mandibular: inferior alveolar(1st part of Maxillary A.) |
|
|
Maxillary Buccal and labial ginigivae
|
superior alveolar
|
|
|
Palatine Gingivae
|
greater palatine(molars/premolars) and nasopalatine nerve(incisor)
|
|
|
Mandibular Buccal Gingivae
|
long buccal V3
|
|
|
Mandibular Lingual gingivae
|
Lingual nerve V3
|
|
|
Mandibular Labial Gingivae
|
incisive br. of the inferior alveolar nerve
|
|
|
PSA Nerve Block
|
anestehesia of maxillary molar teeth up to 1st molar
risks hematoma formation due to accidential injection into pterygoid plexus of veins or accidental puncture of maxillary artery |
|
|
MSA nerve Block
|
Maxillary Premolar teeth or mesiobuccal root of 1st molar
sometimes absent-->PSA ASA |
|
|
ASA
|
anesthesize maxillary central and lateral incisors/canine as well as soft tissue on buccal aspect
may also innervate premoalr teeth and mesibuccal root of 1st molar |
|
|
Greater Palatine Nerve Block
|
Palatal aspect of maxillary premoalr/molar dentition
targets anterior to palatine canal |
|
|
Nasopalatine Nerve Block
|
anesethtizes nasopalatine nerves bilaterally, anesthesia of lingual aspect of multiple anterior teeth
|

